?CW32學(xué)習(xí)開發(fā)筆記
?
硬件原理圖:
主芯片
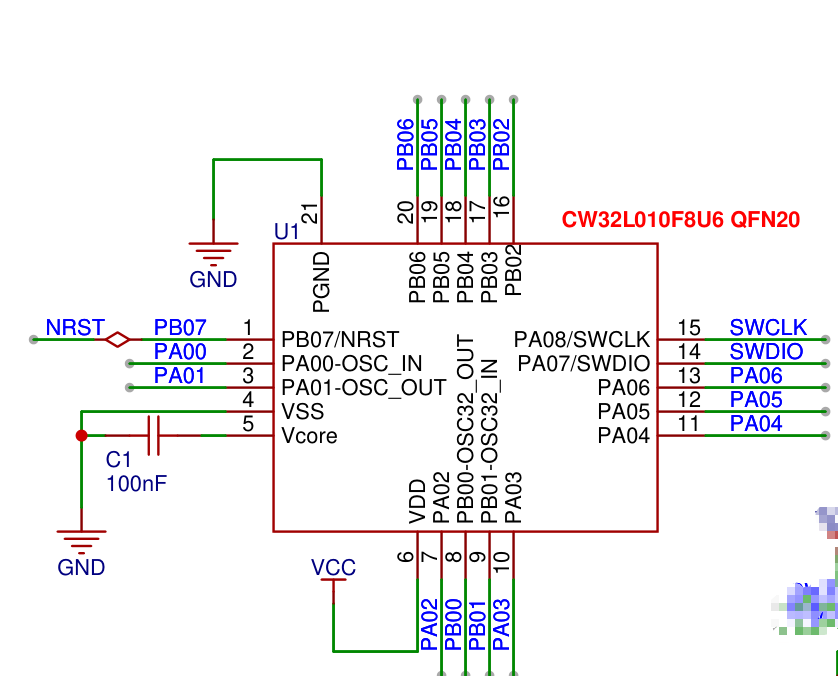
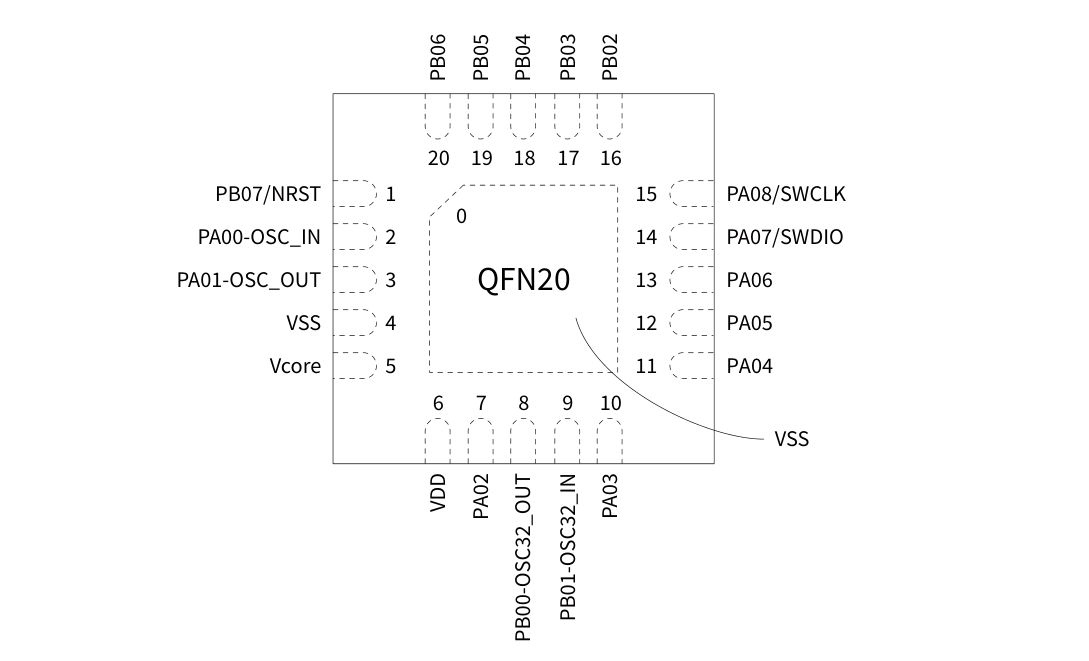
引腳封裝圖:
** CW32L010 是基于 eFlash 的單芯片低功耗微控制器,集成了主頻高達(dá) 48MHz 的 ARM? Cortex?-M0+ 內(nèi)核、**
高速嵌入式存儲(chǔ)器(多至 64K 字節(jié) FLASH 和多至 4K 字節(jié) SRAM)以及一系列全面的增強(qiáng)型外設(shè)和 I/O 口。
所有型號(hào)都提供全套的通信接口(二路 UART、一路 SPI 和一路 I2C)、12 位高速 ADC、四組通用和基本定時(shí)器、
一組低功耗定時(shí)器以及一組高級(jí)控制 PWM 定時(shí)器。
供電電源
** 使用type-c直接供電即可,不需要再接其他電源轉(zhuǎn)換芯片,CW32L010 可以在 -40℃到 85℃的溫度范圍內(nèi)工作,供電電壓寬達(dá) 1.62V ~ 5.5V。支持 Sleep 和 DeepSleep兩種低功耗工作模式。**
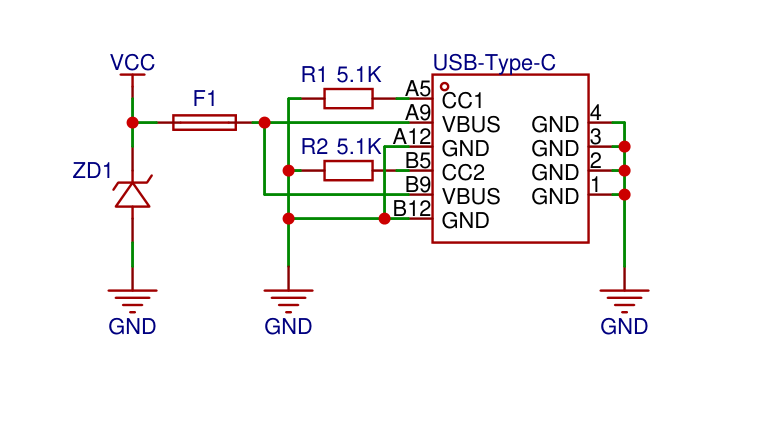
復(fù)位電路
濾波電路
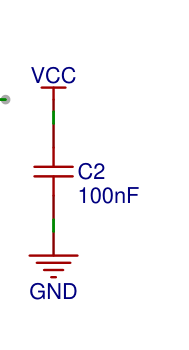
內(nèi)部穩(wěn)壓
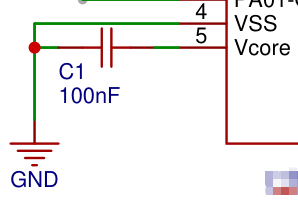
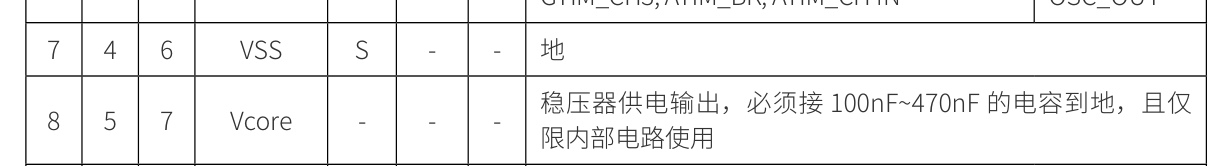
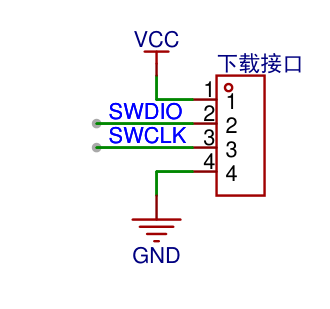
調(diào)試下載
默認(rèn)使用SWD接口下載程序,原理圖如下:
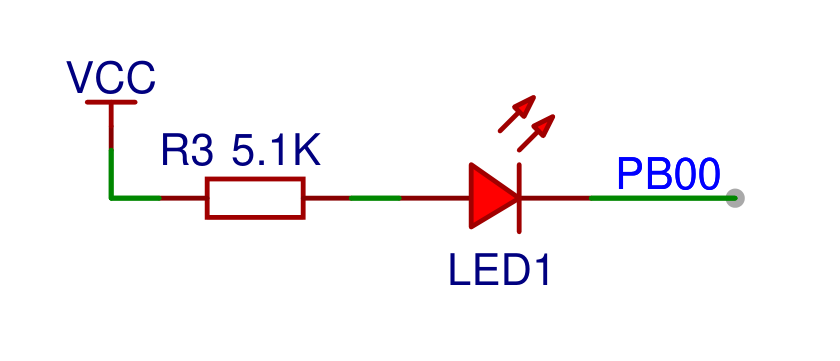
板載指示燈
用于查看系統(tǒng)運(yùn)行狀態(tài),原理圖如下:
軟件功能
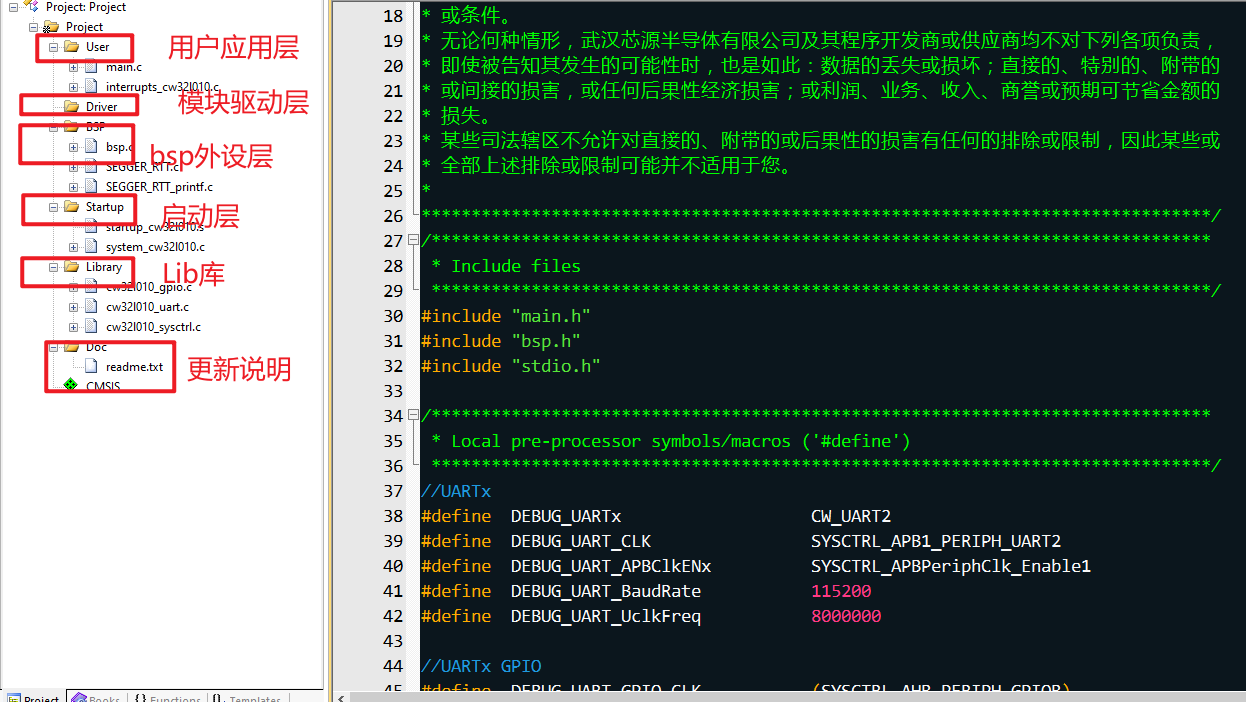
工程創(chuàng)建
具體如何創(chuàng)建工程就不所說明了,官方例程都有說明,我主要說下的我的目錄結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計(jì):
串口通訊
** 內(nèi)部集成 2 個(gè)通用異步收發(fā)器 (UART),支持異步全雙工、同步半雙工和單線半雙工模式,支持硬件數(shù)據(jù)流控**
和多機(jī)通信,還支持 LIN(局域互連網(wǎng)絡(luò));可編程數(shù)據(jù)幀結(jié)構(gòu),可以通過小數(shù)波特率發(fā)生器提供寬范圍的
波特率選擇。內(nèi)置定時(shí)器模塊,支持等待超時(shí)檢測(cè)、接收空閑檢測(cè)、自動(dòng)波特率檢測(cè)和通用定時(shí)功能。
UART 控制器工作在雙時(shí)鐘域下,允許在深度休眠模式下進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)的接收,接收完成中斷可以喚醒 MCU 回到
運(yùn)行模式。注意:僅 UART1 支持 LIN 和定時(shí)器功能;UART2 可通過片內(nèi)外設(shè)互聯(lián)與 BTIM/GTIM/ATIM 的從模式協(xié)同工
作實(shí)現(xiàn)超時(shí)定時(shí)器相關(guān)功能。我們接著實(shí)現(xiàn)串口通訊功能;
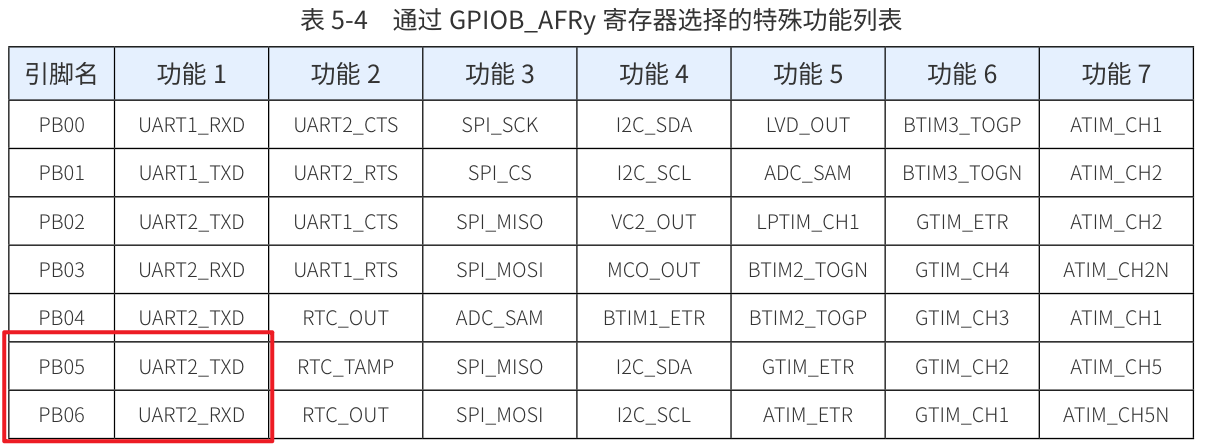
- 1.串口功能硬件引腳

使用串口2來是實(shí)現(xiàn)通訊,再看引腳的復(fù)用功能。
- 2.代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)
#include "bsp_uart2.h"
#include "cw32l010_gpio.h"
#include "cw32l010_uart.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "cw32l010_sysctrl.h"
?
//UARTx
#define DEBUG_UARTx CW_UART2
#define DEBUG_UART_CLK SYSCTRL_APB1_PERIPH_UART2
#define DEBUG_UART_APBClkENx SYSCTRL_APBPeriphClk_Enable1
#define DEBUG_UART_BaudRate 115200
#define DEBUG_UART_UclkFreq HSIOSC_VALUE //串口全速運(yùn)行
?
//UARTx GPIO
#define DEBUG_UART_GPIO_CLK (SYSCTRL_AHB_PERIPH_GPIOB)
#define DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PORT CW_GPIOB
#define DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_PIN_5
#define DEBUG_UART_RX_GPIO_PORT CW_GPIOB
#define DEBUG_UART_RX_GPIO_PIN GPIO_PIN_6
?
//GPIO AF
#define DEBUG_UART_AFTX PB05_AFx_UART2TXD()
#define DEBUG_UART_AFRX PB06_AFx_UART2RXD()
?
?
static void UART_Configuration(void)
{
// //外設(shè)時(shí)鐘使能,放在外設(shè)里面自己進(jìn)行使能
DEBUG_UART_APBClkENx(DEBUG_UART_CLK, ENABLE);
UART_InitTypeDef UART_InitStructure = {0};
?
UART_InitStructure.UART_BaudRate = DEBUG_UART_BaudRate;
UART_InitStructure.UART_Over = UART_Over_16;
UART_InitStructure.UART_Source = UART_Source_PCLK;
UART_InitStructure.UART_UclkFreq = DEBUG_UART_UclkFreq;
UART_InitStructure.UART_StartBit = UART_StartBit_FE;
UART_InitStructure.UART_StopBits = UART_StopBits_1;
UART_InitStructure.UART_Parity = UART_Parity_No ;
UART_InitStructure.UART_HardwareFlowControl = UART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
UART_InitStructure.UART_Mode = UART_Mode_Rx | UART_Mode_Tx;
UART_Init(DEBUG_UARTx, &UART_InitStructure);
?
}
?
?
/**
* @brief 配置GPIO
*
*/
static void GPIO_Configuration(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure = {0};
//外設(shè)時(shí)鐘使能,放在外設(shè)里面自己進(jìn)行使能
SYSCTRL_AHBPeriphClk_Enable(DEBUG_UART_GPIO_CLK, ENABLE);
GPIO_WritePin(DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PORT, DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET); // 設(shè)置TXD的默認(rèn)電平為高,空閑
?
GPIO_InitStructure.Pins = DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_Init(DEBUG_UART_TX_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStructure);
?
GPIO_InitStructure.Pins = DEBUG_UART_RX_GPIO_PIN;
GPIO_InitStructure.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT_PULLUP;
GPIO_Init(DEBUG_UART_RX_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStructure);
?
//UART TX RX 復(fù)用
DEBUG_UART_AFTX;
DEBUG_UART_AFRX;
}
?
?
?
void UART2_Configuration(void)
{
UART_Configuration();
GPIO_Configuration();
}
?
?
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* With GCC/RAISONANCE, small printf (option LD Linker- >Libraries- >Small printf
set to 'Yes') calls __io_putchar() */
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
?
?
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the UART.
*
*/
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
UART_SendData_8bit(DEBUG_UARTx, (uint8_t)ch);
?
while (UART_GetFlagStatus(DEBUG_UARTx, UART_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
?
return ch;
}
?
size_t __write(int handle, const unsigned char * buffer, size_t size)
{
size_t nChars = 0;
?
if (buffer == 0)
{
/*
* This means that we should flush internal buffers. Since we
* don't we just return. (Remember, "handle" == -1 means that all
* handles should be flushed.)
*/
return 0;
}
?
?
for (/* Empty */; size != 0; --size)
{
UART_SendData_8bit(DEBUG_UARTx, *buffer++);
while (UART_GetFlagStatus(DEBUG_UARTx, UART_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
++nChars;
}
?
return nChars;
}
?
/******************************************************************************
* EOF (not truncated)
******************************************************************************/
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
tex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %drn", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
?
- 3.編寫打印測(cè)試函數(shù)
static void Printf_Function(void)
{
DEBUG_LOG("rn");
DEBUG_LOG(" Compile time:");
DEBUG_LOG(__DATE__);
DEBUG_LOG(" ");
DEBUG_LOG(__TIME__);
DEBUG_LOG("rn+-------------------+rn");
DEBUG_LOG("%s,%s,%d,%srn", __FUNCTION__,__FILE__,__LINE__,__DATE__);
DEBUG_LOG("rn+-------------------+rn");
}
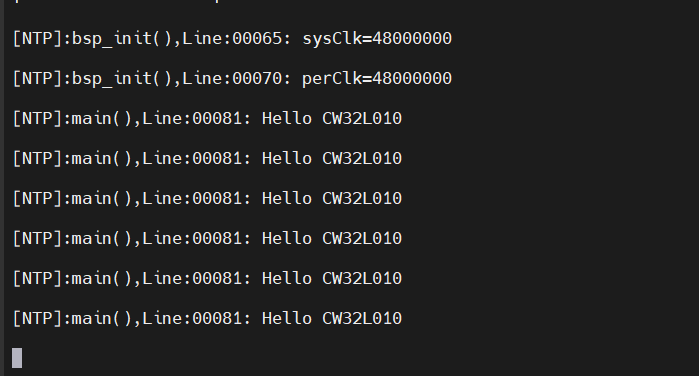
- 4.查看串口終端信息
使用MobaXterm終端工具查看:
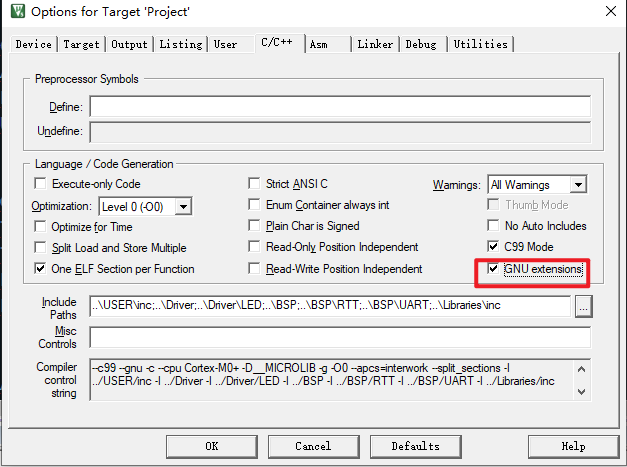
- 5.注意點(diǎn)
為了讓代碼支持GNU擴(kuò)展,keil設(shè)置需要注意:
同時(shí),串口打印的時(shí)候,添加頭文件"stdio.h";
GPIO口輸入輸出
根據(jù)板載資源,使用板載的LED來測(cè)試。前面硬件說明的時(shí)候提到,使用的引腳為PB00;就直接上代碼了。
- 1.編寫驅(qū)動(dòng)代碼
#include "drv_led.h"
?
?
?
?
// 初始化 LED 引腳
void LED_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
?
__SYSCTRL_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
?
GPIO_InitStruct.IT = GPIO_IT_NONE;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pins = LED_GPIO_PINS;
?
GPIO_Init(LED_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
?
// 控制 LED 開關(guān)
void LED_Control(GPIO_PinState state)
{
GPIO_WritePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_GPIO_PINS,state);
}
?
// 切換 LED 狀態(tài)
void LED_Toggle(void) {
GPIO_TogglePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_GPIO_PINS);
}
?
// 讀取 LED 狀態(tài)
int LED_Read(void) {
return GPIO_ReadPin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_GPIO_PINS) == GPIO_Pin_SET ? 1 : 0;
}
?
// 定義并初始化 LED 操作結(jié)構(gòu)體實(shí)例
LED_Ops_t myLED = {
.init = LED_Init,
.control = LED_Control,
.toggle = LED_Toggle,
.read = LED_Read
};
?
- 2.編寫測(cè)試程序
int32_t main(void)
{
bsp_init();
driver_init();
?
while(1)
{
SysTickDelay(1000);
myLED.toggle();
}
}
調(diào)試下載之后,可直接觀察板載LED燈是否在循環(huán)閃爍。
調(diào)試等級(jí)
- 1.直接上代碼,調(diào)試等級(jí)頭文件;
#ifndef __LOG_H
#define __LOG_H
#include < stdio.h >
#include < stdlib.h >
#include < string.h >
#include < stdarg.h >
#define GLOB_LOG_EVEL LOG_DEBUG
?
typedef enum {
FALSE,
TRUE
} status;
// 定義日志級(jí)別
typedef enum {
LOG_DEBUG,
LOG_INFO,
LOG_WARNING,
LOG_ERROR
} LogLevel;
?
?
?
//extern LogMsg lmsg;
// 顏色
#define Blue "?33[34m" // Blue
#define Green "?33[32m" // Green
#define Yellow "?33[33m" // Yellow
#define Red "?33[31m" // Red
#define Reset "?33[0m" // Reset color
?
?
// 記錄日志的宏定義
?
#define LOG_MESSAGE(format, ...) printf("[NTP]:%s(),Line:%05d: " format "rn", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__)
?
void LOG_MSG(LogLevel level, const char *message);
#endif
?
- 2.功能函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)文件:
#include "log.h"
?
// 日志輸出函數(shù)
void LOG_MSG(LogLevel level, const char *message) {
switch (level) {
case LOG_DEBUG:
printf(Blue "DEBUG: %s" Reset "rn", message);
break;
case LOG_INFO:
printf(Green "INFO: %s" Reset "rn", message);
break;
case LOG_WARNING:
printf(Yellow "WARNING: %s" Reset "rn", message);
break;
case LOG_ERROR:
printf(Red "ERROR: %s" Reset "rn", message);
break;
default:
printf("UNKNOWN: %sn", message);
break;
}
}
- 3.編寫測(cè)試函數(shù)
/*宏定義錯(cuò)誤碼信息*/
static void Error_Code_Info(void)
{
DEBUG_LOG("%d", SYSTEM_OK);
DEBUG_LOG("%d", SYSTEM_ERR_E_1);
DEBUG_LOG("%d", SYSTEM_ERR_E_2);
DEBUG_LOG("%d", SYSTEM_ERR_MQTT_INFO_ERROR);
?
?
LOG_MSG(LOG_DEBUG, "This is a debug message");
LOG_MSG(LOG_INFO, "This is an info message");
LOG_MSG(LOG_WARNING, "This is a warning message");
LOG_MSG(LOG_ERROR, "This is an error message");
}
- 4.終端輸出
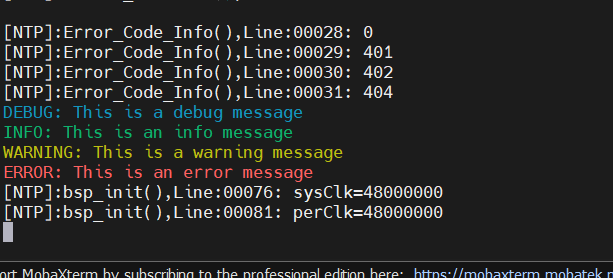
串口中斷
CW32單片機(jī)的串口有好幾種工作方式,異步全雙工,同步半雙工,單線半雙工,由于沒有DMA通道,為了避免頻繁的進(jìn)入中斷,采用串口接收中斷,串口查詢發(fā)送方式實(shí)現(xiàn)收發(fā);
配置簡(jiǎn)單隊(duì)列消息,實(shí)現(xiàn)方式如下:
- 1、定義隊(duì)列結(jié)構(gòu)
#define myQ2_SIZE 512
#define RxBuffer2_SIZE myQ2_SIZE
?
typedef volatile struct
{
uint8_t m_getIdx;
uint8_t m_putIdx;
uint8_t m_entry[ myQ2_SIZE ];
} myQ2;
?
extern myQ2 volatile RxBuffer2;
extern myQ2 volatile TxBuffer2;
?
void UART2_Buffer_Init(void);
- 2、初始化隊(duì)列結(jié)構(gòu)
myQ2 volatile RxBuffer2;
myQ2 volatile TxBuffer2;
?
?
void UART2_Buffer_Init(void)
{
CBUF_Init(RxBuffer2);
CBUF_Init(TxBuffer2);
}
?
- 3、使能串口接收中斷
void NVIC_Configuration(void)
{
//優(yōu)先級(jí),無優(yōu)先級(jí)分組
NVIC_SetPriority(DEBUG_UART_IRQ, 0);
//UARTx中斷使能
NVIC_EnableIRQ(DEBUG_UART_IRQ);
//使能UARTx RC中斷
UART_ITConfig(DEBUG_UARTx, UART_IT_RC, ENABLE);
UART_ClearITPendingBit(CW_UART2, UART_IT_RC);
}
- 4、編寫測(cè)試函數(shù),實(shí)現(xiàn)串口功能收發(fā)
int32_t main(void)
{
bsp_init();
driver_init();
while(1)
{
uint16_t dataLen=0;
dataLen = CBUF_Len(RxBuffer2);
if(dataLen!=0)
{
//拷貝數(shù)據(jù)
memcpy((char*)TxBuffer2.m_entry,(char*)RxBuffer2.m_entry,dataLen);
//查詢發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù)
UART_SendBuf_Polling(CW_UART2,TxBuffer2.m_entry,dataLen);
USART2_Clear();
}
SysTickDelay(1000);
myLED.toggle();
}
}
- 5、查看串口終端收發(fā)
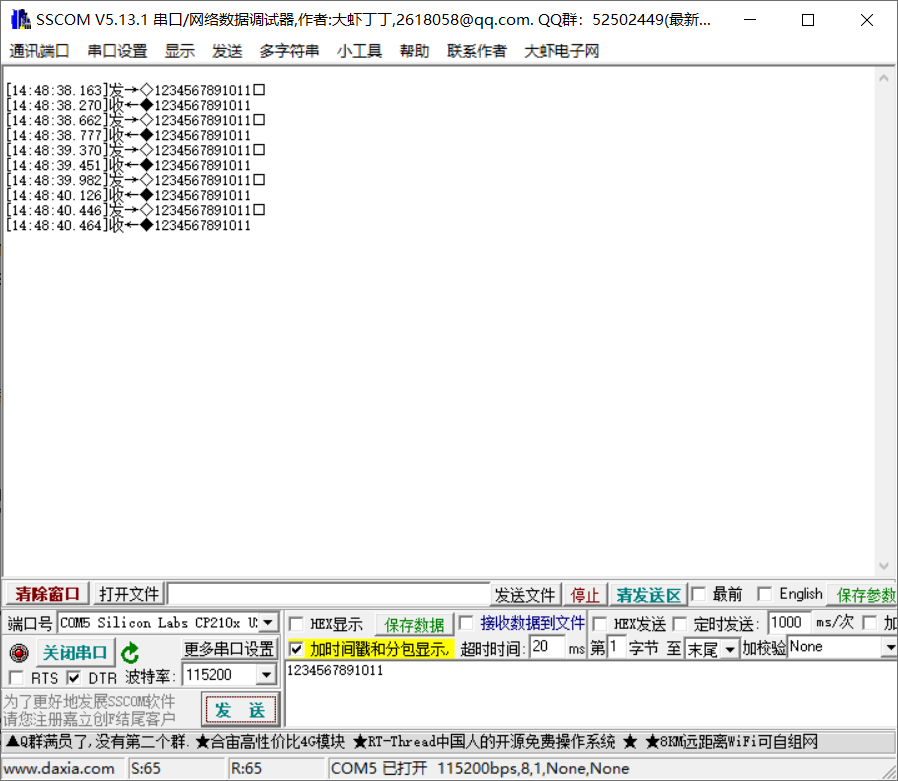
從截圖可以看出,當(dāng)前收發(fā)數(shù)據(jù)一致;
控制臺(tái)Shell
下面介紹下開源項(xiàng)目是 letter-shell,一個(gè)功能強(qiáng)大的嵌入式shell,letter shell 3.x是一個(gè)C語言編寫的,可以嵌入在程序中的嵌入式shell,通俗一點(diǎn)說就是一個(gè)串口命令行,可以通過命令行調(diào)用、運(yùn)行程序中的函數(shù)。目前 letter-shell 3.0版本支持的功能有:
- 命令自動(dòng)補(bǔ)全
- 快捷鍵功能定義
- 命令權(quán)限管理
- 用戶管理
- 變量支持
項(xiàng)目地址: [https://github.com/NevermindZZT/letter-shell]
移植過程:
- 1.復(fù)制源碼到工程中:
- 2.在自定義接口
shell_port.c中實(shí)現(xiàn)自己的串口讀寫函數(shù)
#include "shell.h"
#include "main.h"
#include "bsp_uart2.h"
#include "shell_port.h"
?
Shell shell;
char shellBuffer[512];
?
?
/**
* @brief 用戶shell寫
*
* @param data 數(shù)據(jù)
* @param len 數(shù)據(jù)長(zhǎng)度
*
* @return short 實(shí)際寫入的數(shù)據(jù)長(zhǎng)度
*/
short userShellWrite(char *data, unsigned short len)
{
UART_SendBuf_Polling(CW_UART2,(uint8_t *)data, len);
return len;
}
?
?
/**
* @brief 用戶shell讀
*
* @param data 數(shù)據(jù)
* @param len 數(shù)據(jù)長(zhǎng)度
*
* @return short 實(shí)際讀取到
*/
short userShellRead(char *data, unsigned short len)
{
return UART2_GetString((uint8_t *)data, len);
}
?
/**
* @brief 用戶shell上鎖
*
* @param shell shell
*
* @return int 0
*/
int userShellLock(Shell *shell)
{
return 0;
}
?
/**
* @brief 用戶shell解鎖
*
* @param shell shell
*
* @return int 0
*/
int userShellUnlock(Shell *shell)
{
return 0;
}
?
/**
* @brief 用戶shell初始化
*
*/
void userShellInit(void)
{
?
//注冊(cè)自己實(shí)現(xiàn)的寫函數(shù)
shell.write = userShellWrite;
//shell.read = userShellRead;
//調(diào)用shell初始化函數(shù)
shellInit(&shell, shellBuffer, 512);
}
- 3.在終端函數(shù)中定義
對(duì)于裸機(jī)環(huán)境,在主循環(huán)中調(diào)用shellTask,或者在接收到數(shù)據(jù)時(shí),調(diào)用shellHandler,我這里在中斷中調(diào)用
void UART2_IRQHandler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN */
uint8_t TxRxBuffer;
if (UART_GetITStatus(CW_UART2, UART_IT_RC) != RESET)
{
/*使用簡(jiǎn)易隊(duì)列進(jìn)行接收數(shù)據(jù)*/
TxRxBuffer = UART_ReceiveData_8bit(CW_UART2);
shellHandler(&shell,TxRxBuffer);
CBUF_Push(RxBuffer2, TxRxBuffer);
UART_ClearITPendingBit(CW_UART2, UART_IT_RC);
}
/* USER CODE END */
}
- 4.調(diào)用初始化shell
userShellInit();
- 5.串口終端實(shí)現(xiàn)結(jié)果
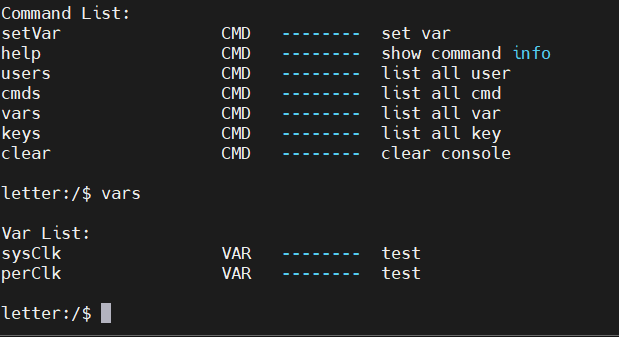
查看當(dāng)前系統(tǒng)時(shí)鐘:
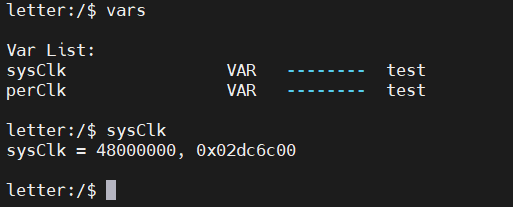
其他實(shí)現(xiàn)方式,參考官方文檔說明。
審核編輯 黃宇
-
芯片
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
455文章
50844瀏覽量
423845 -
CW32
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
1文章
210瀏覽量
655
發(fā)布評(píng)論請(qǐng)先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
基于CW32L010單片機(jī)的低成本電動(dòng)工具方案

【產(chǎn)品方案】基于CW32L010低成本電動(dòng)工具方案

【產(chǎn)品方案】基于CW32L010的低成本USB充電檢測(cè)儀產(chǎn)品方案

CW32L010安全低功耗MCU,樹立M0+產(chǎn)品行業(yè)新標(biāo)桿!
【CW32L010 Mini Board 測(cè)評(píng)】簡(jiǎn)介、點(diǎn)燈
方案介紹|CW32L010安全低功耗MCU:驅(qū)動(dòng)高速風(fēng)筒新力量
CW32L010demo
CW32L010安全低功耗MCU,樹立M0+產(chǎn)品行業(yè)新標(biāo)桿!

CW32L0100核心板的使用體驗(yàn)

CW32L010 新品初體驗(yàn)

基于CW32L010F8P6的電機(jī)驅(qū)動(dòng)板簡(jiǎn)易測(cè)試
CW32L010低成本工業(yè)儀表介紹

【產(chǎn)品方案】CW32L010低成本工業(yè)儀表(方案組成框圖、硬件原理圖)

關(guān)于CW32L010電動(dòng)工具控制板中SWD下載口占用時(shí)的下載解決方法

CW32L010 Motor Control Driver無刷電機(jī)驅(qū)動(dòng)板上手體驗(yàn)





 CW32L010學(xué)習(xí)筆記
CW32L010學(xué)習(xí)筆記










評(píng)論