前一陣子,一位小伙伴咨詢我一款新IC芯片怎么使用,借此機會我順便把我日常工作中經常用到的一種調試方法介紹給小伙伴們,希望對對大家有所幫助。準備倉促,文中難免有技術性錯誤,歡迎大家給予指正,并給出好的建議...
前言:
我們在單片機的項目開發過程中經常會遇到使用新IC芯片的情況,某寶賣家有個時候也提供不了對應開發程序,到網上找資料也找不到;很多初學者面對這樣的問題往往束手無策,這里我給大家介紹我經常用的其中一種新IC調試的方法。
因為這個芯片比較簡單我這里采用下面步驟進行:
第一步: 先用arduino+面包板快速搭建電路驗證芯片功能
第二步: 使用STM32CubeIDE快速搭建工程驗證在STM32上工作是否正常
Tips :由于我手頭沒有 萬用表 ,這里我使用arduino的模擬電壓采集功能通過串口打印出來作為電位計的電壓監控用。
首先,我們先快速瀏覽芯片數據手冊,獲取重要信息
IC型號:TLP0501
電壓范圍:2.7~5.5V
溫度范圍:-40~125℃
通信方式:SPI
阻值:100KΩ
阻值偏差:±20%
該芯片是德州儀器的一款單通道數字電位計,通信方式是SPI總線,單方向的,即只能控制芯片,不能讀取輸入數據,下面是數據手冊的具體介紹。
環境參數:主要包括溫度使用范圍、電壓使用范圍、誤差、溫度漂移以及實物引腳對應關系都在這里
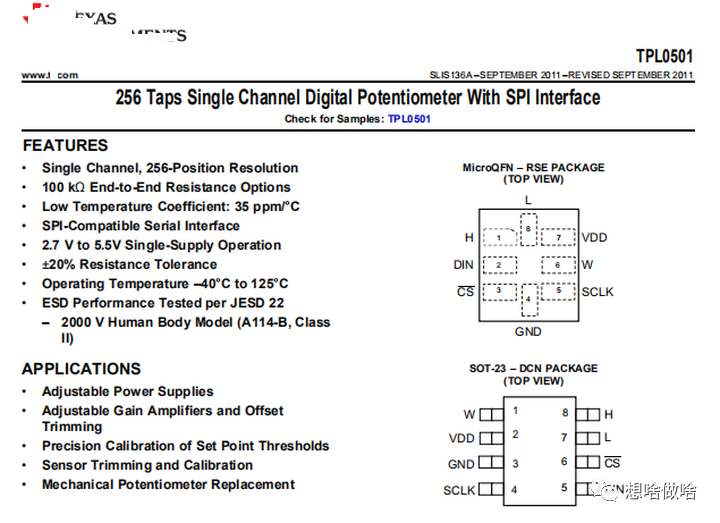
環境參數
功能框圖:主要介紹該芯片的內部組成和工作原理

功能框圖
引腳定義:每個引腳的功能介紹

引腳定義
SPI通信說明:主要介紹芯片的通信方式,這個芯片因為沒有設置模式功能,只需要對芯片直接寫數據即可,通信方式與我們所使用的74HC595的方式類似

SPI通信說明
真值對照表:也就是數字量對應的實際電阻值,我這里只截取了一部分,剩下的大家可以自行去參考詳細手冊

真值對照表
對于要調通這個芯片這些介紹基本滿足我們的需求了
芯片模塊的快速制作
在芯片商城上買了兩片回來調試,芯片購買的費用知乎小伙伴給付了
準備好芯片+轉接板

焊接兩塊是為了防止在使用過程中意外弄壞另一塊可以立馬補上,確保調試正常進行而不耽誤太多時間

焊接好排針,并在供電端加上0.1uF的濾波電容,降低高頻供電干擾

這樣我們的模塊就制作完成了
arduino快速搭建工程:
電路原理圖

電路原理圖
引腳對應關系:
arduino uno 引腳4 -> CLK
arduino uno 引腳5 -> DIN
arduino uno 引腳6 -> CS
arduino uno 引腳5v -> VCC、VREF
arduino uno 引腳GND -> GND、L
arduino uno 引腳A0 -> VRES_OUT
首先用面包板+杜邦線搭好電路
說明:我在這里使用的供電電壓和數字電位計參考電壓都是使用的5V,相應的輸出結果也是在0~5V范圍

然后使用arduino自帶的庫,編寫代碼,再變動阻值參數,看下輸出的實際結果和真值表是否對應的上
數值為0x00時對應的模擬電壓輸出

數值為0x88時對應的模擬電壓輸出
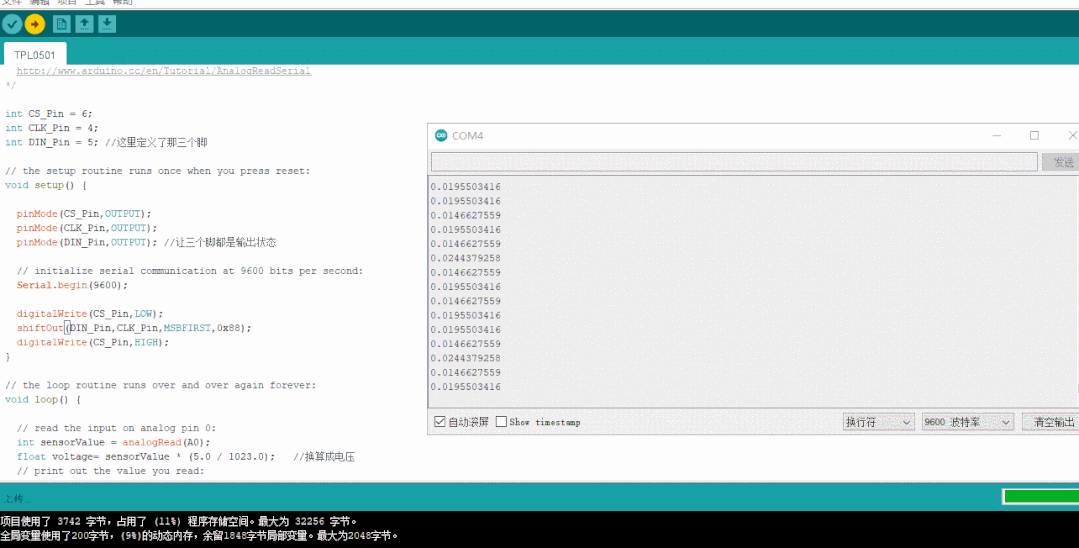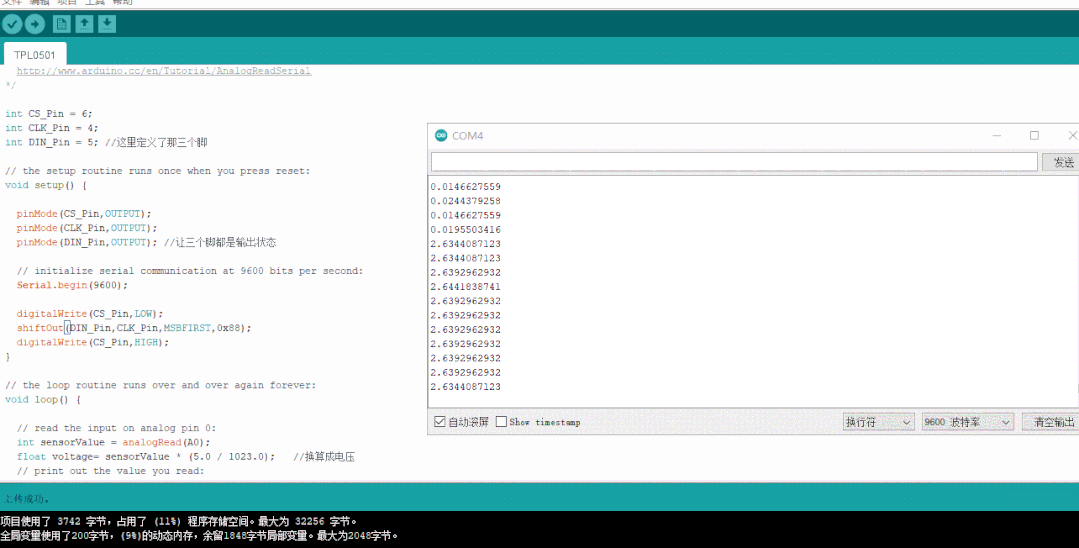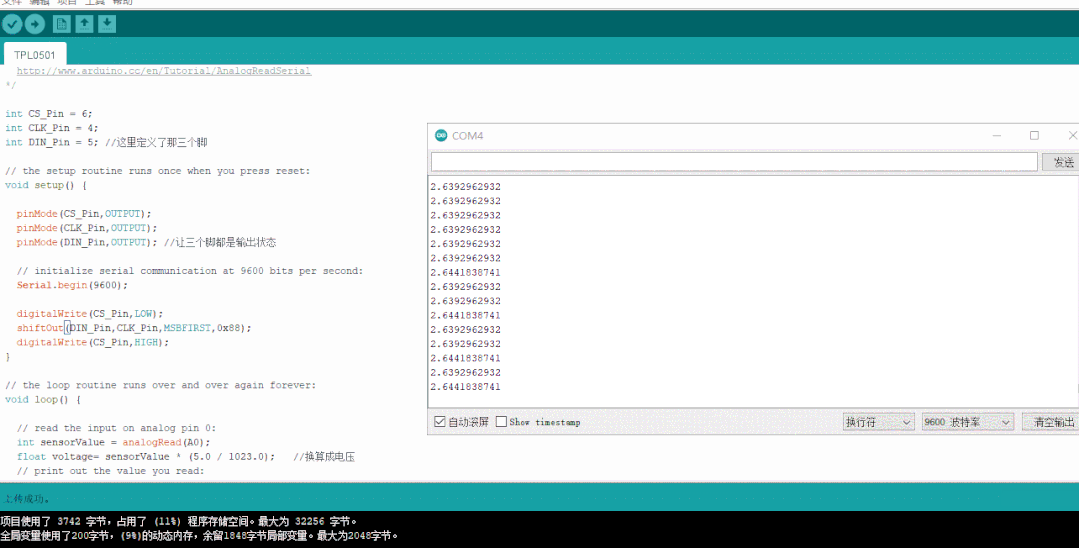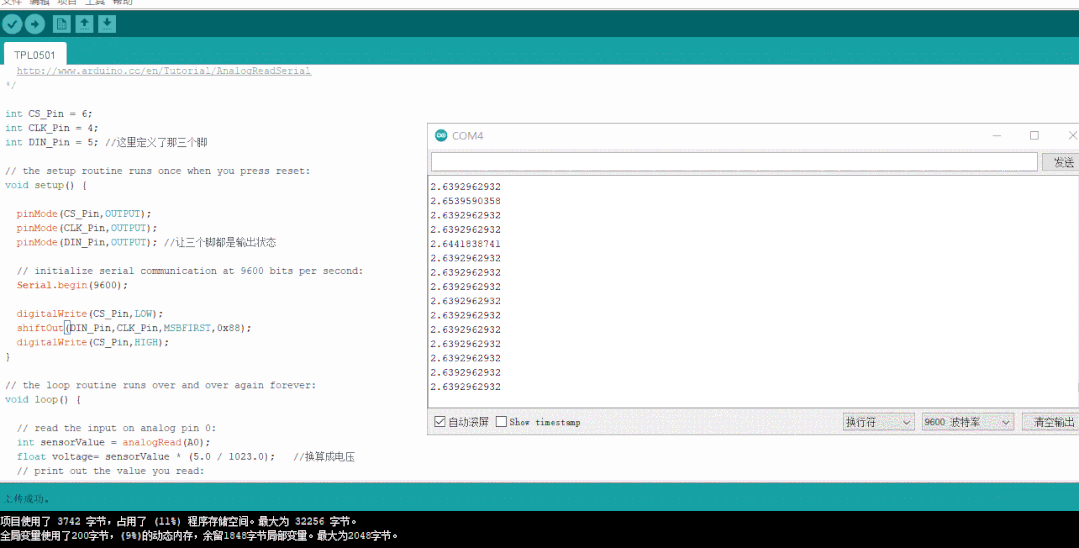
數值為0xFF時對應的模擬電壓輸出

經過驗證,在arduino上跑沒有問題,接下來我們準備在STM32上去運行
arduino代碼部分:
/*
AnalogReadSerial
Reads an analog input on pin 0, prints the result to the Serial Monitor.
Graphical representation is available using Serial Plotter (Tools > Serial Plotter menu).
Attach the center pin of a potentiometer to pin A0, and the outside pins to +5V and ground.
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/AnalogReadSerial
*/
int CS_Pin = 6;
int CLK_Pin = 4;
int DIN_Pin = 5; //這里定義了那三個腳
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
pinMode(CS_Pin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(CLK_Pin,OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIN_Pin,OUTPUT); //讓三個腳都是輸出狀態
// initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(9600);
digitalWrite(CS_Pin,LOW);
shiftOut(DIN_Pin,CLK_Pin,MSBFIRST,0xFF);
digitalWrite(CS_Pin,HIGH);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
// read the input on analog pin 0:
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
float voltage= sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); //換算成電壓
// print out the value you read:
Serial.println(voltage,DEC);
delay(100); // delay in between reads for stability
}
STM32搭建工程驗證
說明:STM32使用的供電電壓和數字電位計參考電壓都是3V3,相應的輸出結果也是在0~3V3范圍

電路原理圖
引腳對應關系:
PA4 -> CLK
PA5 -> DIN
PA6 -> CS
3V3 -> VCC、VREF
arduino uno 引腳GND -> GND、L
arduino uno 引腳A0 -> VRES-OUT
開發板+面包板搭建電路

用STM32CubeIDE建立一個工程

配置好PA4、PA5、PA6引腳為輸出

生成代碼,并添加TLP0501的驅動代碼

編譯看運行的效果,輸入值為0x55
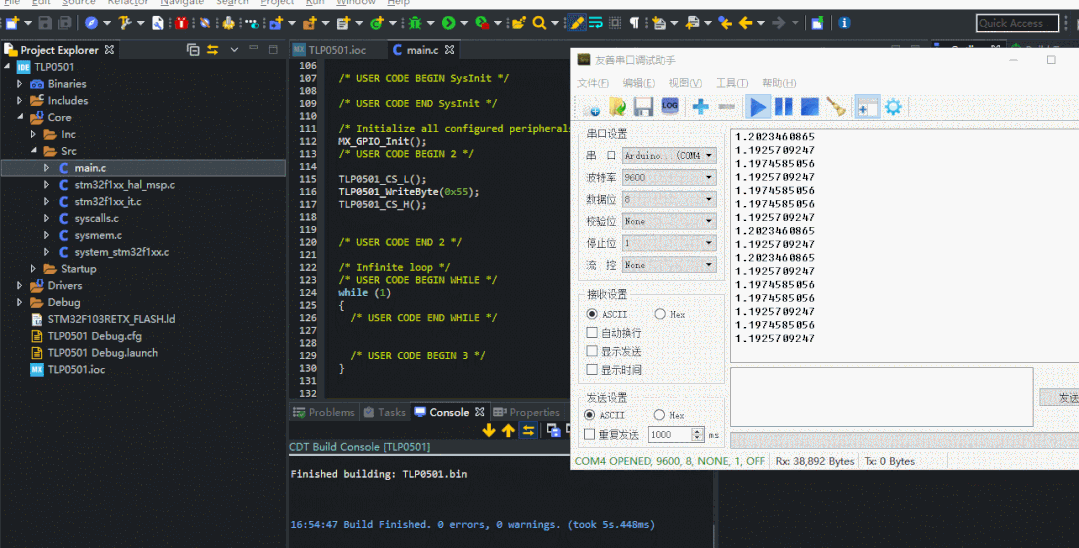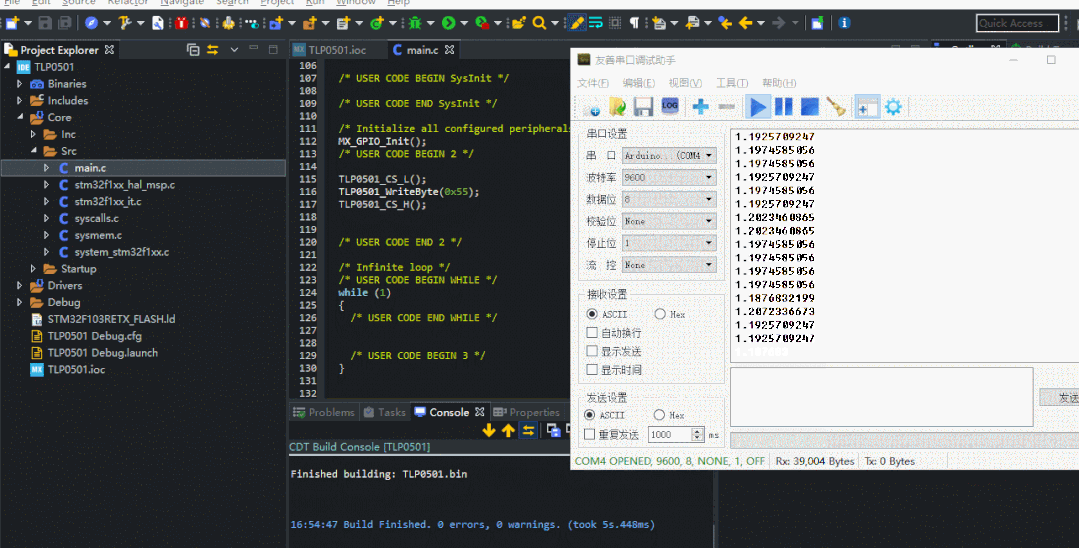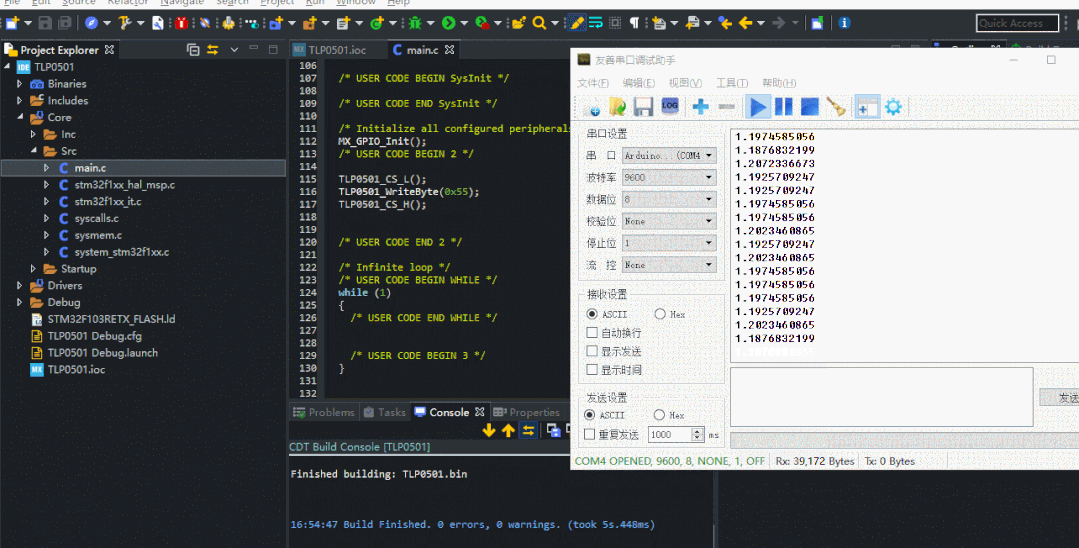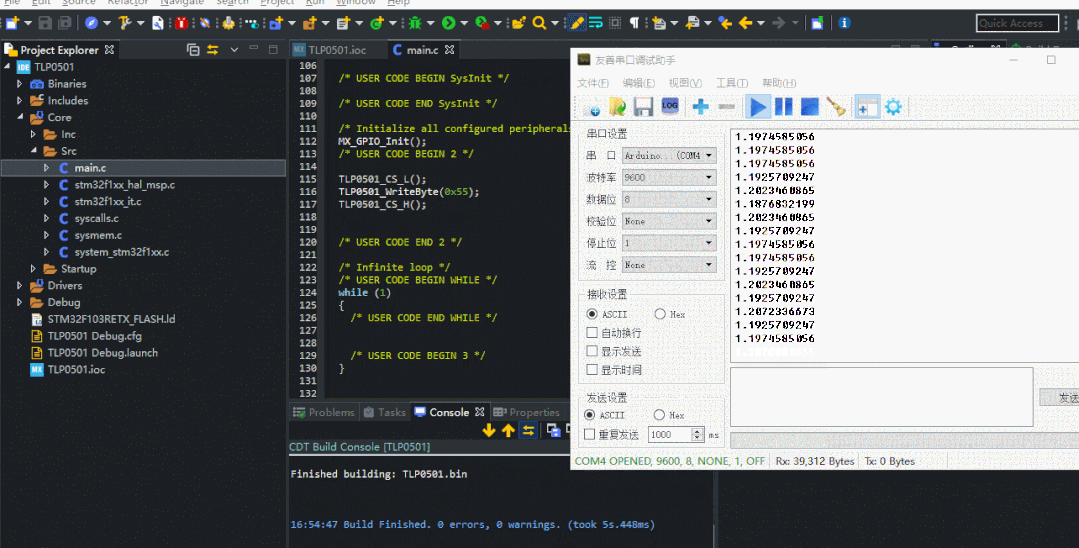
更改輸入的數值為0x22,驗證是否正確

main函數代碼部分:
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* < h2 >< center >? Copyright (c) 2021 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.< /center >< /h2 >
*
* This software component is licensed by ST under BSD 3-Clause license,
* the "License"; You may not use this file except in compliance with the
* License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
* opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
#define TLP0501_DIN_H() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_SET)
#define TLP0501_DIN_L() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_5, GPIO_PIN_RESET)
#define TLP0501_CS_H() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_SET)
#define TLP0501_CS_L() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_RESET)
#define TLP0501_CLK_H() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_SET)
#define TLP0501_CLK_L() HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_RESET)
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
void TLP0501_WriteByte( uint8_t data )
{
uint8_t j;
for ( j=8; j >=1; j--)
{
TLP0501_CLK_L();
__NOP();
if(data & 0x80 ){ TLP0501_DIN_H(); }
else { TLP0501_DIN_L(); }
data < <= 1;
TLP0501_CLK_H();
}
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
TLP0501_CS_L();
TLP0501_WriteByte(0x22);
TLP0501_CS_H();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_NONE;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_HSI;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_0) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOD_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_4|GPIO_PIN_5|GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
/*Configure GPIO pins : PA4 PA5 PA6 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_4|GPIO_PIN_5|GPIO_PIN_6;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
tex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %drn", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT STMicroelectronics *****END OF FILE****/
總結:
1、這里介紹了眾多新IC芯片調試方式中的一種,后期有機會再陸續介紹其他IC或新模塊的調試方法。
2、文中只是簡單的對芯片進行功能測試,實際項目中還會有移植、驅動的可靠性、穩定性等測試工作 。
3、我們要善于運用手頭的工具、arduino等快速驗證開發環境;模塊的快速驗證,特別是在項目開發過程中,時間就是金錢,對每一種工具的熟練掌握也是單片機開發過程中不可或缺的重要技能。
4、硬件調試與軟件調試有很大的區別,很多時候是一次性,不可逆轉的,不像軟件Ctl+Z可以撤銷;硬件在使用過程中出現意外損壞情況很正常:焊接不當、意外插錯,靜電防護不到位等等;我們要善于運用一些項目技巧,權衡時間或花費;這里之所以選擇焊接兩個芯片模塊也是為了防止這種意外的發生而對調試造成不必要的時間耽擱。
-
電路圖
+關注
關注
10354文章
10723瀏覽量
532147 -
單片機
+關注
關注
6041文章
44615瀏覽量
637368 -
IC芯片
+關注
關注
8文章
251瀏覽量
26310 -
Arduino
+關注
關注
188文章
6477瀏覽量
187541 -
面包板
+關注
關注
3文章
298瀏覽量
17605
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
單片機串口模塊調試方法
單片機如何控制調試信息輸出
單片機開發調試應注意的問題
單片機控制調試信息輸出的方法

單片機項目中LED的重要性~





 單片機項目中使用新IC芯片調試方法
單片機項目中使用新IC芯片調試方法










評論