很多Jetson用戶在自動化解決方案中選擇激光雷達進行定位和感知。激光雷達使用3D點云描繪周圍的空間環境。點云可以高精度長距離采樣物體表面信息以便于上層應用的障礙感知、繪圖、定位和路徑規劃算法。
使用CUDA-PCL處理點云
CUDA PCL 1.0是基于CUDA開發的點云處理庫,在本文中,我們將介紹目前所有的三個庫:ICP,segmentation 和 filter。
CUDA-ICP
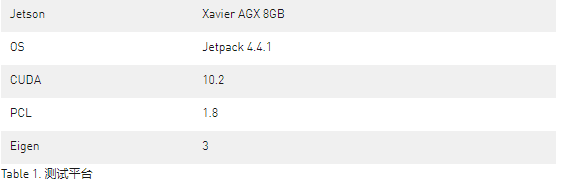
迭代最近點算法(Iterative Closest Point,ICP) 用于計算兩幀點云數據之間的坐標變換矩陣,從而能夠使不同的坐標下的點云數據合并到同一個坐標系統中。ICP算法 通過計算兩幀點云的距離誤差從而修正變換矩陣(平移和旋轉)以便最小化距離誤差,通常兩幀點云之間的距離誤差是通過匹配點的距離計算得來。ICP算法應用廣泛,能夠獲得很高的匹配結果且有很高的魯棒性,同時會耗費大量的計算資源。為了改進ICP算法在Jetson上的性能,我們推薦使用基于CUDA加速的CUDA-ICP。
使用CUDA-ICP
以下是CUDA ICP的使用實例
我們僅僅需要初始化相關的類對象,并調用接口函數即可。
cudaICP icpTest(nPCountM, nQCountM, stream);
icpTest.icp(cloud_source, nPCount,
float *cloud_target, int nQCount,
int Maxiterate, double threshold,
Eigen::Matrix4f &transformation_matrix, stream);
CUDA-ICP 計算的輸出是 transformation_matrix,代表的含義如下:
源點云(P)* transformation = 目標坐標系的點云(Q)
因為激光類型的輸出點云的數量為固定值,所以CUDA-ICP在輸出化的時候,要求輸入兩幀點云的最大數量,從而分配計算資源。
class cudaICP
{
public:
/*
nPCountM and nQCountM are the maximum of count for input clouds
They are used to pre-allocate memory.
*/
cudaICP(int nPCountM, int nQCountM, cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaICP(void);
/*
cloud_target = transformation_matrix *cloud_source
When the Epsilon of transformation_matrix is less than threshold,
the function will return transformation_matrix.
Input:
cloud_source, cloud_target: data pointer for points cloud
nPCount: the points number of cloud_source
nQCount: the points number of cloud_target
Maxiterate: the threshold for iterations
threshold: When the Epsilon of transformation_matrix is less than
threshold, the function will return transformation_matrix.
Output:
transformation_matrix
*/
void icp(float *cloud_source, int nPCount,
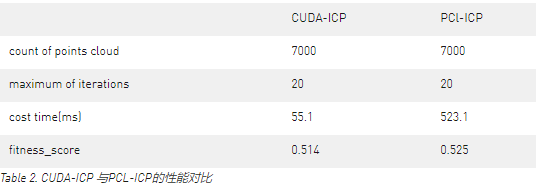

Figure 1. 執行ICP之前的兩幀點云。

Figure 2. 經過ICP匹配后的兩幀點云。
CUDA-Segmentation
點云地圖包含大量的地面點,不僅會使得地圖變的雜亂,也會干擾之后的點云的分類和識別。因此在實際處理中,我們會首先使用點云分割移除點云中的地面。CUDA-Segmentation 使用隨機樣本一致性算法(random sample consensus, Ransac)進行點云的分割。
使用CUDA- Segmentation
以下代碼是CUDA Segmentation的使用實例。
我們直接初始化對象并調用相關的接口函數即可。

//Now Just support: SAC_RANSAC + SACMODEL_PLANE
std::vector indexV;
cudaSegmentation cudaSeg(SACMODEL_PLANE, SAC_RANSAC, stream);
segParam_t setP;
setP.distanceThreshold = 0.01;
setP.maxIterations = 50;
setP.probability = 0.99;
setP.optimizeCoefficients = true;
cudaSeg.set(setP);
cudaSeg.segment(input, nCount, index, modelCoefficients);
for(int i = 0; i < nCount; i++)
{
if(index[i] == 1)
indexV.push_back(i);
}
CUDA Segmentation分割擁有nCount個的點云,并輸出索引表index用于指示輸入點云中的被分割掉的點和modelCoefficients用于指示尋找的平面公式。
typedef struct {
double distanceThreshold;
int maxIterations;
double probability;
bool optimizeCoefficients;
} segParam_t;
class cudaSegmentation
{
public:
//Now Just support: SAC_RANSAC + SACMODEL_PLANE
cudaSegmentation(int ModelType, int MethodType, cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaSegmentation(void);
/*
Input:
cloud_in: data pointer for points cloud
nCount: count of points in cloud_in
Output:
Index: data pointer which has the index of points in a plane from input
modelCoefficients: data pointer which has the group of coefficients of the plane
*/
int set(segParam_t param);
void segment(float *cloud_in, int nCount,
int *index, float *modelCoefficients);
private:
void *m_handle = NULL;
};
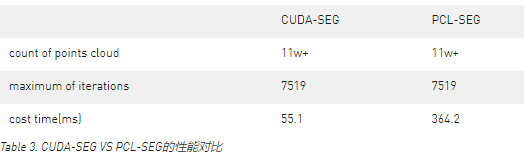
讓我們查看下面的實例,第一張圖是原始的點云,第二張圖是經過算法尋找到的平面。這是一個非常典型的平面移除的應用。

Figure 3. cuda-segmentaion處理之前的點云。

Figure 4. cuda-segmentaion找到的點云平面。
CUDA-Filter
帶通點云濾波是最簡單的方法,僅僅是過濾X,Y和Z軸方向的點云。
目前CUDA-Filter僅支持帶通操作,更多的濾波器會在后續加入。
使用CUDA- Filter
這個是CUDA Filter的使用實例。
我們僅僅需要初始化對象并調用相關的接口函數即可。
我們僅僅需要初始化對象并調用相關的接口函數即可。
cudaFilter filterTest(stream);
FilterParam_t setP;
FilterType_t type = PASSTHROUGH;
setP.type = type;
setP.dim = 2;
setP.upFilterLimits = 1.0;
setP.downFilterLimits = 0.0;
setP.limitsNegative = false;
filterTest.set(setP);
filterTest.filter(output, &countLeft, input, nCount);
CUDA-Filter使用指定的參數過濾nCount有個點的點云數據,過濾后輸出的點云數量為countLeft。
typedef struct {
FilterType_t type;
//0=x,1=y,2=z
int dim;
float upFilterLimits;
float downFilterLimits;
bool limitsNegative;
} FilterParam_t;
class cudaFilter
{
public:
cudaFilter(cudaStream_t stream = 0);
~cudaFilter(void);
int set(FilterParam_t param);
/*
Input:
source: data pointer for points cloud
nCount: count of points in cloud_in
Output:
output: data pointer which has points filtered by CUDA
countLeft: count of points in output
*/
int filter(void *output, unsigned int *countLeft, void *source, unsigned int nCount);
void *m_handle = NULL;
};
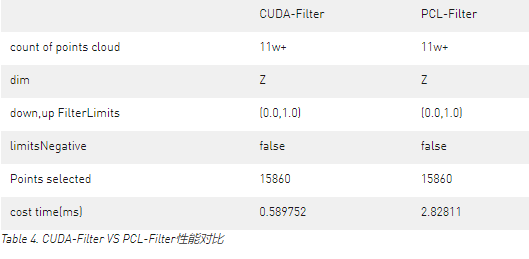
讓我們看下X軸方向的帶通濾波實例。

Figure 5. 原始點云。

Figure 6. X周過濾后的數據。
開始使用 CUDA-PCL
我們希望通過本文介紹使用CUDA-PCL從而獲得更好的點云處理性能。
因為PCL在Jetson上無法使用CUDA進行點云的加速處理,所以我們開發了基于CUDA的點云處理庫CUDA-PCL。
關于作者
范磊是英偉達高級CUDA軟件工程師,在TSE China 小組致力于CUDA軟件方案的開發和優化。
李雨倩負責基于Jetson的自主機器解決方案和生態發展建設,讓開發者在Jetson上開發機器人應用獲得更好更全面的體驗和支持。
審核編輯:郭婷
-
激光雷達
+關注
關注
968文章
4024瀏覽量
190264 -
CUDA
+關注
關注
0文章
121瀏覽量
13656
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
GPU加速云服務器怎么用的
基于深度學習的三維點云分類方法
怎么在TMDSEVM6678: 6678自帶的FFT接口和CUDA提供CUFFT函數庫選擇?
LiDAR激光點云數據處理軟件處理流程
如何理解云計算?
打破英偉達CUDA壁壘?AMD顯卡現在也能無縫適配CUDA了
軟件生態上超越CUDA,究竟有多難?
友思特案例 | 自研創新!三維工件尺寸測量及點云處理解決方案
借助NVIDIA Aerial CUDA增強5G/6G的DU性能和工作負載整合
NVIDIA 通過 CUDA-Q 平臺為全球各地的量子計算中心提供加速
Keil使用AC6編譯提示CUDA版本過高怎么解決?
基于深度學習的方法在處理3D點云進行缺陷分類應用




 使用CUDA PCL 1.0加速Jetson的點云處理
使用CUDA PCL 1.0加速Jetson的點云處理










評論