進程和程序的區別:
進程是動態的,程序是靜態的
一、進程的創建(fork()函數)

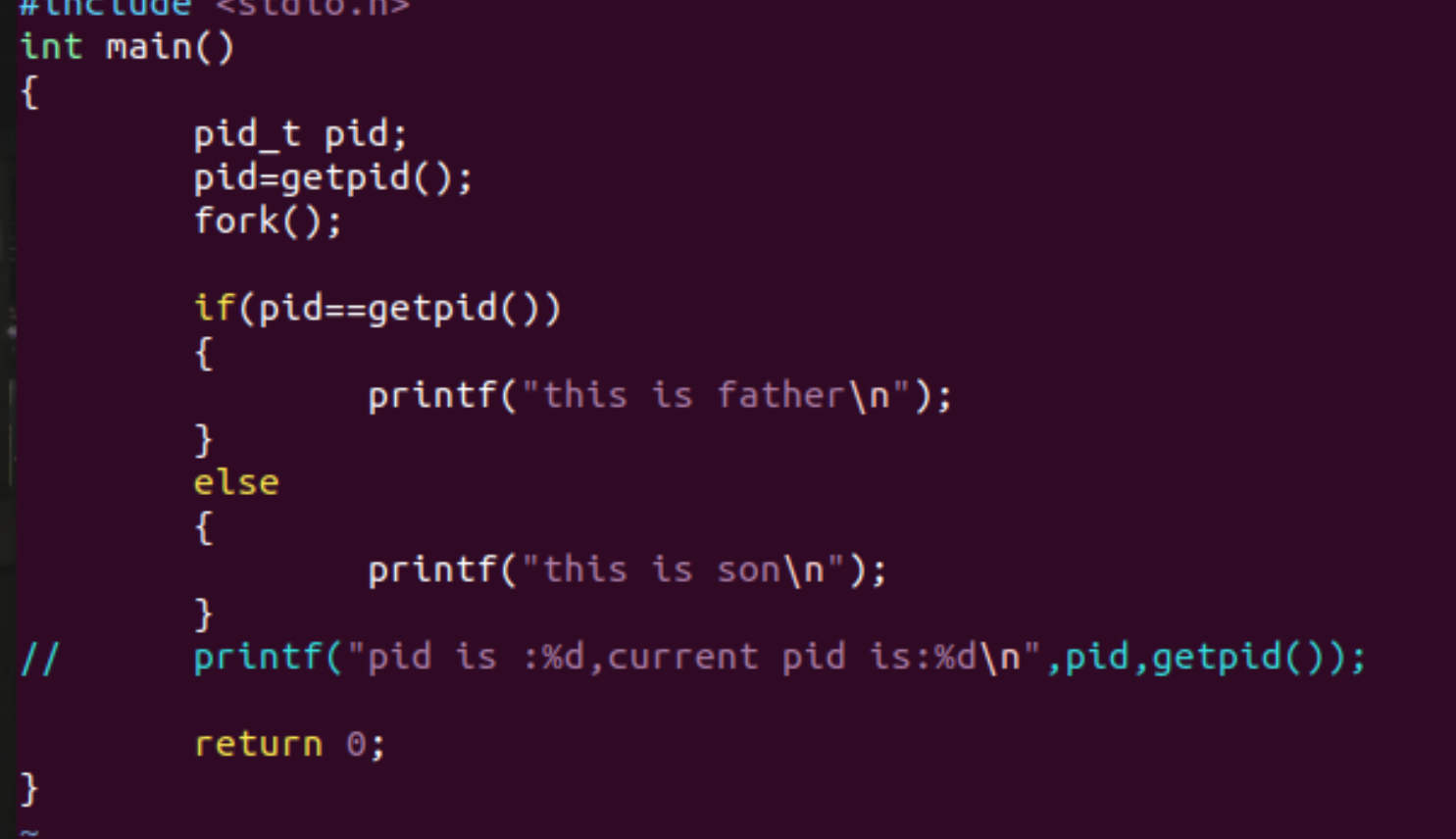
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
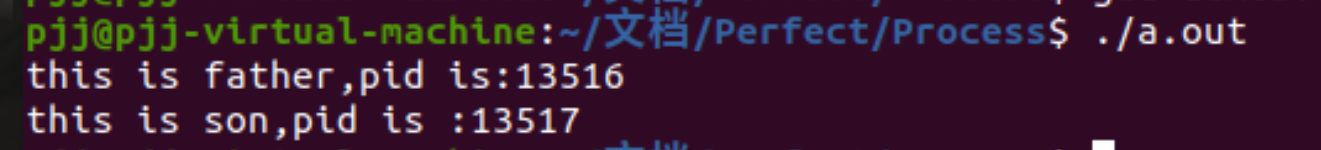
pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("this is father,pid is:%dn",getpid());
}
else if(pid==0)
{
printf("this is son,pid is :%dn",getpid());
}
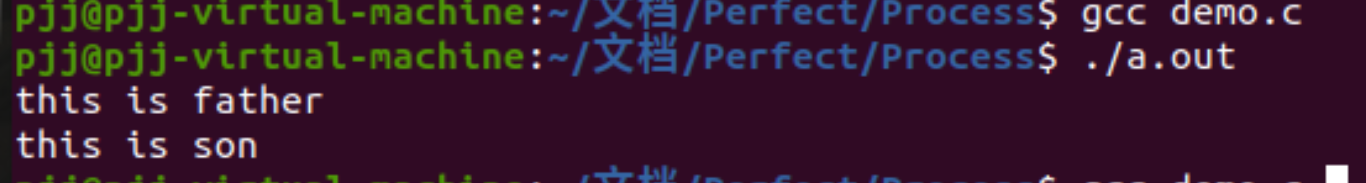
// printf("pid is :%d,current pid is:%dn",pid,getpid());
return 0;
}
~
結果:
結果:

二、進程退出



三、exec族函數的用法
用perror()的方式打印錯誤碼信息
//文件execl.c
#include
#include
#include
//函數原型:int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int main(void)
{
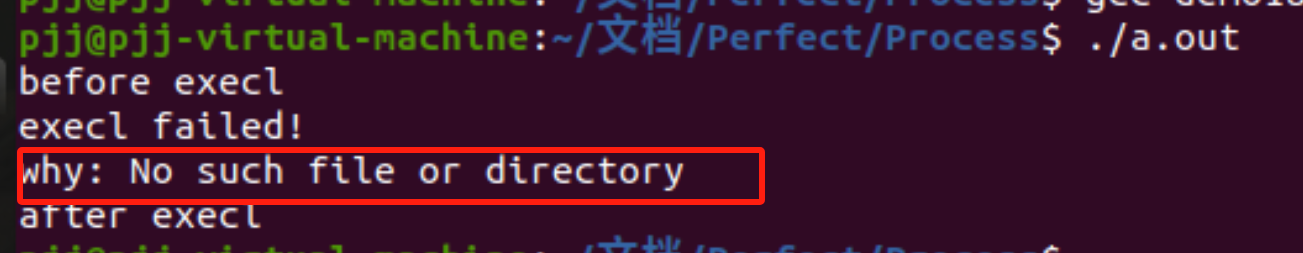
printf("before execln");
if(execl("./bin/echoarg","echoarg","abc",NULL) == -1)
{
printf("execl failed!n");
perror("why");
}
printf("after execln");
return 0;
}
四、system系統函數
聲明:本文內容及配圖由入駐作者撰寫或者入駐合作網站授權轉載。文章觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表電子發燒友網立場。文章及其配圖僅供工程師學習之用,如有內容侵權或者其他違規問題,請聯系本站處理。
舉報投訴
-
Linux
+關注
關注
87文章
11342瀏覽量
210147 -
進程
+關注
關注
0文章
204瀏覽量
13974
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
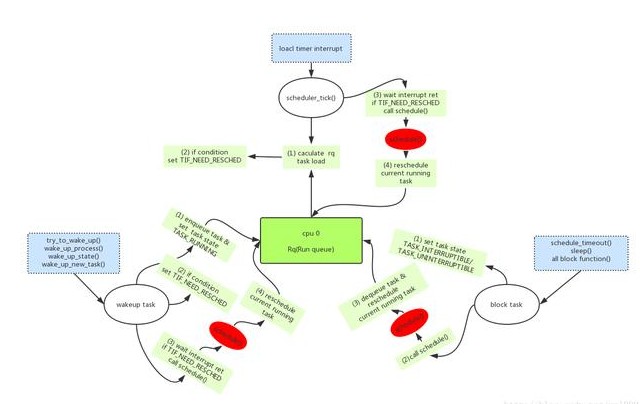
Linux進程的睡眠和喚醒
在Linux中,僅等待CPU時間的進程稱為就緒進程,它們被放置在一個運行隊列中,一個就緒進程的狀 態標志位為 TASK_RUNNING。一旦一個運行中的
發表于 06-07 12:26
?502次閱讀
Linux下的進程結構
`#嵌入式培訓#華清遠見嵌入式linux學習資料《Linux下的進程結構》,進程不但包括程序的指令和數據,而且包括程序計數器和處理器的所有寄存器及存儲臨時數據的
發表于 08-05 11:05
淺談多進程多線程的選擇
魚還是熊掌:淺談多進程多線程的選擇關于多進程和多線程,教科書上最經典的一句話是“進程是資源分配的最小單位,線程是CPU調度的最小單位”,這句話應付考試基本上夠了,但如果在工作中遇到類似
發表于 08-24 07:38
Linux 2.6進程調度
分析了與Linux 2.6 進程調度密切相關的一些重要數據結構,詳細描述了進程調度的時機、調度的策略和調度器的工作流程,并從算法分析和HackBench 測試兩個方面對Linux 2.
發表于 06-13 10:13
?11次下載
LINUX 進程源代碼分析
LINUX 進程源代碼分析
task_struct 數據結構表示進程的數據結構是struct task_struct。task_struct 結構是進程實體的核心,
發表于 02-09 15:13
?16次下載
Linux進程權限的分析說明
在linux下,關于文件權限,大部分人接觸比較多,也比較熟悉了解。但是對進程權限一般知之甚少。本文總結一下linux系統下進程權限問題和現象。
發表于 07-17 10:55
?895次閱讀
linux查看weblogic進程
在Linux操作系統中,WebLogic是一種常用的Java應用服務器,用于部署和管理企業級Java應用程序。為了確保WebLogic服務器正常運行,有時我們需要查看WebLogic進程以了解其狀態




 淺談Linux的進程
淺談Linux的進程














評論