數(shù)碼管的一種是半導(dǎo)體發(fā)光器件,數(shù)碼管可分為七段數(shù)碼管和八段數(shù)碼管,區(qū)別在于八段數(shù)碼管比七段數(shù)碼管多一個(gè)用于顯示小數(shù)點(diǎn)的發(fā)光二極管單元DP(decimal point),其基本單元是發(fā)光二極管。
7段數(shù)碼管顯示的VHDL設(shè)計(jì)一:7段數(shù)碼顯示譯碼器
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL; ENTITY DecL7S IS
PORT(A :IN STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(3 DOWNTO 0);
LED7S:OUT STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(6 DOWNTO 0) ); END;
ARCHITECTURE one OF DecL7S IS BEGIN
PROCESS(A) BEGIN
CASE A(3 DOWNTO 0) IS
WHEN “0000”=》LED7S《=”0111111”;
WHEN “0001”=》LED7S《=”0000110”;
WHEN “0010”=》LED7S《=”1011011”;
WHEN “0011”=》LED7S《=”1001111”;
WHEN “0100”=》LED7S《=”1100110”;
WHEN “0101”=》LED7S《=”1101101”;
WHEN “0110”=》LED7S《=”1111101”;
WHEN “0111”=》LED7S《=”0000111”;
WHEN “1000”=》LED7S《=”1111111”;
WHEN “1001”=》LED7S《=”1101111”;
WHEN “1010”=》LED7S《=”1110111”;
WHEN “1011”=》LED7S《=”1111100”;
WHEN “1100”=》LED7S《=”0111001”;
WHEN “1101”=》LED7S《=”1011110”;
WHEN “1110”=》LED7S《=”1111001”;
WHEN “1111”=》LED7S《=”1110001”;
WHEN OTHERS=》 NULL;
END CASE; END PROCESS;
END;
波形仿真
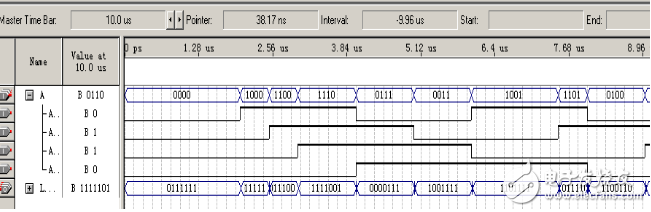
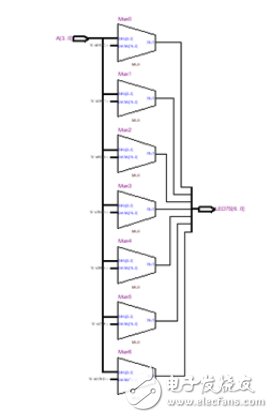
調(diào)出VHDL描述產(chǎn)生的2選1多路選擇器的原理圖。點(diǎn)擊TOOLS-》NELIST VIEWERS-》RTL VIEWERS,即調(diào)出VHDL描述產(chǎn)生的2選1多路選擇器的RTL電路圖,如下所示:
7段數(shù)碼管顯示譯碼器的VHDL設(shè)計(jì)二:基于vhdl 實(shí)現(xiàn)的4位七段數(shù)碼管顯示
顯示內(nèi)容為4位16進(jìn)制數(shù),數(shù)碼管共陰極連接。 有置數(shù)及自加一功能。
LIBRARY IEEE;
USE IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
USE ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
ENTITY counter0000_ffff IS PORT ( clk, en :in STD_LOGIC;
set_ch:in std_logic_vector( 1 downto 0);
set_num :in std_logic_vector( 3 downto 0);
data : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(6 DOWNTO 0);
sel : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(2 DOWNTO 0) );
END counter0000_ffff;
architecture behave of counter0000_ffff is
signal num,num1,num2,num3,num4: std_logic_vector (3 downto 0);
signal num_counter:std_logic;
begin
a:process( clk )
variable cc: integer range 0 to 3:=0;
begin
if( clk = ‘0’ ) then
case cc is
when 0 =》 num 《= num2;sel 《= “011”;cc:=1;
when 1 =》 num 《= num3;sel 《= “010”;cc:=2;
when 2 =》 num 《= num4;sel 《= “001”;cc:=3;
when 3 =》 num 《= num1;sel 《= “000”;cc:=0;
end case;
case num is
when “0000” =》 data 《= “0111111”;
when “0001” =》 data 《= “0000110”;
when “0010” =》 data 《= “1011011”;
when “0011” =》 data 《= “1001111”;
when “0100” =》 data 《= “1100110”;
when “0101” =》 data 《= “1101101”;
when “0110” =》 data 《= “1111101”;
when “0111” =》 data 《= “0000111”;
when “1000” =》 data 《= “1111111”;
when “1001” =》 data 《= “1101111”;
when “1010” =》 data 《= “1110111”;
when “1011” =》 data 《= “1111100”;
when “1100” =》 data 《= “0111001”;
when “1101” =》 data 《= “1011110”;
when “1110” =》 data 《= “1111001”;
when “1111” =》 data 《= “1110001”;
end case;
end if;
end process;
b:process( clk ) –自加一
begin
if( clk = ‘0’) then
if( en = ‘1’) then
CASE set_ch IS
when “00” =》 num1《=set_num;
when “01” =》 num2《=set_num;
when “10” =》 num3《=set_num;
when “11” =》 num4《=set_num;
end case; else if num_counter = ‘0’ then
if num1 = “1111” then num1 《= “0000”;
num2 《= num2 + 1;
else num1 《= num1 +1;
end if;
if num2 = “1111” then num2 《= “0000”;
num3 《= num3 + 1;
end if;
if num3 = “1111” then
num3 《= “0000”;
num4 《= num4 + 1;
end if;
if num4 = “1111” then
num4 《= “0000”;
end if;
end if;
END IF;
end if;
end process;
c:process( clk ) –分頻
variable a:integer range 0 to 9999:=0;
begin if( clk = ‘1’) then
if( a = 9999 ) then
num_counter 《= not num_counter;
a := 0;
else a := a + 1;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end behave;
