概述
這些傳感器使用固態技術來確定氣溫。也就是說,它們不使用汞(例如舊溫度計),雙金屬條(例如在某些家用溫度計或火爐中),也不使用熱敏電阻(對溫度敏感的電阻器)。取而代之的是,他們利用溫度升高的事實,二極管兩端的電壓以已知的速率增加。 (從技術上講,這實際上是晶體管的基極和發射極之間的電壓降-Vbe。)通過精確地放大電壓變化,很容易生成與溫度成正比的模擬信號。該技術已有一些改進,但本質上是如何測量溫度。
好消息是,所有復雜的計算都在內部進行 芯片-它只是吐出溫度,供您使用!
因為這些傳感器沒有活動部件,所以它們精確,永不磨損,不需要校準,在許多環境條件下工作且在傳感器之間保持一致和閱讀。此外,它們非常便宜并且易于使用。
一些基本統計數據
這些統計數據適用于Adafruit商店中的溫度傳感器,即TMP36(-40至150C)。它與LM35/TMP35(攝氏輸出)和LM34/TMP34(華氏輸出)非常相似。我們使用‘36而不是’35或‘34的原因是該傳感器具有非常寬的范圍,并且不需要負電壓即可讀取低于零的溫度。否則,功能基本相同。
尺寸: TO-92封裝(約0.2“ x 0.2” x 0.2“),帶有三根引線
價格:在Adafruit商店中為1.50美元
溫度范圍::-40°C至150°C/-40°F至302° F
輸出范圍: 0.1V(-40°C)至2.0V(150°C),但在125°C之后精度會降低
數據表
如何測量溫度
使用TMP36很簡單,只需連接左引腳接電源(2.7-5.5V),右引腳接地,然后中間引腳將具有與溫度成正比(線性)的模擬電壓,該模擬電壓與電源無關。
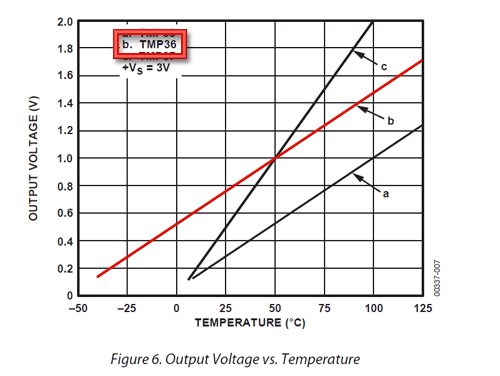
要轉換電壓電壓只需使用以下基本公式即可:
以°C為單位的溫度= [(以VV為單位的Vout)-500 ] /10
因此,例如,如果輸出電壓為1V,則表示溫度為((1000 mV-500)/10)= 50°C
如果使用LM35或類似產品,在上圖中使用“ a”行和公式:以°C為單位的溫度=(以mV為單位的Vout) /10
多個傳感器可能遇到的問題:如果,添加更多傳感器時,您會發現溫度不一致,這表明在將模擬讀取電路從一個引腳切換到另一個引腳時,傳感器會相互干擾。您可以通過延遲閱讀兩次并扔掉第一個閱讀器來解決此問題
有關更多信息,請參閱此帖子
測試溫度傳感器
測試這些傳感器非常容易,但是您需要電池組或電源。
連接2.7-5.5 V電源(2-4節AA電池工作出色),以便將接地線連接到第3針(右引腳),并且將電源連接到第1針(左引腳)
然后用直流電壓連接萬用表模式接地,其余引腳2(中間)。如果您擁有TMP36及其大約室溫(25°C),則電壓應約為0.75V。請注意,如果您使用的是LM35,則電壓為0.25V
傳感器指示溫度為26.3°C,也稱為79.3°F
您可以通過用手指按壓傳感器的塑料外殼來更改電壓范圍,您將看到溫度/電壓升高。
用我的手指在傳感器上加熱一點,現在溫度讀數為29.7°C/85.5°F
或者您可以用冰塊觸摸傳感器,最好將其放在塑料袋中,以免電路上積水,并查看溫度/電壓降。
我將冰塊壓在傳感器上,以將溫度降至18.6°C/65.5°F
使用溫度傳感器
溫度傳感器。這些傳感器中幾乎沒有芯片,盡管它們不那么精密,但確實需要正確處理。處理靜電時要小心靜電,并確保電源正確連接并且在2.7至5.5V DC之間-因此,請勿嘗試使用9V電池!
它們帶有“ TO”字樣-92英寸封裝,這意味著芯片被封裝在具有三個支腳的塑料半圓柱體內。支腳可以輕松彎曲,以將傳感器插入面包板。您也可以焊接到引腳以連接長導線。如果您需要對傳感器進行防水處理,則可以在下面看到有關如何制作出色保護套的說明。
讀取模擬溫度數據與我們研究過的FSR或光電傳感器不同,TMP36和朋友并不像電阻器那樣工作。因此,實際上只有一種方法可以從傳感器讀取溫度值,即將輸出引腳直接插入模擬(ADC)輸入。
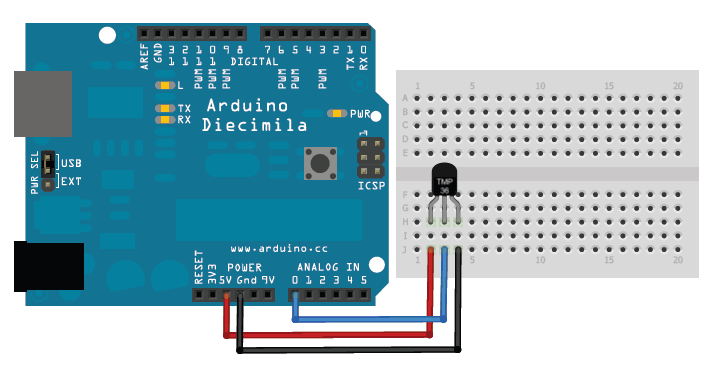
請記住,您可以使用2.7V至5.5V之間的任何電壓作為電源供應。在此示例中,我顯示的是5V電源,但請注意,您可以輕松地將其與3.3v電源一起使用。無論您使用哪種電源,模擬電壓讀數的范圍都將在大約0V(地)到大約1.75V之間。
如果您使用的是5V Arduino,并將傳感器直接連接到模擬引腳,您可以使用以下公式將10位模擬讀數轉換為溫度:
引腳上的電壓,單位為毫伏=(從ADC讀取)*(5000/1024 )
此公式將ADC的數字0-1023轉換為0-5000mV(= 5V)
如果您使用的是3.3V Arduino,則需要使用
引腳上的電壓(單位為毫伏)=(從ADC讀取)*(3300/1024)
此公式將數字轉換為0- 1023從ADC轉換為0-3300mV(= 3.3V)
然后將毫伏轉換為溫度,請使用以下公式:
攝氏度溫度= [(模擬電壓mV)-500]/10
Arduino Sketch-簡單溫度計
此示例代碼顯示了Arduino一種快速創建溫度傳感器的方法,它只需在串行端口上打印攝氏溫度和華氏溫度的當前溫度即可。
下載:文件
復制代碼
//TMP36 Pin Variables
int sensorPin = 0; //the analog pin the TMP36’s Vout (sense) pin is connected to
//the resolution is 10 mV / degree centigrade with a
//500 mV offset to allow for negative temperatures
/*
* setup() - this function runs once when you turn your Arduino on
* We initialize the serial connection with the computer
*/
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Start the serial connection with the computer
//to view the result open the serial monitor
}
void loop() // run over and over again
{
//getting the voltage reading from the temperature sensor
int reading = analogRead(sensorPin);
// converting that reading to voltage, for 3.3v arduino use 3.3
float voltage = reading * 5.0;
voltage /= 1024.0;
// print out the voltage
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(“ volts”);
// now print out the temperature
float temperatureC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100 ; //converting from 10 mv per degree wit 500 mV offset
//to degrees ((voltage - 500mV) times 100)
Serial.print(temperatureC); Serial.println(“ degrees C”);
// now convert to Fahrenheit
float temperatureF = (temperatureC * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0;
Serial.print(temperatureF); Serial.println(“ degrees F”);
delay(1000); //waiting a second
} //TMP36 Pin Variables
int sensorPin = 0; //the analog pin the TMP36‘s Vout (sense) pin is connected to
//the resolution is 10 mV / degree centigrade with a
//500 mV offset to allow for negative temperatures
/*
* setup() - this function runs once when you turn your Arduino on
* We initialize the serial connection with the computer
*/
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Start the serial connection with the computer
//to view the result open the serial monitor
}
void loop() // run over and over again
{
//getting the voltage reading from the temperature sensor
int reading = analogRead(sensorPin);
// converting that reading to voltage, for 3.3v arduino use 3.3
float voltage = reading * 5.0;
voltage /= 1024.0;
// print out the voltage
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(“ volts”);
// now print out the temperature
float temperatureC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100 ; //converting from 10 mv per degree wit 500 mV offset
//to degrees ((voltage - 500mV) times 100)
Serial.print(temperatureC); Serial.println(“ degrees C”);
// now convert to Fahrenheit
float temperatureF = (temperatureC * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0;
Serial.print(temperatureF); Serial.println(“ degrees F”);
delay(1000); //waiting a second
}
獲得更高的精度為獲得更好的結果,使用3.3v參考電壓作為ARef而不是5V會更精確,并且少噪音
光照和溫度數據記錄教程中的此示例有一個光電管,但是您可以忽略它
請注意,我們已將TMP36更改為A1
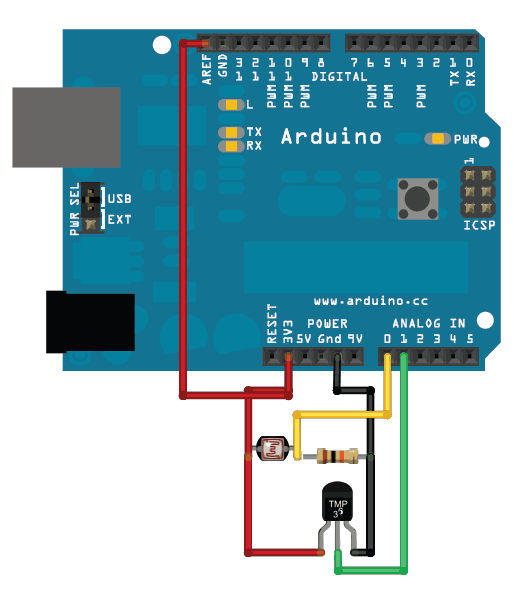
要將3.3v引腳用作模擬參考,請不要忘記在設置中像代碼中那樣指定“ analogReference(EXTERNAL)”下方:
下載:文件
復制代碼
/* Sensor test sketch
for more information see http://www.ladyada.net/make/logshield/lighttemp.html
*/
#define aref_voltage 3.3 // we tie 3.3V to ARef and measure it with a multimeter!
//TMP36 Pin Variables
int tempPin = 1; //the analog pin the TMP36’s Vout (sense) pin is connected to
//the resolution is 10 mV / degree centigrade with a
//500 mV offset to allow for negative temperatures
int tempReading; // the analog reading from the sensor
void setup(void) {
// We‘ll send debugging information via the Serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
// If you want to set the aref to something other than 5v
analogReference(EXTERNAL);
}
void loop(void) {
tempReading = analogRead(tempPin);
Serial.print(“Temp reading = ”);
Serial.print(tempReading); // the raw analog reading
// converting that reading to voltage, which is based off the reference voltage
float voltage = tempReading * aref_voltage;
voltage /= 1024.0;
// print out the voltage
Serial.print(“ - ”);
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(“ volts”);
// now print out the temperature
float temperatureC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100 ; //converting from 10 mv per degree wit 500 mV offset
//to degrees ((volatge - 500mV) times 100)
Serial.print(temperatureC); Serial.println(“ degrees C”);
// now convert to Fahrenheight
float temperatureF = (temperatureC * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0;
Serial.print(temperatureF); Serial.println(“ degrees F”);
delay(1000);
} /* Sensor test sketch
for more information see http://www.ladyada.net/make/logshield/lighttemp.html
*/
#define aref_voltage 3.3 // we tie 3.3V to ARef and measure it with a multimeter!
//TMP36 Pin Variables
int tempPin = 1; //the analog pin the TMP36’s Vout (sense) pin is connected to
//the resolution is 10 mV / degree centigrade with a
//500 mV offset to allow for negative temperatures
int tempReading; // the analog reading from the sensor
void setup(void) {
// We‘ll send debugging information via the Serial monitor
Serial.begin(9600);
// If you want to set the aref to something other than 5v
analogReference(EXTERNAL);
}
void loop(void) {
tempReading = analogRead(tempPin);
Serial.print(“Temp reading = ”);
Serial.print(tempReading); // the raw analog reading
// converting that reading to voltage, which is based off the reference voltage
float voltage = tempReading * aref_voltage;
voltage /= 1024.0;
// print out the voltage
Serial.print(“ - ”);
Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(“ volts”);
// now print out the temperature
float temperatureC = (voltage - 0.5) * 100 ; //converting from 10 mv per degree wit 500 mV offset
//to degrees ((volatge - 500mV) times 100)
Serial.print(temperatureC); Serial.println(“ degrees C”);
// now convert to Fahrenheight
float temperatureF = (temperatureC * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0;
Serial.print(temperatureF); Serial.println(“ degrees F”);
delay(1000);
}
帶有CircuitPython的TMP36
使用CircuitPython,可以使用板載內置的模擬I/O模塊和模數轉換器輕松讀取TMP36傳感器。您只需使用幾行Python代碼就可以輕松地將TMP36輸出電壓轉換為精確的溫度讀數。
要遵循此頁面,請確保如上圖所示將TMP36傳感器連接到CircuitPython板上頁。 A0模擬輸入將用作TMP36溫度輸出的輸入。這是一個在A0模擬輸入上連接到TMP36的Feather M0的示例:
注意:發現以下簡單電路給出了錯誤的提示由于CircuitPython讀取模擬值的速度很快,因此可以使用CircuitPython進行讀數。要解決此問題,請在TMP36的輸出和接地引腳之間添加一個0.01uF或0.1uF的電容以及一個47k的電阻。
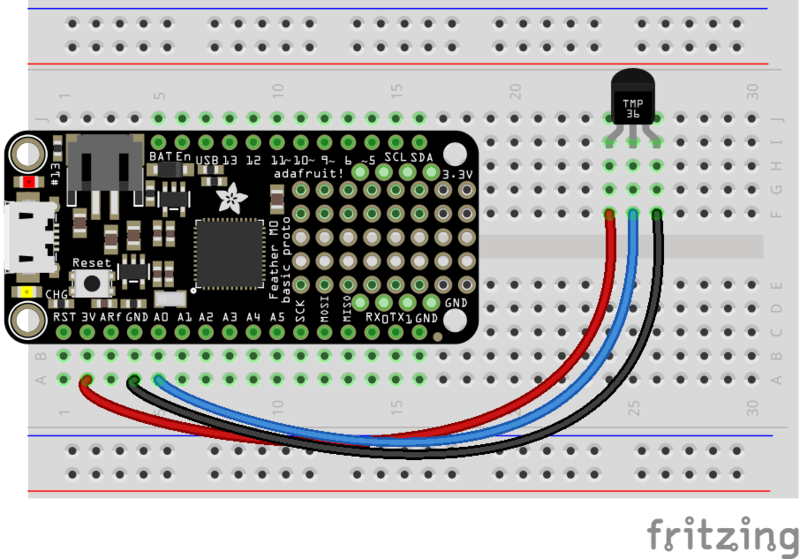
div》
Fritzing Source
首先連接到開發板的串行REPL,因此您位于CircuitPython的》》》 提示符下。
接下來導入必要的 board 和 analogio 模塊:
下載:文件
復制代碼
import board
import analogio import board
import analogio
現在為板上的A0引腳創建一個模擬輸入:
下載:文件
復制代碼
tmp36 = analogio.AnalogIn(board.A0) tmp36 = analogio.AnalogIn(board.A0)
這時,您可以讀取TMP36傳感器輸出的原始ADC值。就像模擬I/O指南中提到的那樣,該值的范圍將與傳感器輸出的電壓成正比,范圍是0到65535(從0到電路板的模擬參考電壓,通常是3.3V到5V)。例如,嘗試讀取原始ADC值:
下載:文件
復制代碼
tmp36.value tmp36.value
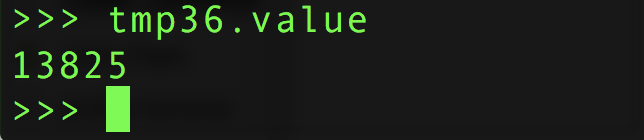
您可以使用上一頁中提到的類似公式將此值轉換為電壓(以毫伏為單位)。但是,有一個很小的變化將值的范圍從1023增加到65535-這是必要的,因為CircuitPython為ADC輸入使用了更大范圍的值。此外,通過CircuitPython,您可以直接訪問電路板的模擬參考電壓,因此一個簡單的公式對于3.3V和5V參考均適用:
下載:文件
復制代碼
tmp36.value * (tmp36.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535) tmp36.value * (tmp36.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)

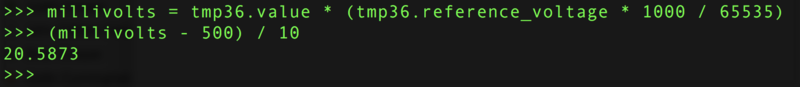
一旦TMP36輸出了模擬電壓值,就可以將其轉換為溫度就像上一頁顯示的那樣:
下載:文件
復制代碼
millivolts = tmp36.value * (tmp36.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
(millivolts - 500) / 10 millivolts = tmp36.value * (tmp36.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
(millivolts - 500) / 10
讓我們為我們執行此函數并返回以攝氏度為單位的溫度:
下載:文件
復制代碼
def tmp36_temperature_C(analogin):
millivolts = analogin.value * (analogin.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
return (millivolts - 500) / 10
tmp36_temperature_C(tmp36) def tmp36_temperature_C(analogin):
millivolts = analogin.value * (analogin.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
return (millivolts - 500) / 10
tmp36_temperature_C(tmp36)


您也可以將其變成一個完整的程序,該程序也每秒讀取和打印溫度。將其另存為板上的 main.py 并檢查串行輸出:
下載:文件
復制代碼
import board
import analogio
import time
TMP36_PIN = board.A0 # Analog input connected to TMP36 output.
# Function to simplify the math of reading the temperature.
def tmp36_temperature_C(analogin):
millivolts = analogin.value * (analogin.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
return (millivolts - 500) / 10
# Create TMP36 analog input.
tmp36 = analogio.AnalogIn(TMP36_PIN)
# Loop forever.
while True:
# Read the temperature in Celsius.
temp_C = tmp36_temperature_C(tmp36)
# Convert to Fahrenheit.
temp_F = (temp_C * 9/5) + 32
# Print out the value and delay a second before looping again.
print(“Temperature: {}C {}F”.format(temp_C, temp_F))
time.sleep(1.0) import board
import analogio
import time
TMP36_PIN = board.A0 # Analog input connected to TMP36 output.
# Function to simplify the math of reading the temperature.
def tmp36_temperature_C(analogin):
millivolts = analogin.value * (analogin.reference_voltage * 1000 / 65535)
return (millivolts - 500) / 10
# Create TMP36 analog input.
tmp36 = analogio.AnalogIn(TMP36_PIN)
# Loop forever.
while True:
# Read the temperature in Celsius.
temp_C = tmp36_temperature_C(tmp36)
# Convert to Fahrenheit.
temp_F = (temp_C * 9/5) + 32
# Print out the value and delay a second before looping again.
print(“Temperature: {}C {}F”.format(temp_C, temp_F))
time.sleep(1.0)
這是將TMP36與CircuitPython一起使用的全部內容!
示例項目
遠程溫度傳感器
視頻使用生物反饋(體溫)的編輯器
如何為用于遙控車輛(機器人潛艇)的LM35傳感器防水
一個“智能杯墊”可讓您知道何時可以安全飲用咖啡/茶。其中一些項目使用熱敏電阻(根據溫度改變電阻的電阻溫度),但很容易適應TMP36等固態傳感器。
責任編輯:wv
-
溫度傳感器
+關注
關注
48文章
2972瀏覽量
156285
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
TMP112在溫度傳感器測量溫度工作時,其電源提供的工作電流是多少?
TMP1826和TMP1827單線溫度傳感器主機控制器的實現

TMP422-EP ±1°C遠程溫度傳感器和±2.5°C本地溫度傳感器數據表

TMP421、TMP422和TMP423 ±1°C遠程和本地溫度傳感器數據表

帶SensorPath總線的數字輸出溫度傳感器TMP141數據表

TMP121 TMP123: 帶SPI接口的1.5°C精確數字溫度傳感器數據表

配備 SMAART Wire? 接口的 TMP104 低功耗數字溫度傳感器數據表

TMP116、TMP116N低功耗、高精度溫度傳感器IC規格書
采用WCSP封裝、具有雙線制串行接口的TMP108低功耗數字溫度傳感器TMP108數據表

帶SPI?接口的1.5°C精確數字溫度傳感器TMP121和TMP123數據表





 TMP36溫度傳感器的使用
TMP36溫度傳感器的使用










評論