DeepMind 最近發(fā)布了一篇新的論文---《神經(jīng)算術(shù)邏輯單元(NALU)》(https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.00508),這是一篇很有趣的論文,它解決了深度學(xué)習(xí)中的一個(gè)重要問題,即教導(dǎo)神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)計(jì)算。 令人驚訝的是,盡管神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)已經(jīng)能夠在許多任務(wù),如肺癌分類中獲得卓絕表現(xiàn),卻往往在一些簡(jiǎn)單任務(wù),像計(jì)算數(shù)字上苦苦掙扎。
在一個(gè)展示網(wǎng)絡(luò)如何努力從新數(shù)據(jù)中插入特征的實(shí)驗(yàn)中,我們的研究發(fā)現(xiàn),他們能夠用 -5 到 5 之間的數(shù)字將訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)分類,準(zhǔn)確度近乎完美,但對(duì)于訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)之外的數(shù)字,網(wǎng)絡(luò)幾乎無法歸納概括。
論文提供了一個(gè)解決方案,分成兩個(gè)部分。以下我將簡(jiǎn)單介紹一下 NAC 的工作原理,以及它如何處理加法和減法等操作。之后,我會(huì)介紹 NALU,它可以處理更復(fù)雜的操作,如乘法和除法。 我提供了可以嘗試演示這些代碼的代碼,您可以閱讀上述的論文了解更多詳情。
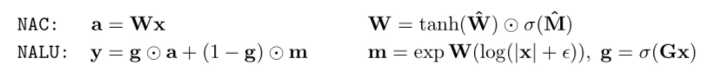
第一神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(NAC)
神經(jīng)累加器(簡(jiǎn)稱 NAC)是其輸入的一種線性變換。什么意思呢? 它是一個(gè)轉(zhuǎn)換矩陣,是 tanh(W_hat)和 sigmoid(M_hat)的元素乘積。 最后,轉(zhuǎn)換矩陣 W 乘以輸入(x)。
Python 中的 NAC
1import tensorflow as tf
2
3# NAC
4W_hat = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
5M_hat = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
6
7W = tf.tanh(W_hat) * tf.sigmoid(M_hat)
8# Forward propogation
9a = tf.matmul(in_dim, W)
NAC
第二神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)(NALU)
神經(jīng)算術(shù)邏輯單元,或者我們簡(jiǎn)稱之為 NALU,是由兩個(gè) NAC 單元組成。 第一個(gè) NAC g 等于 sigmoid(Gx)。 第二個(gè) NAC 在一個(gè)等于 exp 的日志空間 m 中運(yùn)行 (W(log(|x| + epsilon)))
Python 中的 NALU
1import tensorflow as tf
2
3# NALU
4G = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
5
6m = tf.exp(tf.matmul(tf.log(tf.abs(in_dim) + epsilon), W))
7
8g = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(in_dim, G))
9
10y = g * a + (1 - g) * m
NALU
通過學(xué)習(xí)添加來測(cè)試 NAC
現(xiàn)在讓我們進(jìn)行測(cè)試,首先將 NAC 轉(zhuǎn)換為函數(shù)。
1# Neural Accumulator
2def NAC(in_dim, out_dim):
3
4in_features = in_dim.shape[1]
5
6# define W_hat and M_hat
7W_hat = tf.get_variable(name = 'W_hat', initializer=tf.initializers.random_uniform(minval=-2, maxval=2),shape=[in_features, out_dim], trainable=True)
8M_hat = tf.get_variable(name = 'M_hat', initializer=tf.initializers.random_uniform(minval=-2, maxval=2), shape=[in_features, out_dim], trainable=True)
9
10W = tf.nn.tanh(W_hat) * tf.nn.sigmoid(M_hat)
11
12a = tf.matmul(in_dim, W)
13
14return a, W
NAC function in Python
Python 中的 NAC 功能
接下來,讓我們創(chuàng)建一些玩具數(shù)據(jù),用于訓(xùn)練和測(cè)試數(shù)據(jù)。 NumPy 有一個(gè)名為 numpy.arrange 的優(yōu)秀 API,我們將利用它來創(chuàng)建數(shù)據(jù)集。
1# Generate a series of input number X1 and X2 for training
2x1 = np.arange(0,10000,5, dtype=np.float32)
3x2 = np.arange(5,10005,5, dtype=np.float32)
4
5
6y_train = x1 + x2
7
8x_train = np.column_stack((x1,x2))
9
10print(x_train.shape)
11print(y_train.shape)
12
13# Generate a series of input number X1 and X2 for testing
14x1 = np.arange(1000,2000,8, dtype=np.float32)
15x2 = np.arange(1000,1500,4, dtype= np.float32)
16
17x_test = np.column_stack((x1,x2))
18y_test = x1 + x2
19
20print()
21print(x_test.shape)
22print(y_test.shape)
添加玩具數(shù)據(jù)
現(xiàn)在,我們可以定義樣板代碼來訓(xùn)練模型。 我們首先定義占位符 X 和 Y,用以在運(yùn)行時(shí)提供數(shù)據(jù)。 接下來我們定義的是 NAC 網(wǎng)絡(luò)(y_pred,W = NAC(in_dim = X,out_dim = 1))。 對(duì)于損失,我們使用 tf.reduce_sum()。 我們將有兩個(gè)超參數(shù),alpha,即學(xué)習(xí)率和我們想要訓(xùn)練網(wǎng)絡(luò)的時(shí)期數(shù)。在運(yùn)行訓(xùn)練循環(huán)之前,我們需要定義一個(gè)優(yōu)化器,這樣我們就可以使用 tf.train.AdamOptimizer() 來減少損失。
1# Define the placeholder to feed the value at run time
2X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape =[None , 2]) # Number of samples x Number of features (number of inputs to be added)
3Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None,])
4
5# define the network
6# Here the network contains only one NAC cell (for testing)
7y_pred, W = NAC(in_dim=X, out_dim=1)
8y_pred = tf.squeeze(y_pred)# Remove extra dimensions if any
9
10# Mean Square Error (MSE)
11loss = tf.reduce_mean( (y_pred - Y) **2)
12
13
14# training parameters
15alpha = 0.05 # learning rate
16epochs = 22000
17
18optimize = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=alpha).minimize(loss)
19
20with tf.Session() as sess:
21
22#init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
23cost_history = []
24
25sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
26
27# pre training evaluate
28print("Pre training MSE: ", sess.run (loss, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y:y_test}))
29print()
30for i in range(epochs):
31_, cost = sess.run([optimize, loss ], feed_dict={X:x_train, Y: y_train})
32print("epoch: {}, MSE: {}".format( i,cost) )
33cost_history.append(cost)
34
35# plot the MSE over each iteration
36plt.plot(np.arange(epochs),np.log(cost_history)) # Plot MSE on log scale
37plt.xlabel("Epoch")
38plt.ylabel("MSE")
39plt.show()
40
41print()
42print(W.eval())
43print()
44# post training loss
45print("Post training MSE: ", sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
46
47print("Actual sum: ", y_test[0:10])
48print()
49print("Predicted sum: ", sess.run(y_pred[0:10], feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
訓(xùn)練之后,成本圖的樣子:
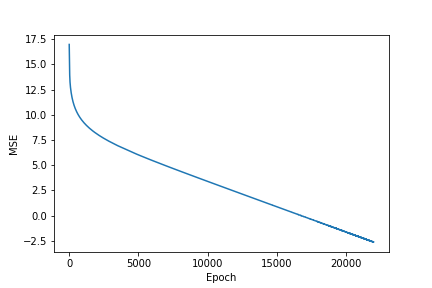
NAC 訓(xùn)練之后的成本
Actual sum: [2000. 2012. 2024. 2036. 2048. 2060. 2072. 2084. 2096. 2108.]Predicted sum: [1999.9021 2011.9015 2023.9009 2035.9004 2047.8997 2059.8992 2071.8984 2083.898 2095.8975 2107.8967]
雖然 NAC 可以處理諸如加法和減法之類的操作,但是它無法處理乘法和除法。 于是,就有了 NALU 的用武之地。它能夠處理更復(fù)雜的操作,例如乘法和除法。
通過學(xué)習(xí)乘法來測(cè)試 NALU
為此,我們將添加片段以使 NAC 成為 NALU。
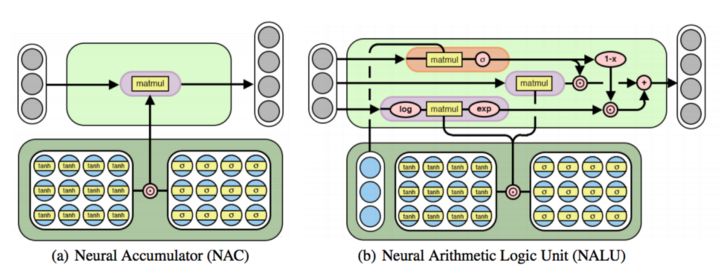
神經(jīng)累加器(NAC)是其輸入的線性變換。神經(jīng)算術(shù)邏輯單元(NALU)使用兩個(gè)帶有綁定的權(quán)重的 NACs 來啟用加法或者減法(較小的紫色單元)和乘法/除法(較大的紫色單元),由一個(gè)門(橙色單元)來控制。
1# The Neural Arithmetic Logic Unit
2def NALU(in_dim, out_dim):
3
4shape = (int(in_dim.shape[-1]), out_dim)
5epsilon = 1e-7
6
7# NAC
8W_hat = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
9M_hat = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
10G = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.02))
11
12W = tf.tanh(W_hat) * tf.sigmoid(M_hat)
13# Forward propogation
14a = tf.matmul(in_dim, W)
15
16# NALU
17m = tf.exp(tf.matmul(tf.log(tf.abs(in_dim) + epsilon), W))
18g = tf.sigmoid(tf.matmul(in_dim, G))
19y = g * a + (1 - g) * m
20
21return y
Python 中的 NALU 函數(shù)
現(xiàn)在,再次創(chuàng)建一些玩具數(shù)據(jù),這次我們將進(jìn)行兩行更改。
1# Test the Network by learning the multiplication
2
3# Generate a series of input number X1 and X2 for training
4x1 = np.arange(0,10000,5, dtype=np.float32)
5x2 = np.arange(5,10005,5, dtype=np.float32)
6
7
8y_train = x1 * x2
9
10x_train = np.column_stack((x1,x2))
11
12print(x_train.shape)
13print(y_train.shape)
14
15# Generate a series of input number X1 and X2 for testing
16x1 = np.arange(1000,2000,8, dtype=np.float32)
17x2 = np.arange(1000,1500,4, dtype= np.float32)
18
19x_test = np.column_stack((x1,x2))
20y_test = x1 * x2
21
22print()
23print(x_test.shape)
24print(y_test.shape)
用于乘法的玩具數(shù)據(jù)
第 8 行和第 20 行是進(jìn)行更改的地方,將加法運(yùn)算符切換為乘法。
現(xiàn)在我們可以訓(xùn)練的是 NALU 網(wǎng)絡(luò)。 我們唯一需要更改的地方是定義 NAC 網(wǎng)絡(luò)改成 NALU(y_pred = NALU(in_dim = X,out_dim = 1))。
1# Define the placeholder to feed the value at run time
2X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape =[None , 2]) # Number of samples x Number of features (number of inputs to be added)
3Y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None,])
4
5# Define the network
6# Here the network contains only one NAC cell (for testing)
7y_pred = NALU(in_dim=X, out_dim=1)
8y_pred = tf.squeeze(y_pred) # Remove extra dimensions if any
9
10# Mean Square Error (MSE)
11loss = tf.reduce_mean( (y_pred - Y) **2)
12
13
14# training parameters
15alpha = 0.05 # learning rate
16epochs = 22000
17
18optimize = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=alpha).minimize(loss)
19
20with tf.Session() as sess:
21
22#init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
23cost_history = []
24
25sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
26
27# pre training evaluate
28print("Pre training MSE: ", sess.run (loss, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
29print()
30for i in range(epochs):
31_, cost = sess.run([optimize, loss ], feed_dict={X: x_train, Y: y_train})
32print("epoch: {}, MSE: {}".format( i,cost) )
33cost_history.append(cost)
34
35# Plot the loss over each iteration
36plt.plot(np.arange(epochs),np.log(cost_history)) # Plot MSE on log scale
37plt.xlabel("Epoch")
38plt.ylabel("MSE")
39plt.show()
40
41
42# post training loss
43print("Post training MSE: ", sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
44
45print("Actual product: ", y_test[0:10])
46print()
47print("Predicted product: ", sess.run(y_pred[0:10], feed_dict={X: x_test, Y: y_test}))
NALU 訓(xùn)練后的成本
Actual product: [1000000. 1012032. 1024128. 1036288. 1048512. 1060800. 1073152. 1085568. 1098048. 1110592.]Predicted product: [1000000.2 1012032. 1024127.56 1036288.6 1048512.06 1060800.8 1073151.6 1085567.6 1098047.6 1110592.8 ]
在 TensorFlow 中全面實(shí)現(xiàn)
-
神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
42文章
4779瀏覽量
101052 -
深度學(xué)習(xí)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
73文章
5512瀏覽量
121415
原文標(biāo)題:想理解神經(jīng)算術(shù)邏輯單元嗎?
文章出處:【微信號(hào):tensorflowers,微信公眾號(hào):Tensorflowers】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請(qǐng)注明出處。
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
數(shù)字電路中加法器和減法器邏輯圖分析
減法器電路與原理 減法器電路圖分享
4位帶進(jìn)位的加法+減法計(jì)算器
LUT用作加法器或減法器
減法運(yùn)算
十進(jìn)制加法器,十進(jìn)制加法器工作原理是什么?
本的二進(jìn)制加法/減法器,本的二進(jìn)制加法/減法器原理
補(bǔ)碼減法,補(bǔ)碼減法原理是什么?
8位加法器和減法器設(shè)計(jì)實(shí)習(xí)報(bào)告
加法器與減法器_反相加法器與同相加法器
fpga實(shí)現(xiàn)加法和減法運(yùn)算的方法是什么
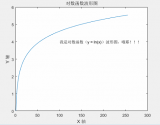




 NAC的工作原理,以及它如何處理加法和減法等操作
NAC的工作原理,以及它如何處理加法和減法等操作











評(píng)論