在Linux系統下,你可以使用 exit()、_exit() 和 _Exit() 來終止程序運行,特別是在出現錯誤或執行失敗的情況下。這樣可以確保程序在發生嚴重錯誤時能夠安全地退出。
1
exit() 函數
用法:void exit(int status)。
exit() 函數是標準 C 庫的一部分,常用于 C 和 C++ 程序中。
當調用時,它執行一系列的清理操作(如調用使用 atexit() 注冊的函數),刷新 I/O 緩沖區,然后終止程序。
status 參數是一個整數值,返回給調用進程的父進程。
通常,零狀態表示正常終止,而非零狀態可能表示錯誤或異常終止。
以下例子中,exit(0) 將立即終止程序,不會執行 printf("After exit() "); 后的代碼。exit(0) 表示正常終止。
#include
#include
int main() {
printf("Before exit()
");
// The exit() function performs cleanup actions and terminates the program.
exit(0);
// The following code will not be executed.
printf("After exit()
");
return 0;
}
2
_exit() 函數
用法: void _exit(int status)。
_exit() 函數是一個系統調用,立即終止調用的進程,而不執行 exit() 所做的清理操作。
它不刷新 I/O 緩沖區,也不關閉打開的文件描述符,并且不調用使用 atexit() 注冊的函數。
status 參數被返回給父進程。
與 exit() 不同,_exit(0) 不會執行任何清理動作,而是立即終止程序。與 exit() 不同,_exit() 函數是一個系統調用,不執行標準庫的清理操作。
#include
#include
int main() {
printf("Before _exit()
");
// The _exit() function immediately terminates the program without cleanup.
_exit(0);
// The following code will not be executed.
printf("After _exit()
");
return 0;
}
3
_Exit() 函數
用法: void _Exit(int status)。
與 _exit() 類似,_Exit() 是一個系統調用,它在不執行清理操作的情況下立即終止調用的進程。
_Exit() 的行為類似于 _exit(),但其設計與 exit() 具有相同的函數簽名。
它在 POSIX 兼容系統中得到標準化。
_Exit(0) 與 _exit(0) 類似,都是立即終止程序。在 POSIX 系統中,_Exit() 是標準化的版本。
#include
#include
int main() {
printf("Before _Exit()
");
// The _Exit() function immediately terminates the program without cleanup.
_Exit(0);
// The following code will not be executed.
printf("After _Exit()
");
return 0;
}
總的來說,exit() 是一個更高級別的函數,在終止之前執行各種清理操作,而 _exit() 和 _Exit() 是低級別的函數,立即終止進程而不執行清理操作。_Exit() 是 POSIX 兼容系統中對 _exit() 的標準化版本。
審核編輯:劉清
-
Linux系統
+關注
關注
4文章
594瀏覽量
27441
原文標題:exit()、_exit()和_Exit()終止程序運行
文章出處:【微信號:美男子玩編程,微信公眾號:美男子玩編程】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
linux的exit()與_exit()有什么區別
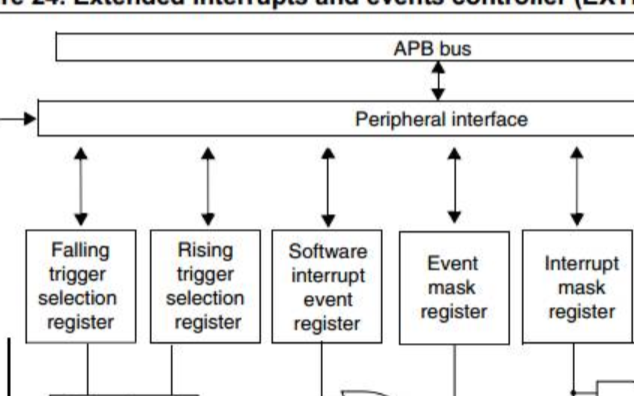
STM32筆記之 EXIT(外部中斷)精選資料分享
STM32F0中外部中斷EXIT
定時器外部中斷(EXIT)概念
基于EXIT圖和自適應微粒群算法的度分布對優化方法
Shell內建命令:exit命令
瑞薩e2studio(6)----EXIT





 如何使用exit()、_exit()和_Exit()來終止程序運行呢?
如何使用exit()、_exit()和_Exit()來終止程序運行呢?










評論