1. 概論
inotify是Linux中用于監(jiān)控文件系統(tǒng)變化的一個(gè)框架,不同于前一個(gè)框架dnotify, inotify可以實(shí)現(xiàn)基于inode的文件監(jiān)控。也就是說監(jiān)控對(duì)象不再局限于目錄,也包含了文件。不僅如此,在事件的通知方面,inotify擯棄了dnotify的信號(hào)方式,采用在文件系統(tǒng)的處理函數(shù)中放置hook函數(shù)的方式實(shí)現(xiàn)。
2. 用戶層
2.1 數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
在inotify中,對(duì)于一個(gè)文件或目錄的監(jiān)控被稱為一個(gè)watch。 給某一個(gè)文件或目錄添加一個(gè)watch就表示要對(duì)該文件添加某一類型的監(jiān)控。監(jiān)控的類型由一個(gè)掩碼Mask表示,mask有:
IN_ACCESS : 文件的讀操作
IN_ATTRIB : 文件屬性變化
IN_CLOSE_WRITE : 文件被關(guān)閉之前被寫
IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE : 文件被關(guān)閉
IN_CREATE : 新建文件
IN_DELETE : 刪除文件
IN_MODIFY : 修改文件
IN_MOVE_SELF : 被監(jiān)控的文件或者目錄被移動(dòng)
IN_MOVED_FROM : 文件從被監(jiān)控的目錄中移出
IN_MOVED_TO : 文件從被監(jiān)控的目錄中移入
IN_OPEN : 文件被打開
事件的類型有了,我們還需要一個(gè)結(jié)構(gòu)體去表示一次事件, 在用戶空間,inotify使用inotify_event表示一個(gè)事件,每一個(gè)事件都有一個(gè)特定的身份標(biāo)示wd, wd是一個(gè)整型變量。每一個(gè)事件都有一組事件類型與其關(guān)聯(lián)(IN_CREATE | IN_OPEN)。 事件中還應(yīng)包含文件名。
struct inotify_event {
int wd;/* Watch descriptor */
uint32_t mask;/* Mask of events */
uint32_t cookie;/* Unique cookie associating related
events (for rename(2)) */
uint32_t len;/* Size of name field */
char name[];/* Optional null-terminated name */
};
2.2函數(shù)及inotify的使用
為了防止文件描述符fd的快速消耗,inotify提出了一個(gè)inotify instance(inotify實(shí)例)的概念。每一個(gè)inotify實(shí)例表示一個(gè)可讀寫的fd, 一個(gè)inotify實(shí)例鏈接有多個(gè)對(duì)于文件的watch。而函數(shù)inotify_init的工作就是生成一個(gè)inotify實(shí)例。
如何添加對(duì)于目標(biāo)文件的watch呢?使用inotify_add_watch完成該任務(wù),inotify_add_watch有三個(gè)參數(shù),第一個(gè)參數(shù)是該watch所屬的實(shí)例的fd, 第二個(gè)參數(shù)是被監(jiān)控的文件名,第三個(gè)參數(shù)要監(jiān)控的事件類型。
有添加就有刪除, inotify_rm_watch(int fd, int wd)完成watch的刪除工作,類似的, fd表示實(shí)例,wd表示即將刪除的watch.
void handle_event(int fd){
for(;;){
int len =0;
char buf[BUFSIZE];
read(fd, buf, BUFSIZE);
int i =0;
char*p;
for(p = buf; p <(buf+len); p +=sizeof(struct inotify_event)+ even->len){
event =(struct inotify_event *)p;
if(event -> mask & IN_OPEN)
printf("IN_OPEN ");
}
}
}
int main(void){
int fd;
if((fd = inotify_init())<0){
perror("init error");
}
if(inotify_add_watch(fd,"/home", IN_OPEN|IN_DELETE)<0){
perror("add watch");
}
handle_event(fd);
return0;
}
從以上代碼可以看出,inotify的使用很簡單,由于一個(gè)inotify實(shí)例被抽象為一個(gè)文件,所以我們可以通過read函數(shù)直接讀取其中的事件。
#include
int inotify_init(void);int inotify_init1(int flags);
int inotify_add_watch(int fd,constchar*pathname,uint32_t mask);
int inotify_rm_watch(int fd,int wd);
3. 內(nèi)核原理
3.1 hook函數(shù)
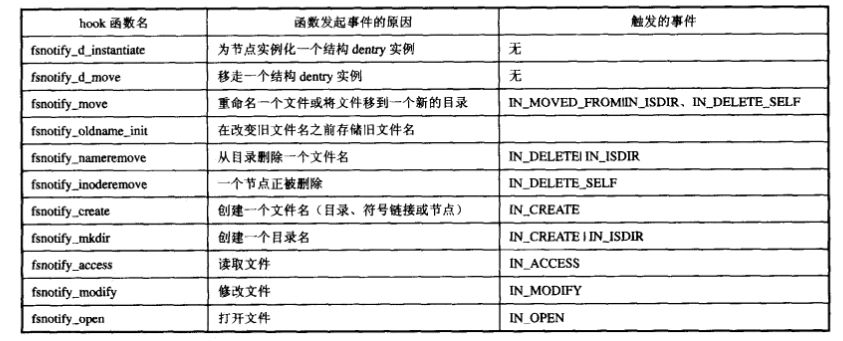
inotify通過在文件系統(tǒng)的操作函數(shù)(vfs_open, vfs_unlink等)中插入hook函數(shù)改變代碼的執(zhí)行路徑,從而產(chǎn)生相應(yīng)的事件。以下是一個(gè)hook函數(shù)的列表:
圖3-1 <圖片來自引用1>
下圖是sys_open函數(shù)的函數(shù)調(diào)用流程,可以看到sys_open函數(shù)調(diào)用的是fsnotify_open函數(shù)去處理open事件。
而fsnotify又調(diào)用inotify_dentry_parent_queue_event函數(shù)和inotify_inode_queue_event函數(shù).
圖3-2
其中inotify_dentry_parent_queue_event本身也調(diào)用了inode_queue_event函數(shù),只是參數(shù)不同罷了.
圖3-3
可見在inotify_dentry_parent_queue_event中,第一個(gè)參數(shù)變成了被監(jiān)控目錄的父目錄的inode. 關(guān)于這兩個(gè)函數(shù),我們先按下不表, 留待后文再說.
3.2 inotifyfs (inotify.c)
在內(nèi)核中inotify被抽象為一個(gè)虛擬文件系統(tǒng). 在inotifyfs的初始化函數(shù)中,完成了以下三件事:
初始化inotifyfs( 調(diào)用register_filesystem() , kern_mount() )
設(shè)置事件隊(duì)列的長度等
創(chuàng)建inotify_event和inotify_watch結(jié)構(gòu)的slab緩存
圖3-5
3.3 數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
3.2.1. inotify_device
struct inotify_device:表示一個(gè)inotify實(shí)例(inotify instance).,在linux2.16.13中,inotify是以模塊的形式出現(xiàn)的,在module_init中會(huì)調(diào)用setup函數(shù).
在inotify_device結(jié)構(gòu)中保存有兩個(gè)鏈表頭部,一個(gè)事件鏈表,鏈表中保存的是該inotify實(shí)例上所有事件,另一個(gè)是watch鏈表,保存的是該實(shí)例上所有的watch.
struct inotify_device {
wait_queue_head_t wq; /* wait queue for i/o */
struct idr idr; /* idr mapping wd -> watch */
struct semaphore sem; /* protects this bad boy */
struct list_head events; /* list of queued events */
struct list_head watches; /* list of watches */
atomic_t count; /* reference count */
struct user_struct *user; /* user who opened this dev */
unsignedint queue_size; /* size of the queue (bytes) */
unsignedint event_count; /* number of pending events */
unsignedint max_events; /* maximum number of events */
u32 last_wd; /* the last wd allocated */
};
圖3-7
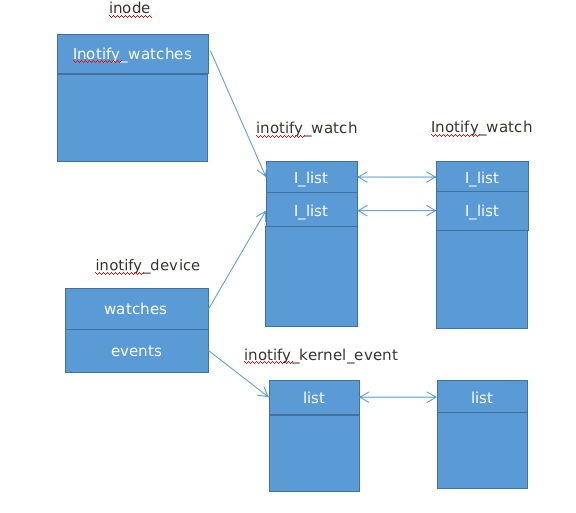
3.2.2 inotify_kernel_event
kernel_event結(jié)構(gòu)封裝了一個(gè)用戶態(tài)的event結(jié)構(gòu), 代表相應(yīng)文件產(chǎn)生的一次事件, 該結(jié)構(gòu)鏈接在inotify_device中的events鏈表.
struct inotify_kernel_event {
struct inotify_event event;/* the user-space event */
struct list_head list;/* entry in inotify_device's list */
char *name;/* filename, if any */
};
3.2.2 inotify_watch
inotify_watch表示我們向文件添加一個(gè)監(jiān)控. 他分別鏈接到兩個(gè)鏈表,一個(gè)鏈表頭在inode結(jié)構(gòu)中, 另一個(gè)在inotify_device結(jié)構(gòu)中.
struct inotify_watch {
struct list_head d_list;/* entry in inotify_device's list */
struct list_head i_list;/* entry in inde's list */
atomic_t count;/* reference count */
struct inotify_device *dev; /* associated device */
struct inode *inode;/* associated inode */
s32 wd; /* watch descriptor */
u32 mask; /* event mask for this watch */
};
3.3 深入api
接下來我以inotify的用戶接口為例, 帶大家深入探索一下這些函數(shù)究竟做了什么.
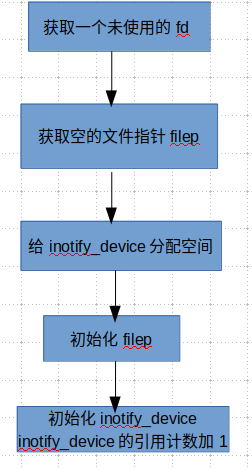
3.3.1 inotify_init
inotify_init函數(shù)的作用是給進(jìn)程分配一個(gè)用于讀寫inotify事件緩沖區(qū)的一個(gè)fd.
圖3-8
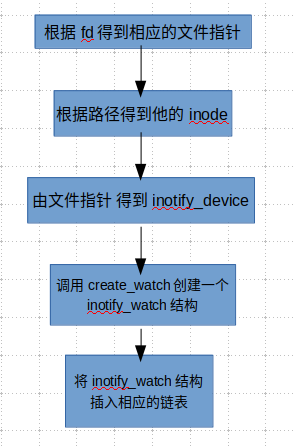
3.3.2 inotify_add_watch
inotify_add_watch有三個(gè)參數(shù), watch所屬的文件描述符,被監(jiān)控的目標(biāo)文件或者目錄的路徑, 事件掩碼.
究竟add_watch是怎樣的一個(gè)過程, 讓我們拭目以待.
圖3-9
3.4 事件究竟從何而來
上文提到, inotify在文件系統(tǒng)的每個(gè)文件操作函數(shù)中插入了一系列的鉤子函數(shù), 由此inotify就可以記錄用戶對(duì)于文件的各種操作. 簡單粗暴有沒有 … …
其中一個(gè)主要的函數(shù)是 inotify_inode_queue_event, 該函數(shù)的主要功能是遍歷Inode的inotify_watches鏈表, 由watch為根, 找到掛在inotify_device上的事件, 并將事件插入事件隊(duì)列(inotify_dev_queue_event).
圖3-10
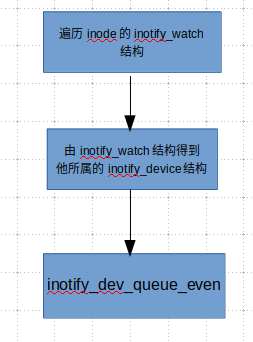
可以看到這個(gè)函數(shù)最終還是調(diào)用了inotify_dev_queue_event函數(shù), inotify_dev_queue_event的主要功能是將生成事件并將其插入inotify_device結(jié)構(gòu)的events鏈表.
總結(jié)
以上我以2.6.13版本的內(nèi)核為例闡述了inotify框架的使用和原理. 本來打算是以最新版本內(nèi)核為例的, 但是在4.15中, 內(nèi)核合并dnotify inotify fanotify這三個(gè)框架并且抽象出一個(gè)新的接口fsnotify, 代碼改動(dòng)較大, 不利于講解inotify的原理, 所以我選擇了第一次合并inotify的2.6.13內(nèi)核.
-
Linux
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
87文章
11336瀏覽量
210101 -
函數(shù)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
4344瀏覽量
62864
原文標(biāo)題:黃東升: inotify學(xué)習(xí)筆記
文章出處:【微信號(hào):LinuxDev,微信公眾號(hào):Linux閱碼場】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
請問keil debug時(shí)watch window里添加的變量怎么保存?
PADS添加對(duì)象,添加一個(gè)BMP文件,為什么只顯示圖標(biāo)?
關(guān)于Inotify對(duì)linux文件系統(tǒng)的監(jiān)控
對(duì)linux中的inotify機(jī)制的一點(diǎn)認(rèn)識(shí)
請問u32 omap_bootmode=MMCSD_MODE_FAT要添加 bootmode的選擇,該怎么添加?我想增加對(duì)nand的支持?
為工業(yè)物聯(lián)網(wǎng)應(yīng)用添加顯示屏的DEVPACK-WATCH包括BOM,PCB文件及CAD文件
在USB庫文件mass_mal.c中添加對(duì)flash和sd讀寫的函數(shù)
全志V853芯片 如何解決getevent運(yùn)行出錯(cuò),報(bào)錯(cuò)為“could not add watch for /dev/input”的問題?
如何在stm32mp1上添加對(duì)動(dòng)畫啟動(dòng)畫面的支持呢?
關(guān)于KEIL5中在線仿真watch窗口的問題求解
教你如何給PDF文件添加水印




 inotify框架的使用和原理!如何添加對(duì)于目標(biāo)文件的watch呢?
inotify框架的使用和原理!如何添加對(duì)于目標(biāo)文件的watch呢?










評(píng)論