電報是與樹莓派結(jié)合的最佳應(yīng)用程序,用于我們所有的移動控制目的。它具有非常好的開發(fā)人員支持,并且計(jì)劃很快發(fā)布許多功能,以提高電報機(jī)器人的性能。
現(xiàn)在,我們將繼續(xù)下一步,學(xué)習(xí)如何使用 Telegram 控制樹莓引腳上的 GPIO 引腳,以便我們?yōu)闄C(jī)器人提供一些硬件支持。在本教程中,我們將四個 LED 連接到 Raspberry Pi GPIO 引腳,并使用 Telegram 中的自然語言(像聊天一樣)切換它們。聽起來很有趣吧?讓我們開始吧。
所需材料:
四個指示燈(任何顏色)
樹莓派(帶互聯(lián)網(wǎng)連接)
面包板
連接線
先決條件:
在繼續(xù)本教程之前,請確保您的樹莓派已連接到互聯(lián)網(wǎng),并且可以在 Pi 上運(yùn)行 python 程序。另請閱讀前面的教程以了解如何使用Raspberry Pi Pi設(shè)置Telegram機(jī)器人,因?yàn)槲壹僭O(shè)您熟悉這些東西以繼續(xù)進(jìn)行該項(xiàng)目。
如果您不熟悉樹莓派,請按照我們的樹莓派介紹文章和其他樹莓派教程進(jìn)行操作。
電路圖:
使用Raspberry Pi和Telegram Android應(yīng)用程序控制LED的電路圖無非是四個LED和一些連接線。我們不需要限流電阻,因?yàn)镽aspberry Pi GPIO引腳在3.3V TTL上工作。按照下面的電路連接您的 LED。
下表將幫助您確定連接四個 LED 的引腳編號和 GPIO 編號。
| 發(fā)光二極管端子 | 引腳編號 | 通用信息辦公室編號 |
| 綠色陽極 | 引腳 31 | GPIO 6 |
| 紅色陽極 | 引腳 33 | 通用信息總局 13 |
| 黃色陽極 | 引腳 35 | GPIO 19 |
| 白色陽極 | 引腳 37 | GPIO 26 |
| 所有四個陰極 | 引腳 39 | 地 |
下面是根據(jù)上表連接四個LED的電路圖:
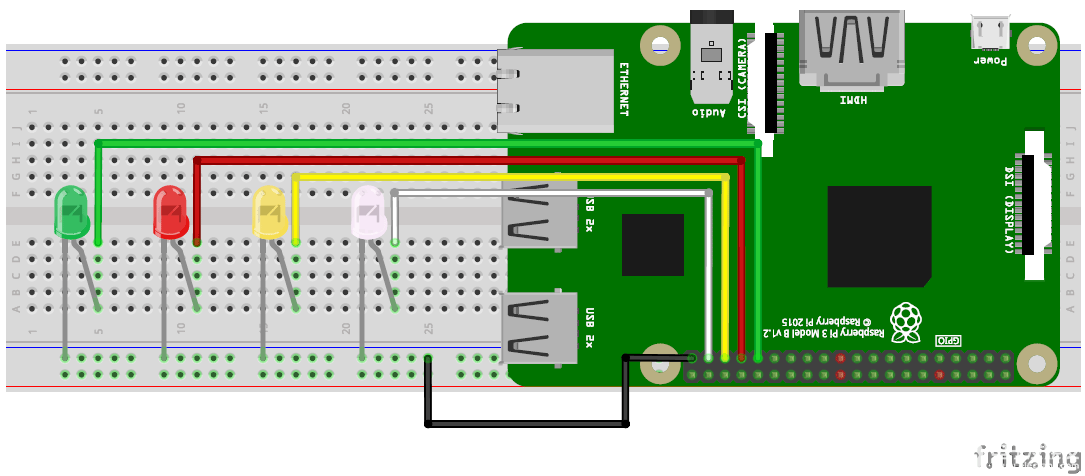
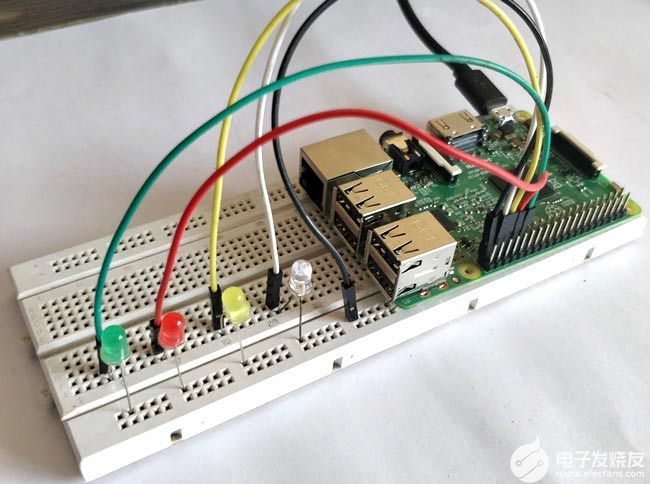
連接后,您的硬件設(shè)置應(yīng)如下所示。
Raspberry Python Program:
硬件準(zhǔn)備就緒后,我們可以繼續(xù)進(jìn)行 Python 程序。在這個程序中,我們必須讀取從電報機(jī)器人發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)(消息)并相應(yīng)地切換 LED。為了使它更自然,我們可以檢查單詞并相應(yīng)地進(jìn)行相應(yīng)的操作,而不是檢查每個句子并在程序中對這些句子進(jìn)行硬編碼。
因此,程序?qū)⒅饕獧z查兩個單詞,它們是打開和關(guān)閉的。一旦檢測到這兩個單詞中的任何一個,它將查找其他關(guān)鍵字,如白色、黃色、綠色和紅色。僅當(dāng)檢測到單詞時,才會切換相應(yīng)的顏色 LED。我們還將更新檢測到的單詞的字符串,以將消息發(fā)送回電報機(jī)器人。
完整的程序可以在此頁面底部找到;就在下面,我通過將程序分解為有意義的小垃圾來解釋該程序。
為了使該程序正常工作,我們需要將telepot下載并導(dǎo)入到我們的樹莓派中。在我們之前的教程中,我們已經(jīng)在樹莓派中下載了傳送,所以現(xiàn)在我們只需要將其與 GPIO 庫一起導(dǎo)入我們的程序,如下所示。
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import telepot
from telepot.loop import MessageLoop
我們將使用此程序控制 LED 燈,LED 的顏色將為白色、黃色、紅色和綠色。它們連接到電路圖所示的引腳;讓我們根據(jù)顏色定義這些LED的引腳名稱,以便在程序中使用它們。
white = 26
yellow = 19
red = 13
green = 6
下一步是將所有這些 LED 引腳定義為輸出引腳,并使用以下行將它們定義為默認(rèn)關(guān)閉。
#LED White
GPIO.setup(white, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(white, 0) #Off initially
#LED Yellow
GPIO.setup(yellow, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(yellow, 0) #Off initially
#LED Red
GPIO.setup(red, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(red, 0) #Off initially
#LED green
GPIO.setup(green, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(green, 0) #Off initially
正如我們在前面的教程中學(xué)到的那樣,Raspberry 機(jī)器人必須完成的所有操作都將在函數(shù)操作中定義。在這里,我們必須讓機(jī)器人收聽從移動設(shè)備發(fā)送的消息,將其與某些關(guān)鍵字進(jìn)行比較并相應(yīng)地切換 LED。
對于我們從移動設(shè)備發(fā)送的每條消息,都會有一個聊天ID和命令。程序需要此聊天 ID 才能回復(fù)發(fā)件人。因此,我們保存聊天ID和消息,如下所示。
chat_id = msg['chat']['id']
command = msg['text']
現(xiàn)在,我們從手機(jī)發(fā)送的任何內(nèi)容都將在變量命令中保存為字符串。因此,我們所要做的就是檢查此變量中的關(guān)鍵字。Python有一個命令使事情變得簡單。例如,如果我們必須檢查存儲在命令變量中的字符串中是否存在單詞“on”,我們可以簡單地使用以下行。
if 'on' in command:
同樣,我們檢查所有關(guān)鍵字,一旦收到“on”,我們繼續(xù)檢查用戶提到的顏色。這也是通過比較相同的關(guān)鍵字來使用相同的命令來完成的。我們還更新名為 message 的字符串,該字符串可以作為狀態(tài)消息回復(fù)給用戶。
if 'on' in command:
message = "Turned on "
if 'white' in command:
message = message + "white "
GPIO.output(white, 1)
if 'yellow' in command:
message = message + "yellow "
GPIO.output(yellow, 1)
if 'red' in command:
message = message + "red "
GPIO.output(red, 1)
if 'green' in command:
message = message + "green "
GPIO.output(green, 1)
if 'all' in command:
message = message + "all "
GPIO.output(white, 1)
GPIO.output(yellow, 1)
GPIO.output(red, 1)
GPIO.output(green, 1)
message = message + "light(s)"
telegram_bot.sendMessage (chat_id, message)
如上所示,我們僅查找“綠色”、“白色”、“紅色”、“黃色”和“全部”和“打開”等關(guān)鍵字。工作完成后,我們會向用戶發(fā)送一條關(guān)于剛剛發(fā)生的事情的消息。同樣的方法可以用來關(guān)燈。
if 'off' in command:
message = "Turned off "
if 'white' in command:
message = message + "white "
GPIO.output(white, 0)
if 'yellow' in command:
message = message + "yellow "
GPIO.output(yellow, 0)
if 'red' in command:
message = message + "red "
GPIO.output(red, 0)
if 'green' in command:
message = message + "green "
GPIO.output(green, 0)
if 'all' in command:
message = message + "all "
GPIO.output(white, 0)
GPIO.output(yellow, 0)
GPIO.output(red, 0)
GPIO.output(green, 0)
message = message + "light(s)"
telegram_bot.sendMessage (chat_id, message)
使用 Raspberry Pi 和 Telegram bot 控制 LED:
連接您的 LED 并在 python 上啟動您的程序。確保已更改機(jī)器人的令牌地址。并開始輸入您想要的命令。例如,要打開紅燈和黃燈,您可以使用以下命令中的任何一個。
1.開啟紅黃燈
2.打開紅色和黃色右邊
3.關(guān)于紅色和黃色
4.請亮起黃燈和紅燈
什么不是。
如您所見,機(jī)器人僅查找關(guān)鍵字,并會忽略句子中的其他單詞,這樣您就可以自然地與之交談。該項(xiàng)目的完整工作可以在本頁末尾的視頻中找到。
import time, datetime
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import telepot
from telepot.loop import MessageLoop
white = 26
yellow = 19
red = 13
green = 6
now = datetime.datetime.now()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
#LED White
GPIO.setup(white, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(white, 0) #Off initially
#LED Yellow
GPIO.setup(yellow, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(yellow, 0) #Off initially
#LED Red
GPIO.setup(red, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(red, 0) #Off initially
#LED green
GPIO.setup(green, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(green, 0) #Off initially
def action(msg):
chat_id = msg['chat']['id']
command = msg['text']
print 'Received: %s' % command
if 'on' in command:
message = "Turned on "
if 'white' in command:
message = message + "white "
GPIO.output(white, 1)
if 'yellow' in command:
message = message + "yellow "
GPIO.output(yellow, 1)
if 'red' in command:
message = message + "red "
GPIO.output(red, 1)
if 'green' in command:
message = message + "green "
GPIO.output(green, 1)
if 'all' in command:
message = message + "all "
GPIO.output(white, 1)
GPIO.output(yellow, 1)
GPIO.output(red, 1)
GPIO.output(green, 1)
message = message + "light(s)"
telegram_bot.sendMessage (chat_id, message)
if 'off' in command:
message = "Turned off "
if 'white' in command:
message = message + "white "
GPIO.output(white, 0)
if 'yellow' in command:
message = message + "yellow "
GPIO.output(yellow, 0)
if 'red' in command:
message = message + "red "
GPIO.output(red, 0)
if 'green' in command:
message = message + "green "
GPIO.output(green, 0)
if 'all' in command:
message = message + "all "
GPIO.output(white, 0)
GPIO.output(yellow, 0)
GPIO.output(red, 0)
GPIO.output(green, 0)
message = message + "light(s)"
telegram_bot.sendMessage (chat_id, message)
telegram_bot = telepot.Bot('470583174:AAG7MPZc93qchp-tjqA_K2meRYcQiOR7X7Y')
print (telegram_bot.getMe())
MessageLoop(telegram_bot, action).run_as_thread()
print 'Up and Running....'
while 1:
time.sleep(10)
-
樹莓派
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
117文章
1710瀏覽量
105807 -
gpio引腳
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
0文章
8瀏覽量
2640
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
樹莓派MCC118
通過Python RPi.GPIO控制樹莓派引腳
HiHope的產(chǎn)品,是否有類似于樹莓派的GPIO引腳的設(shè)計(jì)?
樹莓派gpio接口及編程方法
樹莓派上MAX7219的字符驅(qū)動程序編寫
怎樣在樹莓派上使用Telegram發(fā)送和接收消息
怎樣在樹莓派上設(shè)置Telegram Bot
如何在樹莓派上運(yùn)行Fedora
用網(wǎng)頁控制樹莓派的GPIO引腳





 如何使用Telegram控制樹莓派上的GPIO引腳
如何使用Telegram控制樹莓派上的GPIO引腳










評論