XGBoost 是一種基于決策樹的集成 機器學(xué)習(xí)算法,基于梯度增強。然而,直到最近,它還不支持分類數(shù)據(jù)。分類特征在用于訓(xùn)練或推理之前必須手動編碼。
在序數(shù)類別的情況下,例如學(xué)校成績,這通常使用標(biāo)簽編碼來完成,其中每個類別都分配一個與該類別的位置相對應(yīng)的整數(shù)。等級 A 、 B 和 C 可分別分配整數(shù) 1 、 2 和 3 。
對于基數(shù)類別,類別之間沒有序數(shù)關(guān)系,例如顏色,這通常使用一個熱編碼來完成。這是為類別特征包含的每個類別創(chuàng)建新的二進(jìn)制特征的地方。具有紅色、綠色和藍(lán)色類別的單個分類特征將是一個熱編碼為三個二進(jìn)制特征,一個代表每種顏色。
>>> import pandas as pd >>> df = pd.DataFrame({"id":[1,2,3,4,5],"color":["red","green","blue","green","blue"]}) >>> print(df) id color 0 1 red 1 2 green 2 3 blue 3 4 green 4 5 blue >>> print(pd.get_dummies(df)) id color_blue color_green color_red 0 1 0 0 1 1 2 0 1 0 2 3 1 0 0 3 4 0 1 0 4 5 1 0 0
這意味著具有大量類別的分類特征可能會導(dǎo)致數(shù)十甚至數(shù)百個額外的特征。因此,經(jīng)常會遇到內(nèi)存池和最大 DataFrame 大小限制。
對于 XGBoost 這樣的樹學(xué)習(xí)者來說,這也是一種特別糟糕的方法。決策樹通過找到所有特征的分裂點及其可能的值來訓(xùn)練,這將導(dǎo)致純度的最大提高。
由于具有許多類別的一個熱編碼分類特征往往是稀疏的,因此分割算法 經(jīng)常忽略 one-hot 特性有利于較少稀疏的特征,這些特征可以貢獻(xiàn)更大的純度增益。
現(xiàn)在, XGBoost 1.7 包含了一個實驗 特征,它使您可以直接在分類數(shù)據(jù)上訓(xùn)練和運行模型,而無需手動編碼。這包括讓 XGBoost 自動標(biāo)記編碼或?qū)?shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行一次熱編碼的選項,以及 optimal partitioning 算法,用于有效地對分類數(shù)據(jù)執(zhí)行拆分,同時避免一次熱解碼的缺陷。 1.7 版還支持缺失值和最大類別閾值,以避免過度擬合。
這篇文章簡要介紹了如何在包含多個分類特征的示例數(shù)據(jù)集上實際使用新特征。
使用 XGBoost 的分類支持預(yù)測恒星類型
要使用新功能,必須首先加載一些數(shù)據(jù)。在本例中,我使用了 Kaggle star type prediction dataset 。
>>> import pandas as pd >>> import xgboost as xgb >>> from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split >>> data = pd.read_csv("6 class csv.csv") >>> print(data.head())
然后,將目標(biāo)列(星形)提取到其自己的系列中,并將數(shù)據(jù)集拆分為訓(xùn)練和測試數(shù)據(jù)集。
>>> X = data.drop("Star type", axis=1)
>>> y = data["Star type"]
>>> X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y)
接下來,將分類特征指定為category數(shù)據(jù)類型。
>>> Y_train = y_train.astype("category")
>>> X_train["Star color"] = X_train["Star color"].astype("category")
>>> X_train["Spectral Class"] = X_train["Spectral Class"].astype("category")
現(xiàn)在,要使用新功能,必須在創(chuàng)建XGBClassifier對象時將enable_categorical參數(shù)設(shè)置為True。之后,繼續(xù)訓(xùn)練 XGBoost 模型時的正常操作。這適用于 CPU 和 GPU tree_methods。
>>> clf = xgb.XGBClassifier(
tree_method="gpu_hist", enable_categorical=True, max_cat_to_onehot=1
)
>>> clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
XGBClassifier(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', callbacks=None,
colsample_bylevel=1, colsample_bynode=1, colsample_bytree=1,
early_stopping_rounds=None, enable_categorical=True,
eval_metric=None, gamma=0, gpu_id=0, grow_policy='depthwise',
importance_type=None, interaction_constraints='',
learning_rate=0.300000012, max_bin=256, max_cat_to_onehot=4,
max_delta_step=0, max_depth=6, max_leaves=0,
min_child_weight=1, missing=nan, monotone_constraints='()',
n_estimators=100, n_jobs=0, num_parallel_tree=1,
objective='multi:softprob', predictor='auto', random_state=0,
reg_alpha=0, ...)
最后,您可以使用您的模型生成預(yù)測,而無需對分類特征進(jìn)行一次熱編碼或編碼。
>>> X_test["Star color"] = X_test["Star color"]
.astype("category")
.cat.set_categories(X_train["Star color"].cat.categories)
>>> X_test["Spectral Class"] = X_test["Spectral Class"]
.astype("category")
.cat.set_categories(X_train["Spectral Class"].cat.categories)
>>> print(clf.predict(X_test))
[1 0 3 3 2 5 1 1 2 1 4 3 4 0 0 4 1 5 2 4 4 1 4 5 5 3 1 4 5 2 0 2 5 5 4 2 5
0 3 3 0 2 3 3 1 0 4 2 0 4 5 2 0 0 3 2 3 4 4 4]
總結(jié)
我們演示了如何使用 XGBoost 對分類特征的實驗支持,以改善 XGBoost 在分類數(shù)據(jù)上的訓(xùn)練和推理體驗。。
-
NVIDIA
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
14文章
4990瀏覽量
103104 -
AI
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
87文章
30946瀏覽量
269191 -
機器學(xué)習(xí)
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
66文章
8420瀏覽量
132680
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
基于xgboost的風(fēng)力發(fā)電機葉片結(jié)冰分類預(yù)測 精選資料分享
基于xgboost的風(fēng)力發(fā)電機葉片結(jié)冰分類預(yù)測 精選資料下載
基于快速低秩編碼與局部約束的圖像分類算法
色環(huán)電阻識別工具計算器(無需手動計算)
通過學(xué)習(xí)PPT地址和xgboost導(dǎo)讀和實戰(zhàn)地址來對xgboost原理和應(yīng)用分析

基于棧式自編碼的惡意代碼分類算法
一種新的目標(biāo)分類特征深度學(xué)習(xí)模型
面試中出現(xiàn)有關(guān)Xgboost總結(jié)
基于自編碼特征的語音聲學(xué)綜合特征提取
基于XGBoost的樹突狀細(xì)胞算法綜述
常見的11個分類變量編碼方法
XGBoost 2.0介紹




 XGBoost中無需手動編碼的分類特征
XGBoost中無需手動編碼的分類特征
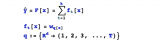










評論