HBase簡介
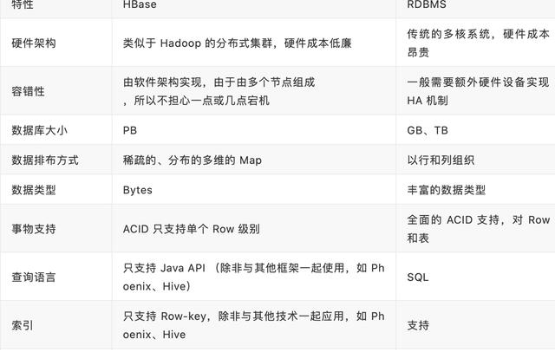
HBase是一個分布式的、面向列的開源數據庫,該技術來源于 Fay Chang 所撰寫的Google論文“Bigtable:一個結構化數據的分布式存儲系統”。就像Bigtable利用了Google文件系統(File System)所提供的分布式數據存儲一樣,HBase在Hadoop之上提供了類似于Bigtable的能力。HBase是Apache的Hadoop項目的子項目。HBase不同于一般的關系數據庫,它是一個適合于非結構化數據存儲的數據庫。另一個不同的是HBase基于列的而不是基于行的模式。
什么時候需要HBase呢?
半結構化或非結構化數據,對于數據結構字段不夠確定或雜亂無章很難按一個概念去進行抽取的數據適合用HBase。當業務發展需要存儲author的email,phone,address信息時RDBMS需要停機維護,而HBase支持動態增加。
記錄非常稀疏
RDBMS的行有多少列是固定的,為null的列浪費了存儲空間。而如上文提到的,HBase為null的Column不會被存儲,這樣既節省了空間又提高了讀性能。
多版本數據
如上文提到的根據Row key和Column key定位到的Value可以有任意數量的版本值,因此對于需要存儲變動歷史記錄的數據,用HBase就非常方便了。比如上例中的author的Address是會變動的,業務上一般只需要最新的值,但有時可能需要查詢到歷史值。
超大數據量
當數據量越來越大,RDBMS數據庫撐不住了,就出現了讀寫分離策略,通過一個Master專門負責寫操作,多個Slave負責讀操作,服務器成本倍增。隨著壓力增加,Master撐不住了,這時就要分庫了,把關聯不大的數據分開部署,一些join查詢不能用了,需要借助中間層。隨著數據量的進一步增加,一個表的記錄越來越大,查詢就變得很慢,于是又得搞分表,比如按ID取模分成多個表以減少單個表的記錄數。經歷過這些事的人都知道過程是多么的折騰。采用HBase就簡單了,只需要加機器即可,HBase會自動水平切分擴展,跟Hadoop的無縫集成保障了其數據可靠性(HDFS)和海量數據分析的高性能(MapReduce)。
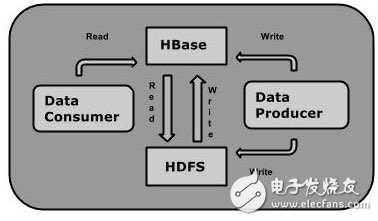
HTable一些基本概念
Row key
行主鍵, HBase不支持條件查詢和Order by等查詢,讀取記錄只能按Row key(及其range)或全表掃描,因此Row key需要根據業務來設計以利用其存儲排序特性(Table按Row key字典序排序如1,10,100,11,2)提高性能。
Column Family(列族)
在表創建時聲明,每個Column Family為一個存儲單元。在上例中設計了一個HBase表blog,該表有兩個列族:article和author。
Column(列)
HBase的每個列都屬于一個列族,以列族名為前綴,如列article:title和article:content屬于article列族,author:name和author:nickname屬于author列族。
Column不用創建表時定義即可以動態新增,同一Column Family的Columns會群聚在一個存儲單元上,并依Column key排序,因此設計時應將具有相同I/O特性的Column設計在一個Column Family上以提高性能。
Timestamp
HBase通過row和column確定一份數據,這份數據的值可能有多個版本,不同版本的值按照時間倒序排序,即最新的數據排在最前面,查詢時默認返回最新版本。如上例中row key=1的author:nickname值有兩個版本,分別為1317180070811對應的“一葉渡江”和1317180718830對應的“yedu”(對應到實際業務可以理解為在某時刻修改了nickname為yedu,但舊值仍然存在)。Timestamp默認為系統當前時間(精確到毫秒),也可以在寫入數據時指定該值。
Value
每個值通過4個鍵唯一索引,tableName+RowKey+ColumnKey+Timestamp=》value,例如上例中{tableName=’blog’,RowKey=’1’,ColumnName=’author:nickname’,Timestamp=’ 1317180718830’}索引到的唯一值是“yedu”。
存儲類型
TableName 是字符串
RowKey 和 ColumnName 是二進制值(Java 類型 byte[])
Timestamp 是一個 64 位整數(Java 類型 long)
value 是一個字節數組(Java類型 byte[])。
將HTable的存儲結構理解為
即HTable按Row key自動排序,每個Row包含任意數量個Columns,Columns之間按Column key自動排序,每個Column包含任意數量個Values。理解該存儲結構將有助于查詢結果的迭代。
HTable使用教程
對于建表,和RDBMS類似,HBase也有namespace的概念,可以指定表空間創建表,也可以直接創建表,進入default表空間。
對于數據操作,HBase支持四類主要的數據操作,分別是:
· Put:增加一行,修改一行;
· Delete:刪除一行,刪除指定列族,刪除指定column的多個版本,刪除指定column的制定版本等;
· Get:獲取指定行的所有信息,獲取指定行和指定列族的所有colunm,獲取指定column,獲取指定column的幾個版本,獲取指定column的指定版本等;
· Scan:獲取所有行,獲取指定行鍵范圍的行,獲取從某行開始的幾行,獲取滿足過濾條件的行等。
這四個類都是org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client的子類,可以到官網API去查看詳細信息,本文僅總結常用方法,力爭讓讀者用20%的時間掌握80%的常用功能。
1. 命名空間Namespace
在關系數據庫系統中,命名空間namespace指的是一個表的邏輯分組,同一組中的表有類似的用途。命名空間的概念為即將到來的多租戶特性打下基礎:
· 配額管理(Quota Management (HBASE-8410)):限制一個namespace可以使用的資源,資源包括region和table等;
· 命名空間安全管理(Namespace Security Administration (HBASE-9206)):提供了另一個層面的多租戶安全管理;
· Region服務器組(Region server groups (HBASE-6721)):一個命名空間或一張表,可以被固定到一組regionservers上,從而保證了數據隔離性。
1.1.命名空間管理
命名空間可以被創建、移除、修改。
表和命名空間的隸屬關系在在創建表時決定,通過以下格式指定:
《namespace》:《table》
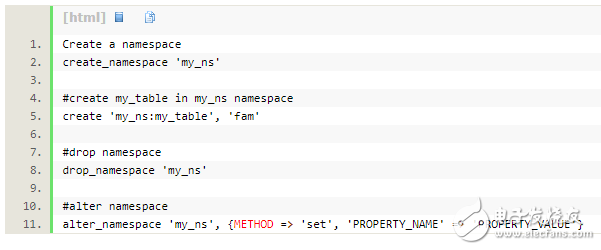
Example:hbase shell中創建命名空間、創建命名空間中的表、移除命名空間、修改命名空間
?
1.2. 預定義的命名空間
有兩個系統內置的預定義命名空間:
· hbase:系統命名空間,用于包含hbase的內部表
· default:所有未指定命名空間的表都自動進入該命名空間
Example:指定命名空間和默認命名空間
#namespace=foo and table qualifier=bar
create ‘foo:bar’, ‘fam’
#namespace=default and table qualifier=bar
create ‘bar’, ‘fam’
2. 創建表
廢話不多說,直接上樣板代碼,代碼后再說明注意事項和知識點:
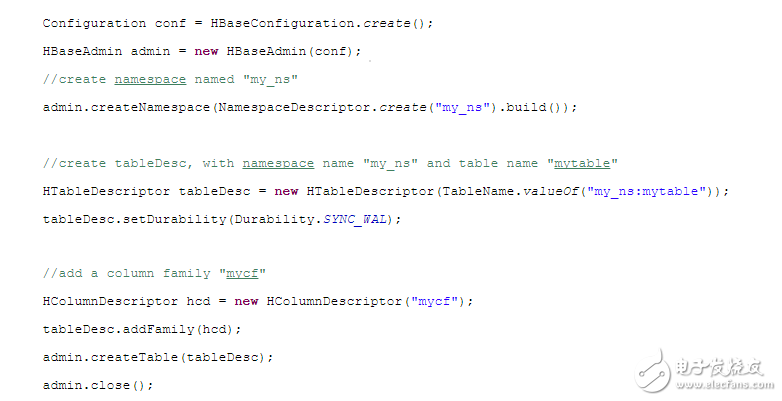
關鍵知識點:
必須將HBase集群的hbase-site.xml文件添加進工程的classpath中,或者通過Configuration對象設置相關屬性,否則程序獲取不到集群相關信息,也就無法找到集群,運行程序時會報錯;
HTableDescriptor tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(“my_ns:mytable”))代碼是描述表mytable,并將mytable放到了my_ns命名空間中,前提是該命名空間已存在,如果指定的是不存在命名空間,則會報錯org.apache.hadoop.hbase.NamespaceNotFoundException;
命名空間一般在建模階段通過命令行創建,在java代碼中通過admin.createNamespace(NamespaceDescriptor.create(“my_ns”).build())創建的機會不多;
創建HBaseAdmin對象時就已經建立了客戶端程序與HBase集群的connection,所以在程序執行完成后,務必通過admin.close()關閉connection;
可以通過HTableDescriptor對象設置表的特性,比如:通過tableDesc.setMaxFileSize(512)設置一個region中的store文件的最大size,當一個region中的最大store文件達到這個size時,region就開始分裂;通過tableDesc.setMemStoreFlushSize(512)設置region內存中的memstore的最大值,當memstore達到這個值時,開始往磁盤中刷數據。更多特性請自行查閱官網API;
可以通過HColumnDescriptor對象設置列族的特性,比如:通過hcd.setTimeToLive(5184000)設置數據保存的最長時間;通過hcd.setInMemory(true)設置數據保存在內存中以提高響應速度;通過 hcd.setMaxVersions(10)設置數據保存的最大版本數;通過hcd.setMinVersions(5)設置數據保存的最小版本數(配合TimeToLive使用)。更多特性請自行查閱官網API;
數據的版本數只能通過HColumnDescriptor對象設置,不能通過HTableDescriptor對象設置;
由于HBase的數據是先寫入內存,數據累計達到內存閥值時才往磁盤中flush數據,所以,如果在數據還沒有flush進硬盤時,regionserver down掉了,內存中的數據將丟失。要想解決這個場景的問題就需要用到WAL(Write-Ahead-Log),tableDesc.setDurability(Durability.SYNC_WAL)就是設置寫WAL日志的級別,示例中設置的是同步寫WAL,該方式安全性較高,但無疑會一定程度影響性能,請根據具體場景選擇使用;
setDurability(Durability d)方法可以在相關的三個對象中使用,分別是:HTableDescriptor,Delete,Put(其中Delete和Put的該方法都是繼承自父類org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Mutation)。分別針對表、插入操作、刪除操作設定WAL日志寫入級別。需要注意的是,Delete和Put并不會繼承Table的Durability級別(已實測驗證)。Durability是一個枚舉變量,可選值參見4.2節。如果不通過該方法指定WAL日志級別,則為默認USE_DEFAULT級別。
3.刪除表
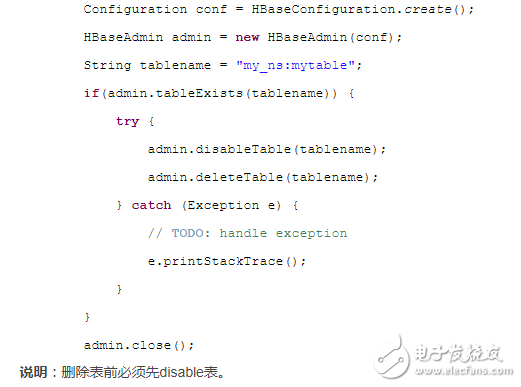
刪除表沒創建表那么多學問,直接上代碼:
?
4、修改表
4.1.實例代碼
(1)刪除列族、新增列族
修改之前,四個列族:
hbase(main):014:0》 describe ‘rd_ns:itable’
DESCRIPTION ENABLED
‘rd_ns:itable’, {NAME =》 ‘info’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘NONE’, BLOOMFILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 ‘0’, V true
ERSIONS =》 ‘10’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, MIN_VERSIONS =》 ‘0’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘false’,
BLOCKSIZE =》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》 ‘true’}, {NAME =》 ‘newcf’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘NONE
’, BLOOMFILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 ‘0’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, VERSIONS =》 ‘10’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’,
MIN_VERSIONS =》 ‘0’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘false’, BLOCKSIZE =》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》 ‘tr
ue’}, {NAME =》 ‘note’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘NONE’, BLOOMFILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 ‘0’, VERSIONS =》
‘10’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, MIN_VERSIONS =》 ‘0’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘false’, BLOCKSIZE
=》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》 ‘true’}, {NAME =》 ‘sysinfo’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘NONE’, BLOOM
FILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 ‘0’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, VERSIONS =》 ‘10’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’, MIN_VERS
IONS =》 ‘0’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘true’, BLOCKSIZE =》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》 ‘true’}
1 row(s) in 0.0450 seconds
修改表,刪除三個列族,新增一個列族,代碼如下:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
String tablename = “rd_ns:itable”;
if(admin.tableExists(tablename)) {
try {
admin.disableTable(tablename);
//get the TableDescriptor of target table
HTableDescriptor newtd = admin.getTableDescriptor(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”));
//remove 3 useless column families
newtd.removeFamily(Bytes.toBytes(“note”));
newtd.removeFamily(Bytes.toBytes(“newcf”));
newtd.removeFamily(Bytes.toBytes(“sysinfo”));
//create HColumnDescriptor for new column family
HColumnDescriptor newhcd = new HColumnDescriptor(“action_log”);
newhcd.setMaxVersions(10);
newhcd.setKeepDeletedCells(true);
//add the new column family(HColumnDescriptor) to HTableDescriptor
newtd.addFamily(newhcd);
//modify target table struture
admin.modifyTable(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”),newtd);
admin.enableTable(tablename);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
admin.close();
修改之后:
hbase(main):015:0》 describe ‘rd_ns:itable’
DESCRIPTION ENABLED
‘rd_ns:itable’, {NAME =》 ‘action_log’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘NONE’, BLOOMFILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 true
‘0’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, VERSIONS =》 ‘10’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’, MIN_VERSIONS =》 ‘0’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘tr
ue’, BLOCKSIZE =》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》 ‘true’}, {NAME =》 ‘info’, DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING =》 ‘
NONE’, BLOOMFILTER =》 ‘ROW’, REPLICATION_SCOPE =》 ‘0’, VERSIONS =》 ‘10’, COMPRESSION =》 ‘NONE’, MIN_VERSIONS =》 ‘
0’, TTL =》 ‘2147483647’, KEEP_DELETED_CELLS =》 ‘false’, BLOCKSIZE =》 ‘65536’, IN_MEMORY =》 ‘false’, BLOCKCACHE =》
‘true’}
1 row(s) in 0.0400 seconds
邏輯很簡單:
通過admin.getTableDescriptor(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”))取得目標表的描述對象,應該就是取得指向該對象的指針了;
修改目標表描述對象;
通過admin.modifyTable(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”),newtd)將修改后的描述對象應用到目標表。
(2)修改現有列族的屬性(setMaxVersions)
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
String tablename = “rd_ns:itable”;
if(admin.tableExists(tablename)) {
try {
admin.disableTable(tablename);
//get the TableDescriptor of target table
HTableDescriptor htd = admin.getTableDescriptor(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”));
HColumnDescriptor infocf = htd.getFamily(Bytes.toBytes(“info”));
infocf.setMaxVersions(100);
//modify target table struture
admin.modifyTable(Bytes.toBytes(“rd_ns:itable”),htd);
admin.enableTable(tablename);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
admin.close();
5. 新增、更新數據Put
5.1.常用構造函數:
(1)指定行鍵
public Put(byte[] row)
參數:row 行鍵
(2)指定行鍵和時間戳
public Put(byte[] row, long ts)
參數:row 行鍵,ts 時間戳
(3)從目標字符串中提取子串,作為行鍵
Put(byte[] rowArray, int rowOffset, int rowLength)
(4)從目標字符串中提取子串,作為行鍵,并加上時間戳
Put(byte[] rowArray, int rowOffset, int rowLength, long ts)
5.2.常用方法:
(1)指定列族、限定符,添加值
add(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier, byte[] value)
(2)指定列族、限定符、時間戳,添加值
add(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier, long ts, byte[] value)
(3)設置寫WAL(Write-Ahead-Log)的級別
public void setDurability(Durability d)
參數是一個枚舉值,可以有以下幾種選擇:
ASYNC_WAL : 當數據變動時,異步寫WAL日志
SYNC_WAL : 當數據變動時,同步寫WAL日志
FSYNC_WAL : 當數據變動時,同步寫WAL日志,并且,強制將數據寫入磁盤
SKIP_WAL : 不寫WAL日志
USE_DEFAULT : 使用HBase全局默認的WAL寫入級別,即SYNC_WAL
5.3.實例代碼
(1)插入行
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(“100001”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“name”), Bytes.toBytes(“lion”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“address”), Bytes.toBytes(“shangdi”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“age”), Bytes.toBytes(“30”));
put.setDurability(Durability.SYNC_WAL);
table.put(put);
table.close();
(2)更新行
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(“100001”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“name”), Bytes.toBytes(“lee”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“address”), Bytes.toBytes(“longze”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“age”), Bytes.toBytes(“31”));
put.setDurability(Durability.SYNC_WAL);
table.put(put);
table.close();
注意:
Put的構造函數都需要指定行鍵,如果是全新的行鍵,則新增一行;如果是已有的行鍵,則更新現有行。
創建Put對象及put.add過程都是在構建一行的數據,創建Put對象時相當于創建了行對象,add的過程就是往目標行里添加cell,直到table.put才將數據插入表格;
以上代碼創建Put對象用的是構造函數1,也可用構造函數2,第二個參數是時間戳;
Put還有別的構造函數,請查閱官網API。
(3)從目標字符串中提取子串,作為行鍵,構建Put
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(“100001_100002”),7,6);
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“name”), Bytes.toBytes(“show”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“address”), Bytes.toBytes(“caofang”));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“age”), Bytes.toBytes(“30”));
table.put(put);
table.close();
注意,關于:Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(“100001_100002”),7,6)
第二個參數是偏移量,也就是行鍵從第一個參數的第幾個字符開始截取;
第三個參數是截取長度;
這個代碼實際是從 100001_100002 中截取了100002子串作為目標行的行鍵。
6.刪除數據Delete
Delete類用于刪除表中的一行數據,通過HTable.delete來執行該動作。
在執行Delete操作時,HBase并不會立即刪除數據,而是對需要刪除的數據打上一個“墓碑”標記,直到當Storefile合并時,再清除這些被標記上“墓碑”的數據。
如果希望刪除整行,用行鍵來初始化一個Delete對象即可。如果希望進一步定義刪除的具體內容,可以使用以下這些Delete對象的方法:
為了刪除指定的列族,可以使用deleteFamily
為了刪除指定列的多個版本,可以使用deleteColumns
為了刪除指定列的指定版本,可以使用deleteColumn,這樣的話就只會刪除版本號(時間戳)與指定版本相同的列。如果不指定時間戳,默認只刪除最新的版本
下面詳細說明構造函數和常用方法:
6.1.構造函數
(1)指定要刪除的行鍵
Delete(byte[] row)
刪除行鍵指定行的數據。
如果沒有進一步的操作,使用該構造函數將刪除行鍵指定的行中所有列族中所有列的所有版本!
(2)指定要刪除的行鍵和時間戳
Delete(byte[] row, long timestamp)
刪除行鍵和時間戳共同確定行的數據。
如果沒有進一步的操作,使用該構造函數將刪除行鍵指定的行中,所有列族中所有列的時間戳小于等于指定時間戳的數據版本。
注意:該時間戳僅僅和刪除行有關,如果需要進一步指定列族或者列,你必須分別為它們指定時間戳。
(3)給定一個字符串,目標行鍵的偏移,截取的長度
Delete(byte[] rowArray, int rowOffset, int rowLength)
(4)給定一個字符串,目標行鍵的偏移,截取的長度,時間戳
Delete(byte[] rowArray, int rowOffset, int rowLength, long ts)
6.2.常用方法
Delete deleteColumn(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier) 刪除指定列的最新版本的數據。
Delete deleteColumns(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier) 刪除指定列的所有版本的數據。
Delete deleteColumn(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier, long timestamp) 刪除指定列的指定版本的數據。
Delete deleteColumns(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier, long timestamp) 刪除指定列的,時間戳小于等于給定時間戳的所有版本的數據。
Delete deleteFamily(byte[] family) 刪除指定列族的所有列的所有版本數據。
Delete deleteFamily(byte[] family, long timestamp) 刪除指定列族的所有列中時間戳小于等于指定時間戳的所有數據。
Delete deleteFamilyVersion(byte[] family, long timestamp) 刪除指定列族中所有列的時間戳等于指定時間戳的版本數據。
voidsetTimestamp(long timestamp) 為Delete對象設置時間戳。
6.3.實例代碼
(1)刪除整行的所有列族、所有行、所有版本
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(“000”));
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
(2)刪除指定列的最新版本
以下是刪除之前的數據,注意看100003行的info:address,這是該列最新版本的數據,值是caofang1,在這之前的版本值是caofang:
hbase(main):007:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405390959464, value=caofang1
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405390959464, value=301
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405390959464, value=show1
3 row(s) in 0.0270 seconds
執行以下代碼:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
delete.deleteColumn(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“address”));
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
然后查看數據,發現100003列的info:address列的值顯示為前一個版本的caofang了!其余值均不變:
hbase(main):008:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405390728175, value=caofang
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405390959464, value=301
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405390959464, value=show1
3 row(s) in 0.0560 seconds
(3)刪除指定列的所有版本
接以上場景,執行以下代碼:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
delete.deleteColumns(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“address”));
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
然后我們會發現,100003行的整個info:address列都沒了:
hbase(main):009:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405390959464, value=301
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405390959464, value=show1
3 row(s) in 0.0240 seconds
(4)刪除指定列族中所有列的時間戳等于指定時間戳的版本數據
為了演示效果,我已經向100003行的info:address列新插入一條數據
hbase(main):010:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405391883886, value=shangdi
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405390959464, value=301
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405390959464, value=show1
3 row(s) in 0.0250 seconds
現在,我們的目的是刪除info列族中,時間戳為1405390959464的所有列數據:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
delete.deleteFamilyVersion(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), 1405390959464L);
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
hbase(main):011:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405391883886, value=shangdi
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405390728175, value=30
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405390728175, value=show
3 row(s) in 0.0250 seconds
可以看到,100003行的info列族,已經不存在時間戳為1405390959464的數據,比它更早版本的數據被查詢出來,而info列族中時間戳不等于1405390959464的address列,不受該delete的影響。
7.獲取單行Get
如果希望獲取整行數據,用行鍵初始化一個Get對象就可以,如果希望進一步縮小獲取的數據范圍,可以使用Get對象的以下方法:
如果希望取得指定列族的所有列數據,使用addFamily添加所有的目標列族即可;
如果希望取得指定列的數據,使用addColumn添加所有的目標列即可;
如果希望取得目標列的指定時間戳范圍的數據版本,使用setTimeRange;
如果僅希望獲取目標列的指定時間戳版本,則使用setTimestamp;
如果希望限制每個列返回的版本數,使用setMaxVersions;
如果希望添加過濾器,使用setFilter
下面詳細描述構造函數及常用方法:
7.1.構造函數
Get的構造函數很簡單,只有一個構造函數:Get(byte[] row) 參數是行鍵。
7.2.常用方法
Get addFamily (byte[] family) 指定希望獲取的列族
Get addColumn (byte[] family, byte[] qualifier) 指定希望獲取的列
Get setTimeRange (long minStamp, long maxStamp) 設置獲取數據的時間戳范圍
Get setTimeStamp (long timestamp) 設置獲取數據的時間戳
Get setMaxVersions (int maxVersions) 設定獲取數據的版本數
Get setMaxVersions() 設定獲取數據的所有版本
Get setFilter (Filter filter) 為Get對象添加過濾器,過濾器詳解請參見:http://blog.csdn.net/u010967382/article/details/37653177
void setCacheBlocks (boolean cacheBlocks) 設置該Get獲取的數據是否緩存在內存中
7.3.實測代碼
測試表的所有數據:
hbase(main):016:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:leetable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405304843114, value=longze
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405304843114, value=31
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405304843114, value=leon
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405305471343, value=caofang
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405305471343, value=30
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405305471343, value=show
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405407883218, value=qinghe
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405407883218, value=28
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405407883218, value=shichao
3 row(s) in 0.0250 seconds
(1)獲取行鍵指定行的所有列族、所有列的最新版本數據
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
Result r = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))
);
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : qinghe
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 28
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : shichao
(2)獲取行鍵指定行中,指定列的最新版本數據
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
get.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(“info”), Bytes.toBytes(“name”));
Result r = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))
);
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : shichao
(3)獲取行鍵指定的行中,指定時間戳的數據
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:leetable”);
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
get.setTimeStamp(1405407854374L);
Result r = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))
);
}
table.close();
代碼輸出了上面scan命令輸出中沒有展示的歷史數據:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : huangzhuang
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 32
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : lily
(4)獲取行鍵指定的行中,所有版本的數據
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:itable”);
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
get.setMaxVersions();
Result r = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))+
“ Time : ”+cell.getTimestamp()
);
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : xierqi Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : longze Time : 1405417448414
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 29 Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 30 Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 31 Time : 1405417448414
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : leon Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : lee Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : lion Time : 1405417448414
?
8.獲取多行Scan
Scan對象可以返回滿足給定條件的多行數據。如果希望獲取所有的行,直接初始化一個Scan對象即可。如果希望限制掃描的行范圍,可以使用以下方法:
如果希望獲取指定列族的所有列,可使用addFamily方法來添加所有希望獲取的列族
如果希望獲取指定列,使用addColumn方法來添加所有列
通過setTimeRange方法設定獲取列的時間范圍
通過setTimestamp方法指定具體的時間戳,只返回該時間戳的數據
通過setMaxVersions方法設定最大返回的版本數
通過setBatch方法設定返回數據的最大行數
通過setFilter方法為Scan對象添加過濾器,過濾器詳解請參見:http://blog.csdn.net/u010967382/article/details/37653177
Scan的結果數據是可以緩存在內存中的,可以通過getCaching()方法來查看當前設定的緩存條數,也可以通過setCaching(int caching)來設定緩存在內存中的行數,緩存得越多,以后查詢結果越快,同時也消耗更多內存。此外,通過setCacheBlocks方法設置是否緩存Scan的結果數據塊,默認為true
我們可以通過setMaxResultSize(long)方法來設定Scan返回的結果行數。
下面是官網文檔中的一個入門示例:假設表有幾行鍵值為 “row1”, “row2”, “row3”,還有一些行有鍵值 “abc1”, “abc2”, 和 “abc3”,目標是返回“row”打頭的行:
HTable htable = 。.. // instantiate HTable
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(“cf”),Bytes.toBytes(“attr”));
scan.setStartRow( Bytes.toBytes(“row”)); // start key is inclusive
scan.setStopRow( Bytes.toBytes(“row” + (char)0)); // stop key is exclusive
ResultScanner rs = htable.getScanner(scan);
try {
for (Result r = rs.next(); r != null; r = rs.next()) {
// process result.。.
} finally {
rs.close(); // always close the ResultScanner!
}
8.1.常用構造函數
(1)創建掃描所有行的Scan
Scan()
(2)創建Scan,從指定行開始掃描,
Scan(byte[] startRow)
參數:startRow行鍵
注意:如果指定行不存在,從下一個最近的行開始
(3)創建Scan,指定起止行
Scan(byte[] startRow, byte[] stopRow)
參數:startRow起始行,stopRow終止行
注意:startRow 《= 結果集 《 stopRow
(4)創建Scan,指定起始行和過濾器
Scan(byte[] startRow, Filter filter)
參數:startRow起始行,filter過濾器
注意:過濾器的功能和構造參見http://blog.csdn.net/u010967382/article/details/37653177
8.2.常用方法
Scan setStartRow(byte[] startRow) 設置Scan的開始行,默認結果集包含該行。如果希望結果集不包含該行,可以在行鍵末尾加上0。
Scan setStopRow(byte[] stopRow) 設置Scan的結束行,默認結果集不包含該行。如果希望結果集包含該行,可以在行鍵末尾加上0。
Scan setTimeRange(long minStamp, long maxStamp) 掃描指定時間范圍的數據
Scan setTimeStamp(long timestamp) 掃描指定時間的數據
Scan addColumn(byte[] family, byte[] qualifier) 指定掃描的列
Scan addFamily(byte[] family) 指定掃描的列族
Scan setFilter(Filter filter) 為Scan設置過濾器
Scan setReversed(boolean reversed) 設置Scan的掃描順序,默認是正向掃描(false),可以設置為逆向掃描(true)。注意:該方法0.98版本以后才可用!!
Scan setMaxVersions() 獲取所有版本的數據
Scan setMaxVersions(int maxVersions) 設置獲取的最大版本數
void setCaching(int caching) 設定緩存在內存中的行數,緩存得越多,以后查詢結果越快,同時也消耗更多內存
void setRaw(boolean raw) 激活或者禁用raw模式。如果raw模式被激活,Scan將返回所有已經被打上刪除標記但尚未被真正刪除的數據。該功能僅用于激活了KEEP_DELETED_ROWS的列族,即列族開啟了hcd.setKeepDeletedCells(true)。Scan激活raw模式后,就不能指定任意的列,否則會報錯
Enable/disable “raw” mode for this scan. If “raw” is enabled the scan will return all delete marker and deleted rows that have not been collected, yet. This is mostly useful for Scan on column families that have KEEP_DELETED_ROWS enabled. It is an error to specify any column when “raw” is set.
hcd.setKeepDeletedCells(true);
8.3.實測代碼
(1)掃描表中的所有行的最新版本數據
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:itable”);
Scan s = new Scan();
ResultScanner rs = table.getScanner(s);
for (Result r : rs) {
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))+
“ Time : ”+cell.getTimestamp()
);
}
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : anywhere Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 24 Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : zhangtao Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 28 Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : shichao Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : xierqi Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 29 Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : leon Time : 1405417500485
(2)掃描指定行鍵范圍,通過末尾加0,使得結果集包含StopRow
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:itable”);
Scan s = new Scan();
s.setStartRow(Bytes.toBytes(“100001”));
s.setStopRow(Bytes.toBytes(“1000020”));
ResultScanner rs = table.getScanner(s);
for (Result r : rs) {
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))+
“ Time : ”+cell.getTimestamp()
);
}
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : anywhere Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 24 Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100001 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : zhangtao Time : 1405417403438
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 28 Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : shichao Time : 1405417426693
(3)返回所有已經被打上刪除標記但尚未被真正刪除的數據
本測試針對rd_ns:itable表的100003行。
如果使用get結合setMaxVersions()方法能返回所有未刪除的數據,輸出如下:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : huilongguan Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : new29 Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : liyang Time : 1405494141522
然而,使用Scan強大的s.setRaw(true)方法,可以獲得所有已經被打上刪除標記但尚未被真正刪除的數據。
代碼如下:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:itable”);
Scan s = new Scan();
s.setStartRow(Bytes.toBytes(“100003”));
s.setRaw(true);
s.setMaxVersions();
ResultScanner rs = table.getScanner(s);
for (Result r : rs) {
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))+
“ Time : ”+cell.getTimestamp()
);
}
}
table.close();
輸出結果如下:
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : huilongguan Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : xierqi Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : Time : 1405417448414
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : longze Time : 1405417448414
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : new29 Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 29 Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 30 Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 31 Time : 1405417448414
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : liyang Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : Time : 1405493879419
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : leon Time : 1405417500485
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : lee Time : 1405417477465
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : lion Time : 1405417448414
(4)結合過濾器,獲取所有age在25到30之間的行
目前的數據:
hbase(main):049:0》 scan ‘rd_ns:itable’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
100001 column=info:address, timestamp=1405417403438, value=anywhere
100001 column=info:age, timestamp=1405417403438, value=24
100001 column=info:name, timestamp=1405417403438, value=zhangtao
100002 column=info:address, timestamp=1405417426693, value=shangdi
100002 column=info:age, timestamp=1405417426693, value=28
100002 column=info:name, timestamp=1405417426693, value=shichao
100003 column=info:address, timestamp=1405494141522, value=huilongguan
100003 column=info:age, timestamp=1405494999631, value=29
100003 column=info:name, timestamp=1405494141522, value=liyang
3 row(s) in 0.0240 seconds
代碼:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HTable table = new HTable(conf, “rd_ns:itable”);
FilterList filterList = new FilterList(FilterList.Operator.MUST_PASS_ALL);
SingleColumnValueFilter filter1 = new SingleColumnValueFilter(
Bytes.toBytes(“info”),
Bytes.toBytes(“age”),
CompareOp.GREATER_OR_EQUAL,
Bytes.toBytes(“25”)
);
SingleColumnValueFilter filter2 = new SingleColumnValueFilter(
Bytes.toBytes(“info”),
Bytes.toBytes(“age”),
CompareOp.LESS_OR_EQUAL,
Bytes.toBytes(“30”)
);
filterList.addFilter(filter1);
filterList.addFilter(filter2);
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setFilter(filterList);
ResultScanner rs = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result r : rs) {
for (Cell cell : r.rawCells()) {
System.out.println(
“Rowkey : ”+Bytes.toString(r.getRow())+
“ Familiy:Quilifier : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell))+
“ Value : ”+Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell))+
“ Time : ”+cell.getTimestamp()
);
}
}
table.close();
代碼輸出:
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : shangdi Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 28 Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100002 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : shichao Time : 1405417426693
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : address Value : huilongguan Time : 1405494141522
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : age Value : 29 Time : 1405494999631
Rowkey : 100003 Familiy:Quilifier : name Value : liyang Time : 1405494141522
注意:
HBase對列族、列名大小寫敏感
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App





















評論