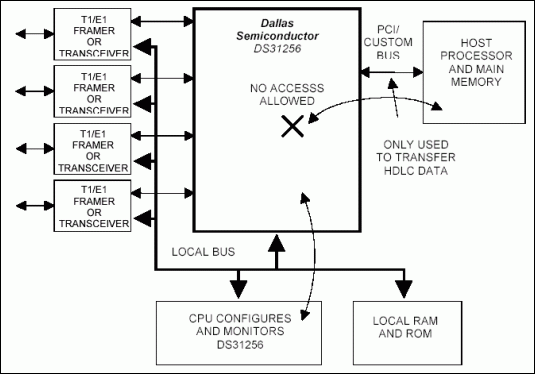
DS31256 HDLC控制器的配置步驟—橋接模式
本應用筆記提供了怎樣配置橋接模式下DS31256 HDLC控制器T1端口的例子。文章提供了一個實際例程,以方便最終用戶使用,幫助他們理解怎樣在環回模式下配置器件,構建數據包,并進行傳送、接收和檢查。
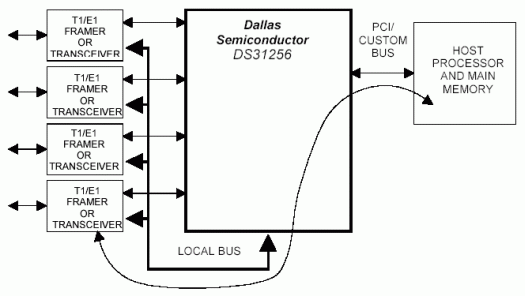
DS31256中的本地總線可以工作在兩種模式下:
- PCI橋接模式
- 配置模式
利用PCI橋接模式,PCI總線上的主機可以訪問本地總線。PCI總線用于控制并監視DS31256,發送分組數據。DS31256將數據從PCI總線映射到本地總線(請參考DS31256數據資料的11.1.1節,了解詳細信息)。
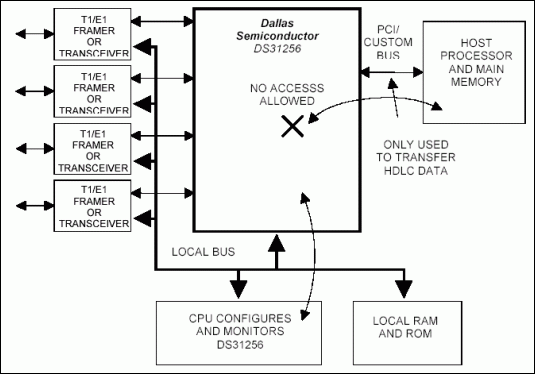
關于使用配置模式的詳細信息,請參考應用筆記2871:“DS31256 HDLC控制器的配置步驟—配置模式”。 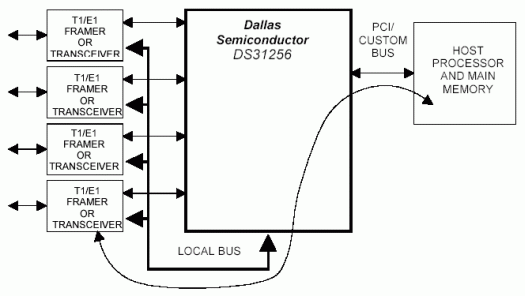
圖1.
這一例子具有以下配置:
| - | DS31256的端口1是通道化T1端口。所有其他端口都沒有使用。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| - | DS31256端口1 DS0的0-3被分配給HDLC通道3。端口1 DS0所有其他端口都沒有分配。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| - | DS31256的HDLC通道3被分配給4個Rx FIFO模塊、4個Tx FIFO模塊、一個Rx FIFO高水線3、一個Tx低水線1。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| - | 使用一個Tx緩沖,一個Tx描述符,一個Tx未決隊列輸入構建主機存儲器中的16字節數據包。由于DS31256處于環回模式,當傳送數據包時,DS31256也會收到它。使用一個Rx緩沖、一個Rx描述符,一個Rx完成隊列輸入,將接收到的數據包寫入主機存儲器。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| - | 主機存儲器進行如下配置:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
代碼實例函數調用定義
為提高可讀性,這個例子中的代碼使用了幾個函數調用。這些函數的定義如下:
- write_reg(address, data)
將指定的數據寫入指定的DS31256寄存器地址
輸入:
輸出:無
地址 = 數據要寫入的寄存器地址 數據 = 要寫入到指定寄存器中的數據
- read_reg(address, data)
讀取DS31256指定地址寄存器中的內容
輸入:
輸出:
地址 = 要讀取的寄存器地址
數據 = 來自寄存器的數值
- write_reg_IS(address, data)
將指定的數據寫入指定的DS31256間接選擇寄存器,然后,在返回前,等待該寄存器的忙比特被清位。
輸入:
輸出:無
地址 = 數據要寫入的間接選擇寄存器 數據 = 要寫入到指定寄存器的數據
函數代碼:
write_reg(address, data)
bit_check = 0x8000;
while(bit_check & 0x8000)
read_reg(address, bit_check);
- wr_dword(address, data)
將指定的32位數據寫入指定的32位主機存儲器地址
輸入:
輸出:無
地址 = 數據要寫入的主機存儲器地址 數據 = 要寫入到指定存儲器地址的數據
- rd_dword(address, data)
從指定的32位主機存儲器地址讀取的32位數據
輸入:
輸出:
地址 = 要讀取的主機存儲器地址
數據 = 從主機存儲器讀取的32位數據
- frame_wait(count)
提供等于幀周期數的延時,幀周期為125微秒。
輸入:
輸出:無
計數 = 要等待的幀周期數
T1配置模式代碼實例
這一代碼實例包括以下步驟:
- 復位DS31256
- 配置DS31256
- 使能HDLC通道
- 使HDLC通道處于環回模式
- 排列、發送、接收、檢查數據包
下面幾節提供簡要說明和代碼實例,詳細介紹了這些步驟。采用了寄存器名稱而不是地址,以提高可讀性。DS31256內部器件配置寄存器對應的地址/偏移列在相應的表格中。此外,縮寫Tx和Rx分別用于表示發送側和接收側。請參考DS31256數據資料,了解詳細信息。
復位DS31256
復位DS31256包括三步。首先,必須復位DS31256內部寄存器,然后,DS31256內部RAM必須置零,最后,再次復位DS31256內部寄存器。
復位DS31256內部寄存器
使用主復位寄存器(MRID)可以對DS31256中的所有寄存器進行軟件復位。當MRID寄存器的比特0被設置為1時,所有內部寄存器將被置為默認值0。在設置器件正常工作之前,主機必須將該位置回0。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0000 | MRID | Master Reset & ID Register | 5.1 |
//Reset DS31256 using MRID registers master reset bit.
write_reg(MRID, 0x0001);
write_reg(MRID, 0x0000);
將DS31256內部RAM置零
復位芯片時,DS31256內部配置RAM并沒有被清零,因此,必須手動清零。使用適當的數據和DS31256間接選擇寄存器,對DS31256的每一內部RAM進行一系列寫操作,完成該任務。本節詳細介紹完成該任務的過程。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 03xx | CP[n]RDIS | Channelized Port n Register Data Indirect Select | 6.3 |
| 03xx | CP[n]RD | Channelized Port n Register Data | 6.3 |
// Zero Rx configuration and Tx configuration RAM's for all ports
for(port = 0; port < 16; port = port + 1)
{
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 128; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
{
// Set bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx Configuration RAM
// Set bits 9-8 = 10 to select Tx Configuration RAM
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, (0x0100 + ds0));
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, (0x0200 + ds0));
}
}
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0400 | RHCDIS | Receive HDLC Channel Definition Indirect Select | 7.2 |
| 0404 | RHCD | Receive HDLC Channel Definition | 7.2 |
// Zero the Rx HDLC channel definition RAM
write_reg(RHCD, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RHCDIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0480 | THCDIS | Transmit HDLC Channel Definition Indirect Select | 7.2 |
| 0484 | THCD | Transmit HDLC Channel Definition | 7.2 |
// Zero the Tx HDLC channel definition RAM
write_reg(THCD, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(THCDIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0900 | RFSBPIS | Receive FIFO Starting Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0904 | RFSBP | Receive FIFO Starting Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Zero the Rx FIFO Starting Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(RFSBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFSBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0910 | RFBPIS | Receive FIFO Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0914 | RFBP | Receive FIFO Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Zero the Rx FIFO Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(RFBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0920 | RFHWMIS | Receive FIFO High Watermark Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0924 | RFHWM | Receive FIFO High Watermark | 8.2 |
// Zero the Rx FIFO High Watermark RAM
write_reg(RFHWM, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RFHWMIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0980 | TFSBPIS | Transmit FIFO Starting Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0984 | TFSBP | Transmit FIFO Starting Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Zero the Tx FIFO Starting Block Pointer registers
write_reg(TFSBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFSBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0990 | TFBPIS | Transmit FIFO Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0994 | TFBP | Transmit FIFO Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Zero the Tx FIFO Block Pointer RAM
write_reg(TFBP, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 09A0 | TFLWMIS | Transmit FIFO Low Watermark Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 09A4 | TFLWM | Transmit FIFO Low Watermark | 8.2 |
// Zero the Tx FIFO Low Watermark RAM
write_reg(TFLWM, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TFLWMIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0770 | RDMACIS | Receive DMA Configuration Indirect Select | 9.3.5 |
| 0774 | RDMAC | Receive DMA Configuration | 9.3.5 |
// Zero the Rx DMA configuration RAM
write_reg(RDMAC, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0870 | TDMACIS | Transmit DMA Configuration Indirect Select | 9.3.5 |
| 0874 | TDMAC | Transmit DMA Configuration | 9.3.5 |
// Zero the Tx DMA configuration RAM
write_reg(TDMAC, 0x0000);
for(channel = 0; channel < 256; channel = channel + 1)
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200 + channel);
復位DS31256內部寄存器
使用主復位寄存器(MRID)可以對DS31256中的所有寄存器進行軟件復位。當MRID寄存器的比特0被設置為1時,所有內部寄存器將被置為默認值0。在設置器件正常工作之前,主機必須將該位置回0。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0000 | MRID | Master Reset and ID Register | 5.1 |
// Reset DS31256 using MRID registers master reset bit.
write_reg(MRID, 0x0001);
write_reg(MRID, 0x0000);
配置DS31256
配置DS31256包括以下步驟:
- 配置PCI寄存器
- 配置1層寄存器
- 配置HDLC寄存器
- 配置FIFO寄存器
- 配置DMA寄存器
下面幾節詳細介紹了配置這些寄存器設置。采用了幾個變量來提高可讀性,提供計算能力更強的代碼結構。下面的代碼對這些變量進行初始化:
// This example uses port 1 channel 3
port = 1;
channel = 3;
// Rx free queue base address
rfq_base_addr = 0x10000000;
// Rx free queue end address
// Rx free queue size = 16
rfq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Rx done queue base address
rdq_base_addr = 0x10000100;
// Rx done queue end address
// Rx done queue size = 16
rdq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Rx descriptor base address
// Rx descriptor table size = 256
rdscr_base_addr = 0x10000200;
// Rx data buffer base address
rx_buf_base_addr = 0x10001000;
// Tx pending queue base address
tpq_base_addr = 0x10000300;
// Tx pending queue end address
// Tx pending queue size = 16
tpq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Tx done queue base address
tdq_base_addr = 0x10000400;
// Tx done queue end address
// Tx done queue size = 16
tdq_end_idx = 0x000F;
// Tx descriptor base address
// Tx descriptor table size = 256
tdscr_base_addr = 0x10000500;
// Tx data buffer base address
tx_buf_base_addr = 0x10002000;
配置PCI寄存器
PCI橋接模式支持PCI總線上的主機對本地總線進行訪問。PCI總線用于控制和監視DS31256,傳送分組數據。DS31256將數據從PCI總線映射到本地總線(請參考DS31256數據資料第10節)。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0x004/0A04 | PCMD0 | PCI Command Status 0 | 10.2 |
// Map DS31256 Configuration Registers to a PCI bus base address
write_reg(PDCM, 32'h80000000);
// PCI command/status register 0 - controls DS31256 DMA functionality
// Set Bit 1 = 1 to enable accesses to internal device configuration registers through PCI bus
//(required for Bridge mode)
// Set Bit 2 = 1 to allow the device operation as bus master on PCI bus (required for DMA)
// Set Bit 6 = 1 to act on parity errors
// Set Bit 8 = 1 to enable the PSERR pin
write_reg(PCMD0, 32'h00000146);
配置1層寄存器
DS31256的每一端口都含有1層控制器,完成以下幾項功能,包括:
通過RP[n]CR、TP[n]CR、CP[n]RD和CP[n]RDIS寄存器,在端口上完成1層配置,其中,n是要配置的端口。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 01xx | RP[n]CR | Receive Port n Control Register | 6.2 |
| 02xx | TP[n]CR | Transmit Port n Control Register | 6.2 |
| 03xx | CP[n]RDIS | Channelized Port n Register Data Indirect Select | 6.3 |
| 03xx | CP[n]RD | Channelized Port n Register Data | 6.3 |
// Set RX Port Control Register
// Set bits 2-0 = 000 for clock, data and sync are not inverted
// Set bits 5-4 = 00 for sync pulse 0 clocks early
// Set bits 7-6 = 00 for T1 mode
// Set bit 10 = 0 to disable local loopback
write_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, 0x0000);
// Set Tx Port Control Register
// Set bit 2-0 = 000 for clock, data and sync are not inverted
// Set bit 3 = 0 to force all data at TD to be 1
// Set bits 5-4 = 00 for sync pulse 0 clocks early
// Set bits 7-6 = 0 for T1 mode
write_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, 0x0000);
// RX Port Configuration Registers
// DS0's 0-3 disabled, assigned to HDLC channel
// CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 for Receive Configuration
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000 + channel);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0100 + ds0);
// Tx Port Configuration Registers
// DS0's 0-3 disabled, assigned to HDLC channel
// CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 10 for Transmit Configuration
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, 0x0000 + channel);
for(ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0200 + ds0);
配置HDLC寄存器
DS31256含有一個256通道HDLC控制器,完成2層功能。該控制器完成的功能包括:
- 零填充和去填充
- 標志探測和字節對齊
- CRC產生和校驗
- 數據置反和位反轉
通過RHCD、RHCDIS、THCD和THCDIS寄存器,在通道上配置HDLC控制器。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0400 | RHCDIS | Receive HDLC Channel Definition Indirect Select | 7.2 |
| 0404 | RHCD | Receive HDLC Channel Definition | 7.2 |
| 0480 | THCDIS | Transmit HDLC Channel Definition Indirect Select | 7.2 |
| 0484 | THCD | Transmit HDLC Channel Definition | 7.2 |
// RX HDLC configuration
// Set bits 3-2 = 10 for 32-bit CRC
write_reg(RHCD, 0x0008);
write_reg_IS(RHCDIS, channel);
// Tx HDLC configuration
// Set bit 1= 0 to select an interfill byte of 7E
// Set bits 3-2 = 10 for 32-bit CRC
// Set bits 11-8 = 1000 for closing flag/no interfill bytes/opening flag
write_reg(THCD, 0x0108);
write_reg_IS(THCDIS, channel);
配置FIFO寄存器
DS31256含有一個16kB發送FIFO和一個16kB接收FIFO。每一FIFO按照4 dword或者16字節被分成1024個模塊。在HDLC通道基礎上分配FIFO存儲器。可以設置分配給每一HDLC通道的FIFO存儲器的數量,最少是4個模塊,最多為1024個模塊。建立圓形鏈表,列出一組模塊,每一模塊指向鏈中的下一模塊,最后一個模塊指向第一個,這樣,將FIFO存儲器分配給HDLC通道。鏈表中的一個模塊分配給該通道的FIFO起始模塊指針,將FIFO模塊鏈表分配給指定的HDLC通道。
在這個例子中,4個Tx FIFO模塊和4個Rx FIFO模塊被分配給HDLC通道。這個例子還使用了一個Rx FIFO高水線3,以及Tx FIFO低水線1。Rx FHFO高水線指示HDLC引擎在DMA開始向PCI總線發送數據之前,應該將多少模塊寫入Rx FIFO。高水線設置必須在一個模塊以及相關某一通道鏈表模塊之間。Tx FIFO低水線指示在DMA開始從PCI總線獲取大量數據之前,有多少模塊應留在Tx FIFO中。HDLC通道用于防止出現傳送下溢以及接收上溢所需要的FIFO存儲器、Rx FIFO高水線和Tx FIFO低水線數量取決于應用程序。通過下表列出的寄存器,在HDLC通道基礎上,單獨配置DS31256的Tx FIFO和Rx FIFO。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0910 | RFBPIS | Receive FIFO Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0914 | RFBP | Receive FIFO Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Build the Rx FIFO block linked list
// 0->1->2->3->0
for (block = 0; block < 4; block = block + 1)
{
// Bits 9-0 in RFBP register indicate which block is next in the linked list
write_reg(RFBP, block + 1);
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, block);
}
// The last block points to the first block to create a circular linked list
write_reg(RFBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RFBPIS, 0x0003);
// Assign the circular linked list to a specific channel
write_reg(RFSBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RFSBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0920 | RFHWMIS | Receive FIFO High Watermark Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0924 | RFHWM | Receive FIFO High Watermark | 8.2 |
// Set RX FIFO high watermark for channel to 3
write_reg(RFHWM, 0x0003);
write_reg_IS(RFHWMIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0990 | TFBPIS | Transmit FIFO Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0994 | TFBP | Transmit FIFO Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Tx FIFO block linked list
// 0->1->2->3->0
for (block = 0; block < 4; block = block + 1)
{
// Bits 9-0 in TFBP register indicate which block is next in the linked list
write_reg(TFBP, block + 1);
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, block);
}
// The last block points to the first block to create a circular linked list
write_reg(TFBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TFBPIS, 0x0003);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0980 | TFSBPIS | Transmit FIFO Starting Block Pointer Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 0984 | TFSBP | Transmit FIFO Starting Block Pointer | 8.2 |
// Assign the circular linked list to a specific channel
write_reg(TFSBP, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TFSBPIS, channel);
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 09A0 | TFLWMIS | Transmit FIFO Low Watermark Indirect Select | 8.2 |
| 09A4 | TFLWM | Transmit FIFO Low Watermark | 8.2 |
// Set Tx FIFO low watermark for channel to 1
write_reg(TFLWM, 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(TFLWMIS, channel);
配置DMA寄存器
DMA模塊處理分組數據在FIFO模塊和PCI模塊之間的傳送。PCI模塊控制數據在DS31256和外部PCI總線之間的傳送。主機定義為CPU或者位于PCI總線上的智能控制器,由它指示DS31256怎樣處理輸入輸出數據。
這通過使用描述符來實現,描述符定義為從主機傳送給DMA模塊以及由DMA模塊傳送給主機并經過格式化預處理的消息。通過這些描述符,主機告知DMA要傳送的分組數據的位置和狀態,把接收到的分組數據放到哪里。DMA使用這些描述符告知主機,已經傳送的分組數據的狀態,以及接收到的分組數據的狀態和位置。
在接收側,主機寫入自由隊列描述符,告知DMA在哪里可以放置到達分組數據。與每一自由隊列輸入相關的是接收數據緩沖位置和數據包描述符。DS31256使用接收自由隊列輸入來將接收到的分組數據寫入主機存儲器,它在Rx完成隊列中建立輸入。這些Rx完成隊列輸入告知主機接收到的數據的位置和狀態。請參考DS31256數據資料,了解詳細信息。主機必須通過寫入下表列出的所有寄存器來配置Rx DMA:
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0700 | RFQBA0 | Receive Free Queue Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.2.3 |
| 0704 | RFQBA1 | Receive Free Queue Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.2.3 |
| 0708 | RFQEA | Receive Free Queue end Address | 9.2.3 |
| 070C | RFQSBSA | Receive Free Small Buffer Start Address | 9.2.3 |
| 0710 | RFQLBWP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer Host Write Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 0714 | RFQSBWP | Receive Free Queue Small Buffer Host Write Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 0718 | RFQLBRP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer DMA Read Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 071C | RFQSBRP | Receive Free Queue Small Buffer DMA Read Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 0730 | RDQBA0 | Receive Done Queue Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.2.4 |
| 0734 | RDQBA1 | Receive Done Queue Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.2.4 |
| 0738 | RDQEA | Receive Done Queue end Address | 9.2.4 |
| 073C | RDQRP | Receive Done Queue Host Read Pointer | 9.2.4 |
| 0740 | RDQWP | Receive Done Queue DMA Write Pointer | 9.2.4 |
| 0750 | RDBA0 | Receive Descriptor Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.2.2 |
| 0754 | RDBA1 | Receive Descriptor Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.2.2 |
| 0770 | RDMACIS | Receive DMA Configuration Indirect Select | 9.3.5 |
| 0774 | RDMAC | Receive DMA Configuration | 9.3.5 |
| 0790 | RLBS | Receive Large Buffer Size | 9.2.1 |
// Rx large buffer size = 256 bytes
write_reg(RLBS, 0x0100);
// Rx free queue base address
write_reg(RFQBA0, rfq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RFQBA1, (rfq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx free queue large buffer read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RFQLBRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RFQLBWP, 0x0000);
// Rx free queue small buffer start address = 16
write_reg(RFQSBSA, rfq_end_idx);
// Rx free queue small buffer read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RFQSBRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RFQSBWP, 0x0000);
// Rx free queue end address
write_reg(RFQEA, rfq_end_idx);
// Rx done queue base address
write_reg(RDQBA0, rdq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RDQBA1, (rdq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx done queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(RDQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(RDQWP, 0x0000);
// Rx done queue end address
write_reg(RDQEA, rdq_end_idx);
// Rx descriptor base address
write_reg(RDBA0, rdscr_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(RDBA1, (rdscr_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Rx DMA Channel Configuration
// The data in RDMAC register is written to or read from the Receive Configuration RAM
// Set bit 0 = 0 to disable the HDLC Channel
// Set bit 201 = 00 for large buffers only
// Set bit 6-3 = 0000 for 0 byte offset from the data buffer address of the first data buffer
// Set Bit 9-7 = 000 for DMA write to the Done Queue only after packet reception is complete
// Set the HDLC Channel Number by RDMACIS register
write_reg(RDMAC, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
在發送側,主機將寫入未決隊列,告知DMA哪一通道有準備要發送的分組數據。與每一未決隊列描述符相關的是一個或者多個發送數據包描述符鏈表,由它描述了分組數據。每一發送數據包描述符還有一個發送數據緩沖指針,含有HDLC數據包的實際數據負載。
DS31256處理發送未決隊列描述符輸入時,它建立發送完成隊列描述符隊列輸入。完成發送一個完整的數據包或者DS31256所配置的數據緩沖后,DMA將寫入完成隊列。通過這些完成隊列描述符,DMA告知主機關于輸出分組數據的狀態。請參考DS31256數據資料,了解詳細信息。主機必須通過寫入下表列出的所有寄存器來配置Tx DMA:
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0800 | TPQBA0 | Transmit Pending Queue Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.3.3 |
| 0804 | TPQBA1 | Transmit Pending Queue Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.3.3 |
| 0808 | TPQEA | Transmit Pending Queue end Address | 9.3.3 |
| 080C | TPQWP | Transmit Pending Queue Host Write Pointer | 9.3.3 |
| 0810 | TPQRP | Transmit Pending Queue DMA Read Pointer | 9.3.3 |
| 0830 | TDQBA0 | Transmit Done Queue Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.3.4 |
| 0834 | TDQBA1 | Transmit Done Queue Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.3.4 |
| 0838 | TDQEA | Transmit Done Queue end Address | 9.3.4 |
| 083C | TDQRP | Transmit Done Queue Host Read Pointer | 9.3.4 |
| 0840 | TDQWP | Transmit Done Queue DMA Write Pointer | 9.3.4 |
| 0850 | TDBA0 | Transmit Descriptor Base Address 0 (lower word) | 9.3.2 |
| 0854 | TDBA1 | Transmit Descriptor Base Address 1 (upper word) | 9.3.2 |
| 0870 | TDMACIS | Transmit DMA Configuration Indirect Select | 9.3.5 |
| 0874 | TDMAC | Transmit DMA Configuration | 9.3.5 |
// Tx pending queue base address
write_reg(TPQBA0, tpq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TPQBA1, (tpq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx pending queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(TPQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(TPQWP, 0x0000);
// Tx pending queue end address
write_reg(TPQEA, tpq_end_idx);
// Tx done queue base address
write_reg(TDQBA0, tdq_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TDQBA1, (tdq_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx done queue read and write pointers = 0
write_reg(TDQRP, 0x0000);
write_reg(TDQWP, 0x0000);
// Tx done queue end address
write_reg(TDQEA, tdq_end_idx);
// Tx descriptor base address
write_reg(TDBA0, tdscr_base_addr & 0x0000FFFF);
write_reg(TDBA1, (tdscr_base_addr >> 16) & 0x0000FFFF);
// Tx DMA Channel Configuration
// The data in TDMAC register is written to or read from the Transmit Configuration RAM
// Set bit 0 = 0 to disable HDLC Channel
// Set bit 1 = 0 for write done queue after packet transmitted
// Set the HDLC Channel Number by TDMACIS register
write_reg(TDMAC, 0x0000);
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200 + channel);
使能HDLC通道
DS31256初始化后,下一步是使能HDLC通道。除了已經闡述的配置步驟之外,必須完成以下步驟來使能DS31256數據包傳送和接收:
- 使能端口Tx和Rx配置RAM中的HDLC通道(使能HDLC通道)
- 初始化Rx自由隊列(裝入DMA描述符)
- 針對DS31256使能Tx DMA和Rx DMA (使能DMA)
- 使能HDLC通道Tx和Rx DMA
- 使能1層的端口數據傳送(打開HDLC通道)
使能端口Tx和Rx配置RAM中的HDLC通道
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 03xx | CP[n]RDIS | Channelized Port n Register Data Indirect Select | 6.3 |
| 03xx | TPQBA1 | Channelized Port n Register Data | 6.3 |
// Enable packet reception in port layer 1 Rx configuration RAM
for (ds0 = 0; ds0 < 4; ds0 = ds0 + 1)
{
// Read the current data value from the Rx Configuration RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 6-0 = DS0
// Set CP[n]RDIS bit 14 = 1 to read data from the RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx configuration RAM
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x4100 + ds0);
read_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, data);
// Update memory with new value
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 6-0 = DS0
// Set CP[n]RDIS bit 14 = 0 to write data to the RAM
// Set CP[n]RDIS bits 9-8 = 01 to select Rx configuration RAM
// Enable DS0 by setting bit 15 = 1 in CP[0]RD register
write_reg(CP[0]RD + 8 * port, data | 0x8000);
write_reg_IS(CP[0]RDIS + 8 * port, 0x0100 + ds0);
}
初始化Rx自由隊列
在DS31256將DMA接收到的數據包從其內部FIFO發送到主機存儲器之前,主機必須告知DS31256把數據放到哪里。這通過Rx自由隊列完成。Rx自由隊列中的每一輸入都含有指向Rx數據緩沖和Rx數據包描述符索引的指針。這一例子使用了一個Rx自由隊列輸入。該輸入含有一個Rx自由隊列大緩沖和一個Rx數據包描述符。DS31256 Rx大數據緩沖容量被設置為256字節(RLBS = 256)。此外,DS31256被配置為使用4字節CRC,將Rx CRC寫入Rx數據緩沖。因此,一個Rx大數據緩沖可以支持252字節的分組數據。
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0710 | RFQLBWP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer Host Write Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 0718 | RFQLBRP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer DMA Read Pointer | 9.2.3 |
// check for space in Rx large free queue
read_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
read_reg(RFQLBRP, rd_ptr);
if (rd_ptr < wr_ptr)
else
// If room in Rx free queue then put 1 entry in the queue
// dword 0 = Rx data buffer address (use Rx data buffer starting at Rx buffer area base address)
// dword 1 = corresponding Rx descriptor index (use Rx descriptor table index 0)
if (cnt < 0)
rx_dscr_idx = 0;
wr_dword(rfq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 8, rx_buf_base_addr);
wr_dword(rfq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 8 + 4, rx_dscr_idx);
// Advance the Rx free queue large buffer write pointer by 1
if (wr_ptr = rfq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
}
使能DS31256 Tx和Rx DMA
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0010 | MC | Master Configuration | 5.2 |
// Enable Tx and Rx DMA in the DS31256 master configuration register
// Set bit 0 = 1 to enable Receive DMA
// Set bits 2-1 = 00 to burst length maximum is 32 dwords
// Set bit 3 = 1 to enable Transmit DMA
// Set bits 6 = 1 for HDLC packet data on PCI bus is big endian
// Set bits 11-7 = 00000 to select Port 0 has the dedicated resources of the BERT
write_reg(MC, 0x0049);
使能HDLC通道Tx和Rx
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0770 | RDMACIS | Receive DMA Configuration Indirect Select Register | 9.3.5 |
| 0774 | RDMAC | Receive DMA Configuration Register | 9.3.5 |
| 0870 | TDMACIS | Transmit DMA Configuration Indirect Select Register | 9.3.5 |
| 0874 | TDMAC | Transmit DMA Configuration Register | 9.3.5 |
// Read the current channel value from the Rx DMA Configuration RAM
// Set RDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 10-8 = 100 to read lower word of dword 2
// Set RDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x4400 + channel);
read_reg(RDMAC, data);
// Enable channel Rx DMA
// Update RAM with new value
// Set RDMAC bit 0 = 1 to enable the HDLC channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set RDMACIS bits 10-8 = 100 to read lower word of dword 2
// Set RDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg(RDMAC, data | 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(RDMACIS, 0x0400 + channel);
// Read the current channel value from the Tx DMA Configuration RAM
// Set TDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 11-8 = 0010 to read lower word of dword 1
// Set TDMACIS bit 14 = 1 to read from RAM
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x4200 + channel);
read_reg(TDMAC, data);
// Enable channel Tx DMA
// Update RAM with new value
// Set TDMAC bit 0 = 1 to enable the HDLC channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 7-0 = channel
// Set TDMACIS bits 11-8 = 0010 to read lower word of dword 1
// Set TDMACIS bit 14 = 0 to write to RAM
write_reg((TDMAC, data | 0x0001);
write_reg_IS(TDMACIS, 0x0200, + channel);
使能1層的端口數據傳輸
| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 02xx | TP[n]CR | Transmit Port n Control Register | 6.2 |
// Tx port control register
// Set Bit 3 TFDA1 = 1 to allow data to be transmitted normally
read_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, data);
write_reg(TP[0]CR + 4 * port, data | 0x0008);
使HDLC通道進入環回模式
完成通道配置后,使能它需要大約5個幀周期,即625μs,使DS31256內部邏輯完成向新配置的轉換。轉換完成后,HDLC通道可以進入環回模式,這樣,通道上傳送的所有數據也會在該通道上接收到。在5個幀等待周期之前使HDLC通道進入環回模式會導致無用數據寫入通道的Rx FIFO。| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 01xx | RP[n]CR | Receive Port n Control Register | 6.2 |
// Wait for at least 5 frame periods for the internal DS31256 initialization to complete
frame_wait(5);
// Set Bit 10 = 1 to enable loopback - routes transmit data back to the receive port
read_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, data);
write_reg(RP[0]CR + 4 * port, data | 0x0400);
排列、發送、接收、檢查數據包
完成DS31256初始化之后,可以開始發送和接收數據。由于DS31256處于環回模式,HDLC通道傳送的所有數據也會在該通道上接收到。本節將討論構建主機存儲器中數據包的過程,以及數據的發送、接收和結果檢查。下面幾節詳細介紹這一過程。構建主機存儲器中的數據包
這一個例子將發送一個16字節數據包。在數據包發送之前,必須在主機存儲器中構建它。此外,也必須在主機存儲器中構建對應的Tx數據包描述符。下面的代碼詳細介紹了這些任務。// Create a 16-byte data packet in memory in a Tx buffer whose start address is the Tx buffer area base
// address
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr, 0x01234567);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 4, 0x89ABCDEF);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 8, 0x02468ACE);
wr_dword(tx_buf_base_addr + 12, 0x13579BDF);
// Create a Tx descriptor (4 dwords) for the packet at Tx descriptor
// Tx descriptor table index 0
// dword0 = Tx buffer address
// dword1 = EOF, CV, byte count, next descriptor pointer
// dowrd2 = HDLC channel
// dword3 = PV, next pending descriptor pointer (set to 0)
tx_dscr_idx = 0;
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16, tx_buf_base_addr);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 4, 0x80100000);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 8, 0x00000000 + channel);
wr_dword(tdscr_base_addr + tx_dscr_idx * 16 + 12, 0x00000000);
數據包發送和接收
為完成數據包發送,Tx描述符必須放在發送未決隊列中,然后,必須遞增發送未決隊列寫指針(TPQWP)。當DS31256探測到未決隊列不空(TPQWP不等于TPQRP)時,它將開始處理隊列輸入,并發送數據包。| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0028 | SDMA | Status Register for DMA | 5.3.2 |
| 080C | TPQWP | Transmit Pending Queue Host Write Pointer | 9.3.3 |
| 0810 | TPQRP | Transmit Pending Queue DMA Read Pointer | 9.3.3 |
// Read SDMA register to clear any previously set status bits
read_reg(SDMA, data);
// check free space in Tx pending queue
read_reg(TPQWP, wr_ptr);
read_reg(TPQRP, rd_ptr)
if (rd_ptr < wr_ptr)
else
// If room in the Tx pending queue create an entry for the packet
if (cnt < 0)
{
wr_dword(tpq_base_addr + wr_ptr * 4, 0x0000000 + (channel << 16));
// Advance the Tx pending queue write pointer
if (wr_ptr = tpq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(TPQWP, wr_ptr);
}
檢查結果
等待足夠的時間周期以完成數據包發送和接收后,可以進行幾項檢查,確定數據包發送和接收是否成功。以下代碼詳細說明了這幾項檢查。| Offset/Address | Acronym | Register Name | Data Sheet Section |
| 0028 | SDMA | Status Register for DMA | 5.3.2 |
| 0710 | RFQLBWP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer Host Write Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 0718 | RFQLBRP | Receive Free Queue Large Buffer DMA Read Pointer | 9.2.3 |
| 073C | RDQRP | Receive Done Queue Host Read Pointer | 9.2.4 |
| 0740 | RFQLBRP | Receive Done Queue DMA Write Pointer | 9.2.4 |
| 083C | TDQRP | Transmit Done Queue Host Read Pointer | 9.3.4 |
| 0840 | TDQWP | Transmit Done Queue DMA Write Pointer | 9.3.4 |
// wait 2 frame periods for packet to be transmitted/received
frame_wait(2);
// Check SDMA register
// Expected value = 0x6440, if not, it means there was error
read_reg(SDMA, data);
// Check to see how many entries are in the Tx done queue (distance from TDQRP to TDQWP)
// Expected value is 1 - one entry in the Tx done queue corresponding to the packet that was sent
read_reg(TDQRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(TDQWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check Tx done queue descriptor
// Expected value = 0x0003000
// Bits 15-0 indicates the descriptor pointer
// Bits 23-16 indicate the channel number, it should be 3 in this example
// Bits 28-26 indicate the packet status, all 0 means the packet transmission is complete and the
// descriptor pointer field corresponds to the first descriptor in the HDLC packet that has been
// transmitted
rd_dword(tdq_base_addr + rd_ptr*4, tdq_entry);
// Advance the Tx done queue read pointer
if (wr_ptr = tdq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(TDQRP, wr_ptr);
// Check the Rx large free queue to see how many Rx buffers are in the queue (distance from
// RFQLBRP to RFQLBWP)
// Expected number is 0 since the queue had 1 buffer before the packet was received and packet
// reception required 1 buffer
read_reg(RFQLBRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(RFQLBWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check Rx done queue to see if any packets were received (distance from RDQRP to RDQWP)
// Expected value is 1 - one entry in the Rx done queue entry corresponding to the one packet that
// should have been received
read_reg(RDQRP, rd_ptr);
read_reg(RDQWP, wr_ptr);
if (wr_ptr >= rd_ptr)
else
// Check the Rx done queue descriptor
// Expected value = 0x40030000,
// Bits 15-0 indicates the descriptor pointer
// Bits 23-16 indicate the channel number, it should be 3 in this example
// Bits 26-24 indicate the buffer count, all 0 means that a complete packet has been received
rd_dword(rdq_base_addr + 8 * rd_ptr, rdq_entry);
// Check the corresponding Rx descriptor (4 dwords)
// dword 0 expected value = 0x10001000 the Rx buffer address
// dword 1 expected value = 0x80140000
// Bits 15-0 is the next descriptor pointer
// Bits 28-16 is the number of bytes stored in the data buffer
// Bits 31-29 indicates buffer status
// dword 2 excepted value = 0x000B7503
// Bits 7-0 indicates HDLC channel number (should match TDQ entry channel)
// Bits 31-8 indicates the timestamp (can vary)
rdscr_idx = rdq_entry & 0x0000FFFF;
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx, rdscr_dword0);
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx + 4, rdscr_dword1);
rd_dword(rdscr_base_addr + 16 * rdscr_idx + 8, rdscr_dword2);
// Check the data in the Rx buffer
// 16 bytes of data + 4-byte CRC
// Expected values = 0x01234567
// 0x02468ACE
// 0x13579BDF
// 0x05127B09 (4-byte CRC)
byte_count = (rdscr_dword1 >> 16) & 0x00001FFF;
for (addr = rdscr_dword0, addr < rdscr_dword0 + byte_count; addr = addr + 4)
// Advance the Rx done queue read pointer
if (rd_ptr = rdq_end_idx)
else
write_reg(RDQRP, rd_ptr);
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App
























評論