步驟1:了解算法
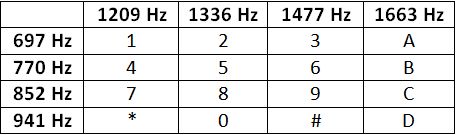
在DTMF中,每個符號根據(jù)圖片上的表格使用兩個頻率進行編碼。
該設(shè)備捕獲麥克風的輸入并計算八個頻率的幅度。具有最大幅度的兩個頻率給出了編碼符號的一行和一列。
數(shù)據(jù)采集
為了執(zhí)行頻譜分析,應(yīng)以某個可預測的頻率捕獲樣本。為了達到這個目的,我使用了具有最大精度的自由運行ADC模式(預分頻器128),它提供了9615Hz的采樣率。下面的代碼顯示了如何配置Arduino的ADC。
void initADC() {
// Init ADC; f = ( 16MHz/prescaler ) / 13 cycles/conversion
ADMUX = 0; // Channel sel, right-adj, use AREF pin
ADCSRA = _BV(ADEN) | // ADC enable
_BV(ADSC) | // ADC start
_BV(ADATE) | // Auto trigger
_BV(ADIE) | // Interrupt enable
_BV(ADPS2) | _BV(ADPS1) | _BV(ADPS0); // 128:1 / 13 = 9615 Hz
ADCSRB = 0; // Free-run mode
DIDR0 = _BV(0); // Turn off digital input for ADC pin
TIMSK0 = 0; // Timer0 off
}
And the interrupt handler looks like this
ISR(ADC_vect) {
uint16_t sample = ADC;samples[samplePos++] = sample - 400;
if(samplePos 》= N) {
ADCSRA &= ~_BV(ADIE); // Buffer full, interrupt off
}
}
頻譜分析
收集樣本后,我計算出8個頻率的幅度,這些頻率編碼符號。我不需要為此運行完整的FFT,因此我使用了Goertzel的算法。
void goertzel(uint8_t *samples, float *spectrum) {
float v_0, v_1, v_2;
float re, im, amp;
for (uint8_t k = 0; k 《 IX_LEN; k++) {
float c = pgm_read_float(&(cos_t[k]));
float s = pgm_read_float(&(sin_t[k]));
float a = 2. * c;
v_0 = v_1 = v_2 = 0;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i 《 N; i++) {
v_0 = v_1;
v_1 = v_2;
v_2 = (float)(samples[i]) + a * v_1 - v_0;
}
re = c * v_2 - v_1;
im = s * v_2;
amp = sqrt(re * re + im * im);
spectrum[k] = amp;
}
}
步驟2:代碼
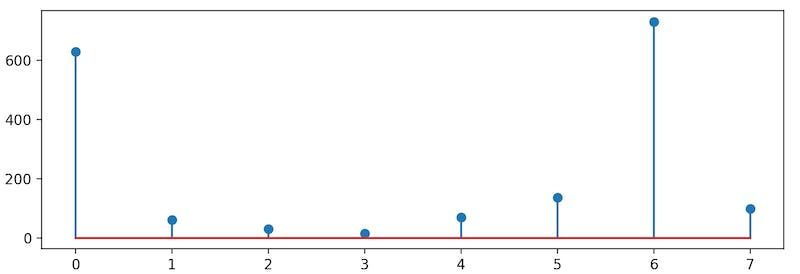
上圖顯示了數(shù)字3的編碼示例,其中最大幅度對應(yīng)于697Hz和1477Hz頻率。
完整的草圖如下
/**
* Connections:
* [ Mic to Arduino ]
* - Out -》 A0
* - Vcc -》 3.3V
* - Gnd -》 Gnd
* - Arduino: AREF -》 3.3V
* [ Display to Arduino ]
* - Vcc -》 5V
* - Gnd -》 Gnd
* - DIN -》 D11
* - CLK -》 D13
* - CS -》 D9
*/
#include
#include
#include
#define CS_PIN 9
#define N 256
#define IX_LEN 8
#define THRESHOLD 20
LEDMatrixDriver lmd(1, CS_PIN);
uint8_t samples[N];
volatile uint16_t samplePos = 0;
float spectrum[IX_LEN];
// Frequences [697.0, 770.0, 852.0, 941.0, 1209.0, 1336.0, 1477.0, 1633.0]
// Calculated for 9615Hz 256 samples
const float cos_t[IX_LEN] PROGMEM = {
0.8932243011955153, 0.8700869911087115, 0.8448535652497071, 0.8032075314806449,
0.6895405447370669, 0.6343932841636456, 0.5555702330196023, 0.4713967368259978
};
const float sin_t[IX_LEN] PROGMEM = {
0.44961132965460654, 0.49289819222978404, 0.5349976198870972, 0.5956993044924334,
0.7242470829514669, 0.7730104533627369, 0.8314696123025451, 0.8819212643483549
};
typedef struct {
char digit;
uint8_t index;
} digit_t;
digit_t detected_digit;
const char table[4][4] PROGMEM = {
{‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘A’},
{‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘B’},
{‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’, ‘C’},
{‘*’, ‘0’, ‘#’, ‘D’}
};
const uint8_t char_indexes[4][4] PROGMEM = {
{1, 2, 3, 10},
{4, 5, 6, 11},
{7, 8, 9, 12},
{15, 0, 14, 13}
};
byte font[16][8] = {
{0x00,0x38,0x44,0x4c,0x54,0x64,0x44,0x38}, // 0
{0x04,0x0c,0x14,0x24,0x04,0x04,0x04,0x04}, // 1
{0x00,0x30,0x48,0x04,0x04,0x38,0x40,0x7c}, // 2
{0x00,0x38,0x04,0x04,0x18,0x04,0x44,0x38}, // 3
{0x00,0x04,0x0c,0x14,0x24,0x7e,0x04,0x04}, // 4
{0x00,0x7c,0x40,0x40,0x78,0x04,0x04,0x38}, // 5
{0x00,0x38,0x40,0x40,0x78,0x44,0x44,0x38}, // 6
{0x00,0x7c,0x04,0x04,0x08,0x08,0x10,0x10}, // 7
{0x00,0x3c,0x44,0x44,0x38,0x44,0x44,0x78}, // 8
{0x00,0x38,0x44,0x44,0x3c,0x04,0x04,0x78}, // 9
{0x00,0x1c,0x22,0x42,0x42,0x7e,0x42,0x42}, // A
{0x00,0x78,0x44,0x44,0x78,0x44,0x44,0x7c}, // B
{0x00,0x3c,0x44,0x40,0x40,0x40,0x44,0x7c}, // C
{0x00,0x7c,0x42,0x42,0x42,0x42,0x44,0x78}, // D
{0x00,0x0a,0x7f,0x14,0x28,0xfe,0x50,0x00}, // #
{0x00,0x10,0x54,0x38,0x10,0x38,0x54,0x10} // *
};
void initADC() {
// Init ADC; f = ( 16MHz/prescaler ) / 13 cycles/conversion
ADMUX = 0; // Channel sel, right-adj, use AREF pin
ADCSRA = _BV(ADEN) | // ADC enable
_BV(ADSC) | // ADC start
_BV(ADATE) | // Auto trigger
_BV(ADIE) | // Interrupt enable
_BV(ADPS2) | _BV(ADPS1) | _BV(ADPS0); // 128:1 / 13 = 9615 Hz
ADCSRB = 0; // Free-run mode
DIDR0 = _BV(0); // Turn off digital input for ADC pin
TIMSK0 = 0; // Timer0 off
}
void goertzel(uint8_t *samples, float *spectrum) {
float v_0, v_1, v_2;
float re, im, amp;
for (uint8_t k = 0; k 《 IX_LEN; k++) {
float c = pgm_read_float(&(cos_t[k]));
float s = pgm_read_float(&(sin_t[k]));
float a = 2. * c;
v_0 = v_1 = v_2 = 0;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i 《 N; i++) {
v_0 = v_1;
v_1 = v_2;
v_2 = (float)(samples[i]) + a * v_1 - v_0;
}
re = c * v_2 - v_1;
im = s * v_2;
amp = sqrt(re * re + im * im);
spectrum[k] = amp;
}
}
float avg(float *a, uint16_t len) {
float result = .0;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i 《 len; i++) {
result += a[i];
}
return result / len;
}
int8_t get_single_index_above_threshold(float *a, uint16_t len, float threshold) {
if (threshold 《 THRESHOLD) {
return -1;
}
int8_t ix = -1;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i 《 len; i++) {
if (a[i] 》 threshold) {
if (ix == -1) {
ix = i;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
}
return ix;
}
void detect_digit(float *spectrum) {
float avg_row = avg(spectrum, 4);
float avg_col = avg(&spectrum[4], 4);
int8_t row = get_single_index_above_threshold(spectrum, 4, avg_row);
int8_t col = get_single_index_above_threshold(&spectrum[4], 4, avg_col);
if (row != -1 && col != -1 && avg_col 》 200) {
detected_digit.digit = pgm_read_byte(&(table[row][col]));
detected_digit.index = pgm_read_byte(&(char_indexes[row][col]));
} else {
detected_digit.digit = 0;
}
}
void drawSprite(byte* sprite) {
// The mask is used to get the column bit from the sprite row
byte mask = B10000000;
for(int iy = 0; iy 《 8; iy++ ) {
for(int ix = 0; ix 《 8; ix++ ) {
lmd.setPixel(7 - iy, ix, (bool)(sprite[iy] & mask ));
// shift the mask by one pixel to the right
mask = mask 》》 1;
}
// reset column mask
mask = B10000000;
}
}
void setup() {
cli();
initADC();
sei();
Serial.begin(115200);
lmd.setEnabled(true);
lmd.setIntensity(2);
lmd.clear();
lmd.display();
detected_digit.digit = 0;
}
unsigned long z = 0;
void loop() {
while(ADCSRA & _BV(ADIE)); // Wait for audio sampling to finish
goertzel(samples, spectrum);
detect_digit(spectrum);
if (detected_digit.digit != 0) {
drawSprite(font[detected_digit.index]);
lmd.display();
}
if (z % 5 == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i 《 IX_LEN; i++) {
Serial.print(spectrum[i]);
Serial.print(“ ”);
}
Serial.println();
Serial.println((int)detected_digit.digit);
}
z++;
samplePos = 0;
ADCSRA |= _BV(ADIE); // Resume sampling interrupt
}
ISR(ADC_vect) {
uint16_t sample = ADC;
samples[samplePos++] = sample - 400;
if(samplePos 》= N) {
ADCSRA &= ~_BV(ADIE); // Buffer full, interrupt off
}
}
步驟3:原理圖
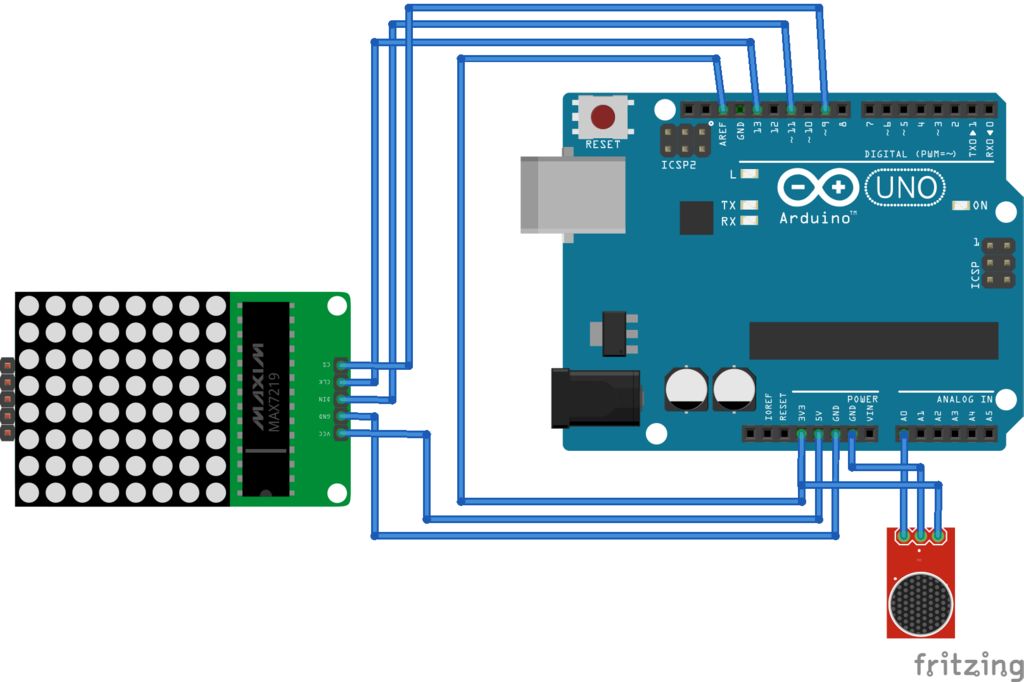
應(yīng)進行以下連接:
麥克風與Arduino
Out -》 A0
Vcc -》 3.3V
Gnd -》 Gnd
將AREF連接到3.3V很重要。
顯示到Arduino
Vcc -》 5V
Gnd -》 Gnd
DIN -》 D11
CLK -》 D13
CS -》 D9
步驟4:結(jié)論
這里可以改進什么?我以9615Hz的速率使用N = 256個樣本,該速率有一些頻譜泄漏,如果N = 205且速率為8000Hz,則所需頻率與離散化網(wǎng)格重合。對于該ADC,應(yīng)在定時器溢出模式下使用。
責任編輯:wv
-
解碼器
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
9文章
1144瀏覽量
40861 -
DTMF
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
74瀏覽量
47116 -
Arduino
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
188文章
6477瀏覽量
187564
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
無線網(wǎng)解碼器怎么連接
無線解碼器的質(zhì)量標準是什么
解碼器和控制器區(qū)別是什么
控制器解碼器的使用方法
遙控器解碼器怎么使用
全景聲解碼器

為什么好的播放器還要配解碼器
9740解碼器配什么光柵
光柵解碼器損壞的表現(xiàn)有哪些
數(shù)字播放器和解碼器

數(shù)字音頻解碼器和聲卡

超低功耗立體聲編解碼器Arduino評估板ARD-AUDIO-DA7212數(shù)據(jù)手冊
音視頻解碼器硬件加速:實現(xiàn)更流暢的播放效果





 如何用Arduino UNO實現(xiàn)DTMF解碼器
如何用Arduino UNO實現(xiàn)DTMF解碼器











評論