本篇文章不會涉及到很多復雜的概念,也沒有寫很難讀懂的模板函數,代碼簡單可讀,本篇文章送給每一個想自己用C++寫一個http服務器的小伙伴!高手們、大佬們當然可以不用看的啦!
正文
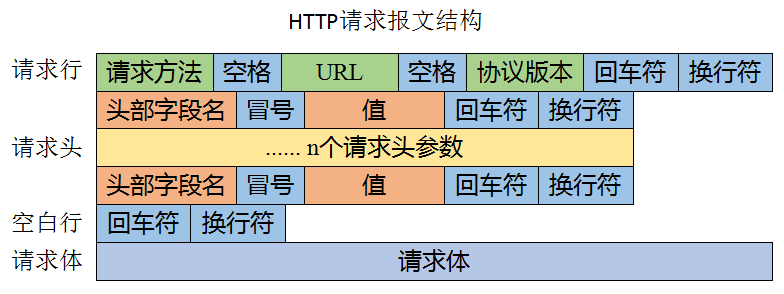
怎么寫一個簡單的http服務器阿?很簡單,只需要返回最基本的3個東西即可。
-
狀態碼
-
發送文件的長度
-
發送文件的類型
?
狀態碼如200(找到請求文件)、404(未找到請求文件),我實現的也比較簡單,就實現了這兩個狀態碼。
文件長度比如客戶請求的是index.html頁面,瀏覽器如何知道收到的這個文件什么時候結束呢?就靠是文件的長度
文件類型?html的類型是html格式,css的是css格式,圖片有圖片的格式,zip有zip格式文件格式對應的文件類型表(https://tool.oschina.net/commons)
返回給客戶端三個這種東西加上請求的文件即可(存在請求文件的情況下)可以了
Http工作流程
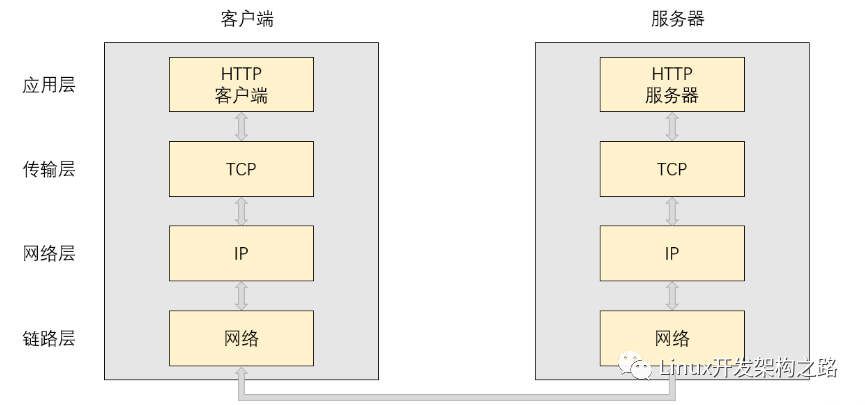
在這個部分大概介紹一下大概的http的工作流程。客戶端通過網址訪問到你的網站(一定要記住客戶端是主動請求連接的,服務端是被動連接的),實則就是通過ip+port訪問的,只不過http的默認端口號是80。比如你還沒有域名、云服務器這些東西,那如何在本地測試呢?就是在瀏覽框輸入ip:port,例如127.0.0.1:9996,按下回車就可以在本地訪問自己的http服務器了。當然了http要給客戶(請求者)一個首頁,當客戶沒有指定網頁,單純的打出域名或者127.0.0.1:9996,就給他一個默認的首頁,這也是我們要實現的事情。客戶寫了請求文件,我們來判斷是否存在,存在就返回狀態碼200和請求文件的內容。不存在就直接返回404。那我們如何判斷啊,拿最簡單的GET為例子吧,其他也大同小異,有興趣的同學可以自行研究其他的。我們利用正則表達式來解析客戶發來的請求是GET還是POST還是其他請求,在解析出來要請求文件。再利用狀態機思想來文件是否存在,若存在在判斷文件的類型。大概的流程就是這些。
Http.h
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
class TcpClient;class Http{// 文件的根目錄const std::string path_ = "./www/dxgzg_src";std::string filePath_;// 具體文件的絕對路徑std::string fileType_;// 請求文件的類型std::string header_; // http頭responseint fileSize_;int fileFd_;struct stat fileStat_;// POST請求的話將留言保存到本地文件中bool isPostMode_ = false;public:Http() = default;void addHeader(const std::string& head);void Header(bool flag);// 把一些頭文件的信息都加進來,只有成功的時候調用這個函數,// 并返回文件中的數據void processHead();// 把請求文件的路徑加上void addFilePath(const std::string& requestFile);// 獲取文件的類型void analyseFileType(const std::string& requestFile);bool analyseFile(const std::string& request);void SendFile(int clientFd,bool isRequestOk);bool fileIsExist();// 用戶自定義的回調函數要正確的處理異常和自己負責關閉套接字void ReadCallback(TcpClient* t);};
?
Http.cpp
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
- ?
// 用于testusing namespace std;void Http::addHeader(const string& head){if (!head.empty()){header_ += head;header_ += " ";// Console.WriteLine("我在這里 head!= null" + header_);}// 自動加個結尾else{header_ += " ";// Console.WriteLine("我在這里 head == null" + header_);}}void Http::Header(bool flag){// 判斷要發送的頭部 true 表示200 false 表示404if(flag == true){header_ = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK ";}else{header_ = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOTFOUND Content-Length:0 ";}}void Http::processHead(){string ContentType = "Content-Type:";if (fileType_ == "html"){ContentType += "text/html";}else if(fileType_ == "js"){ContentType += "application/x-javascript";}else if(fileType_ == "css"){ContentType += "text/css";}else if(fileType_=="jpg" || fileType_== "png"){ContentType += "image/" + fileType_;}else if (fileType_== "zip" || fileType_ == "tar"){ContentType += "application/" + fileType_;}addHeader(ContentType);// 代完善,要打開文件 filePath_是請求文件的路徑fileSize_= fileStat_.st_size;string ContentLength = "Content-Length:" + to_string(fileSize_);addHeader(ContentLength);// 最后加了一個結尾addHeader("");// Console.WriteLine("process fileContent_:" + );}void Http::addFilePath(const string& requestFile){filePath_ += requestFile;}void Http::analyseFileType(const string& requestFile){for (int i = 0; i < requestFile.size(); ++i){if (requestFile[i] == '.'){// 獲取請求文件以什么結尾的fileType_ = requestFile.substr(i + 1);}}}bool Http::fileIsExist(){fileFd_ = ::open(filePath_.c_str(),O_CLOEXEC | O_RDWR);if (fileFd_ < 0){ // 說明為找到請求的文件return false;}return true;}bool Http::analyseFile(const string& request){// 調用header的// 在[]的^是以什么什么開頭,放在[]里面的是非的意思string pattern = "^([A-Z]+) ([A-Za-z./1-9-]*)";regex reg(pattern);smatch mas;regex_search(request,mas,reg);// 因為下標0是代表匹配的整體if(mas.size() < 3){LOG_INFO("不是正常請求");// 啥都不是直接返回falsereturn false;}string requestMode = mas[1];if(requestMode == "POST"){isPostMode_ = true;cout << "POST請求!!!!!" << endl;}// 請求的具體文件string requestFile = mas[2];// 先獲取請求的文件bool flag;if (requestFile == "/"){ // 如果是/的話就給默認值filePath_.clear(); // 先清個零filePath_ = path_;filePath_ += "/run.html";// 文件的類型也要給人家加上fileType_ = "html";}else{filePath_.clear(); // 先清個零filePath_ = path_;addFilePath(requestFile);// 利用open函數}flag = fileIsExist();// 未找到文件的話if(!flag){LOG_INFO("未找到客戶要的文件");cout << filePath_ << endl;return false;}::fstat(fileFd_,&fileStat_);// 如果文件不存在的話也就不需要解析類型analyseFileType(requestFile);return true;}void Http::SendFile(int clientFd,bool isRequestOk){long len = 0;// 頭部一定是有的。while(len < header_.size()){len += ::send(clientFd,header_.c_str(),header_.size(),0);cout << "len header" << header_ <<endl;}// 發完了頭,在發請求文件的信息。如果是404這里是沒有的if (isRequestOk == true){len = 0;int num = 0;int tmpLen = 0;// 連續好幾次沒變的話就加一個numwhile (len < fileSize_){// 發送的文件個數已經寫入在len當中了::sendfile(clientFd,fileFd_,(off_t*)&len,fileStat_.st_size- len);cout << "len sendfile" <<"len:" << len << "fileSize" << fileSize_ <<endl;if(len <= 0 ){break;}if(tmpLen == len){++num;if(num > 10){break;}}tmpLen = len;}}}void Http::ReadCallback(TcpClient* t){cout << "ReadCallback" << endl;int sockFd = t->getFd();char buff[1024];int r = ::recv(sockFd,buff,sizeof(buff),0);if (r == 0){t->CloseCallback();return;}buff[r] = '';string str = buff;cout << str << endl;// 未找到文件直接回應404.bool flag = analyseFile(str);Header(flag);if(!flag){SendFile(sockFd,false);// t->CloseCallback();return ;}// 這個修改頭文件的,先調用這個processHead();//這是文件找到了發送的SendFile(sockFd,true);if(isPostMode_){int fd = ::open("./postLog/message.txt",O_RDWR);if(fd < 0){LOG_ERROR("未找到文件");}else{// 文件偏移到末尾::lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);::write(fd,str.c_str(),str.size());close(fd);}isPostMode_ = true;}// 關閉文件套接字close(fileFd_);// 發完就關閉連接,主要是為了多去幾個線程還能跑的快一些//t->CloseCallback();}
不考慮高并發的情況,設計一個同步阻塞的epoll即可,看完http必備的三要素已經能夠寫出一個服務器了,我的底層socket采用的是自己封裝的網絡庫,Reactor模型,one loop per thread的代碼文件比較多,所以就沒有放上來,但只要把狀態碼、文件類型(那一大段if)、文件的長度這三個實現了就可以搭建一個簡易的http服務器了。可以利用sendfile零拷貝來發送文件
在補充一點就是,http協議是 結尾。最后還有一個 ,就比如404,HTTP/1.1 404 NOTFOUND Content-Length:0 ,最后面再跟一個 ,結束一段跟一個。
 電子發燒友App
電子發燒友App




















評論