動態(tài)輸出使用
打開svcsock.c文件中所有的動態(tài)輸出語句
# echo 'file svcsock.c +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
打開usbcore模塊中所有的動態(tài)輸出語句
# echo 'module usbcore +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
打開svc_process()函數(shù)中所有的動態(tài)輸出語句
# echo 'func svc_process() +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
打開文件路徑包含usb的文件里所有的動態(tài)輸出語句
# echo -n '*usb* +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
打開系統(tǒng)所有的動態(tài)輸出語句
# echo -n '+p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
上面是打開動態(tài)輸出語句的例子,除了能輸出pr_debug()/dev_dbg()函數(shù)中定義的輸出信息外,還能輸出一些額外信息,如函數(shù)名、行號、模塊名字以及線程ID等
- p:打開動態(tài)輸出語句
- f:輸出函數(shù)名
- l:輸出行號
- m:輸出模塊名字
- t:輸出線程ID
另外,還可以在各個子系統(tǒng)的Makefile中添加ccflags來打開動態(tài)輸出語句
< ../Makefile >
ccflags-y += -DDEBUG
ccflags-y += -DVERBOSE_DEBUG
實際案例
例如在一個led驅(qū)動中的open()、write()等函數(shù)開頭添加一句pr_debug("%s entern",
**func **** ** );
#include < linux/module.h >
#include < linux/fs.h >
#include < linux/errno.h >
#include < linux/miscdevice.h >
#include < linux/kernel.h >
#include < linux/major.h >
#include < linux/mutex.h >
#include < linux/proc_fs.h >
#include < linux/seq_file.h >
#include < linux/stat.h >
#include < linux/init.h >
#include < linux/device.h >
#include < linux/tty.h >
#include < linux/kmod.h >
#include < linux/gfp.h >
static int major = 0;
static char kernel_buf[1024];
static struct class *hello_class;
#define MIN(a, b) (a < b ? a : b)
static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
err = copy_to_user(buf, kernel_buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
err = copy_from_user(kernel_buf, buf, MIN(1024, size));
return MIN(1024, size);
}
static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
return 0;
}
static int hello_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
return 0;
}
/* 2. 定義自己的file_operations結(jié)構(gòu)體 */
static struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_drv_open,
.read = hello_drv_read,
.write = hello_drv_write,
.release = hello_drv_close,
};
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
int err;
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_drv); /* /dev/hello */
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
return -1;
}
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
pr_debug("%s entern", __func__);
device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
為了方面查看,先清除內(nèi)核輸出:
# dmesg -c
然后加載驅(qū)動,執(zhí)行dmesg查看是否有打印:
# insmod hello_drv.ko
# dmesg
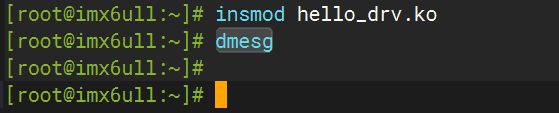
此時沒有pr_debug()的打印。這時再使用動態(tài)輸出打開hello_drv模塊的動態(tài)輸出:
# echo 'module hello_drv +p' > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
然后執(zhí)行該驅(qū)動的應(yīng)用層程序,使其調(diào)用到驅(qū)動的open、write、close函數(shù),從而執(zhí)行pr_debug():
# ./hello_drv_test -w 10
再查看demsg內(nèi)容:

可以看到,當打開了hello_drv模塊的動態(tài)輸出后,驅(qū)動中的pr_debug()語句就可以正常打印了。
再看看debugfs的control節(jié)點:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control

control節(jié)點記錄了剛剛執(zhí)行pr_debug()時的文件名、所在行號、模塊名、函數(shù)名和輸出語句(p表示動態(tài)輸出的語句)。
-
內(nèi)核
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
1382瀏覽量
40377 -
驅(qū)動
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
12文章
1851瀏覽量
85498 -
Linux
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
87文章
11342瀏覽量
210155 -
輸出
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
93瀏覽量
21860
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
Linux內(nèi)核學(xué)習(xí)筆記:動態(tài)輸出調(diào)試
嵌入式Linux系統(tǒng)中內(nèi)核抽象的動態(tài)擴展技術(shù)
嵌入式Linux系統(tǒng)中內(nèi)核抽象的動態(tài)擴展技術(shù)
嵌入式Linux系統(tǒng)中內(nèi)核抽象的動態(tài)擴展技術(shù)
Linux嵌入式系統(tǒng)中內(nèi)核技術(shù)的可動態(tài)拓展技術(shù)有哪些
Linux的內(nèi)核教程
如何配置和使用Linux內(nèi)核printk功能
linux內(nèi)核是什么_linux內(nèi)核學(xué)習(xí)路線
linux內(nèi)核參數(shù)設(shè)置_linux內(nèi)核的功能有哪些
最硬核的Linux內(nèi)核文章
快速理解什么是Linux內(nèi)核以及Linux內(nèi)核的內(nèi)容




 Linux內(nèi)核基礎(chǔ):動態(tài)輸出使用
Linux內(nèi)核基礎(chǔ):動態(tài)輸出使用










評論