1 簡介
簡單工廠方法定義一個用于創(chuàng)建對象的類,該類接受一個參數(shù),通過參數(shù)決定創(chuàng)建不同的對象。
GOF并沒有把簡單工廠方法定義為23種設(shè)計模式之一,可以認為簡單工廠方法是工廠方法的簡化形式。
為了體現(xiàn)簡單工廠方法和工廠方法的區(qū)別和聯(lián)系,此處把簡單工廠方法先單獨講一下。
2 模擬場景
假設(shè)你要生產(chǎn)電腦,電腦由硬盤、內(nèi)存條、CPU、主板的部件組成。你為了保證供應(yīng)鏈可靠,每種部件都選擇了至少兩家供應(yīng)商。比如: 硬盤供應(yīng)商 seagate、Toshiba 內(nèi)存條供應(yīng)商 SAMSUNG、Crucial CPU供應(yīng)商 intel、AMD 主板供應(yīng)商 intel、AMD 此處列出多個部件是為了后面講解工廠方法、抽象工廠方法時使用同一個模擬場景。本章講簡單工廠方法暫時不需要涉及這么多部件,所以僅以硬盤這一個部件為例進行講解。
3 實現(xiàn)的思路
硬盤就是要創(chuàng)建的對象(即:產(chǎn)品)。為了讓不同供應(yīng)商提供的硬盤可以通用,要定義一個硬盤產(chǎn)品類,并讓不同供應(yīng)商的硬盤都繼承硬盤產(chǎn)品類的接口。
還需要定義一個創(chuàng)建硬盤對象的類(即:工廠)。工廠類根據(jù)參數(shù)決定創(chuàng)建哪家供應(yīng)商的硬盤對象。
4 實現(xiàn)硬盤對象創(chuàng)建
參與者: (1)Product: HardDisk 定義硬盤對象的接口 (2)Concrete Product: SeagateHardDisk, ToshibaHardDisk 實現(xiàn)不同供應(yīng)商的硬盤 (3)SimpleFactory: HardDiskFactory 根據(jù)參數(shù),創(chuàng)建不同供應(yīng)商的硬盤對象
UML: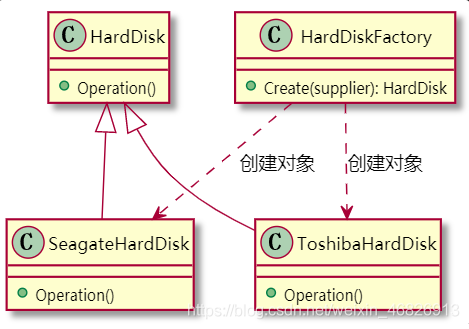
HardDisk代碼示例:
hard_disk.h:
#ifndef HARD_DISK_H
#define HARD_DISK_H
struct HardDisk {
void (*Operation)(struct HardDisk *this);
};
#endif
SeagateHardDisk代碼示例:seagate_hard_disk.h:
#ifndef SEAGATE_HARD_DISK_H
#define SEAGATE_HARD_DISK_H
#include "hard_disk.h"
struct SeagateHardDisk {
struct HardDisk hardDisk;
};
// 構(gòu)造函數(shù)
void SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this);
// 析構(gòu)函數(shù)
void _SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this);
#endif
seagate_hard_disk.c:
#include "seagate_hard_disk.h"
#include "stdio.h"
void SeagateOperation(struct SeagateHardDisk *this)
{
printf("這是 Seagate 硬盤
");
}
void SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this)
{
this->hardDisk.Operation = (void(*)(struct HardDisk *))SeagateOperation;
}
void _SeagateHardDisk(struct SeagateHardDisk *this)
{
this->hardDisk.Operation = NULL;
}
ToshibaHardDisk代碼示例:toshiba_hard_disk.h:
#ifndef TOSHIBA_HARD_DISK_H
#define TOSHIBA_HARD_DISK_H
#include "hard_disk.h"
struct ToshibaHardDisk {
struct HardDisk hardDisk;
};
// 構(gòu)造函數(shù)
void ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this);
// 析構(gòu)函數(shù)
void _ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this);
#endif
toshiba_hard_disk.c:
#include "toshiba_hard_disk.h"
#include "stdio.h"
void ToshibaOperation(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this)
{
printf("這是 Toshiba 硬盤
");
}
void ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this)
{
this->hardDisk.Operation = (void(*)(struct HardDisk *))ToshibaOperation;
}
void _ToshibaHardDisk(struct ToshibaHardDisk *this)
{
this->hardDisk.Operation = NULL;
}
HardDiskFactory代碼示例:hard_disk_factory.h:
#ifndef HARD_DISK_FACTORY_H
#define HARD_DISK_FACTORY_H
#include "hard_disk.h"
enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E {
HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE,
HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA
};
struct HardDiskFactory {
struct HardDisk* (*Create)(struct HardDiskFactory *this,
enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E supplier);
void (*Destroy)(struct HardDiskFactory *this,
struct HardDisk* hardDisk);
};
// 構(gòu)造函數(shù)
void HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this);
// 析構(gòu)函數(shù)
void _HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this);
#endif
hard_disk_factory.c:
#include "hard_disk_factory.h"
#include "seagate_hard_disk.h"
#include "toshiba_hard_disk.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
struct HardDisk *Create(struct HardDiskFactory *this,
enum HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_E supplier)
{
switch (supplier) {
case HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE:
{
struct SeagateHardDisk *seagateHardDisk = NULL;
if ((seagateHardDisk = malloc(sizeof(struct SeagateHardDisk))) == NULL) {
printf("fail in malloc
");
return NULL;
}
SeagateHardDisk(seagateHardDisk);
return (struct HardDisk *)seagateHardDisk;
}
case HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA:
{
struct ToshibaHardDisk *toshibaHardDisk = NULL;
if ((toshibaHardDisk = malloc(sizeof(struct ToshibaHardDisk))) == NULL) {
printf("fail in malloc
");
return NULL;
}
ToshibaHardDisk(toshibaHardDisk);
return (struct HardDisk *)toshibaHardDisk;
}
default:
printf("未知的供應(yīng)商
");
return NULL;
}
}
void Destroy(struct HardDiskFactory *this, struct HardDisk* hardDisk)
{
if (hardDisk != NULL) {
free(hardDisk);
}
}
// 構(gòu)造函數(shù)
void HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this)
{
this->Create = Create;
this->Destroy = Destroy;
}
// 析構(gòu)函數(shù)
void _HardDiskFactory(struct HardDiskFactory *this)
{
this->Create = NULL;
this->Destroy = NULL;
}
客戶端代碼示例:
#include "hard_disk.h"
#include "hard_disk_factory.h"
#include "stddef.h"
void main()
{
struct HardDisk *hardDisk = NULL;
struct HardDiskFactory hardDiskFactory;
HardDiskFactory(&hardDiskFactory);
// 創(chuàng)建 seagate 硬盤對象
hardDisk = hardDiskFactory.Create(&hardDiskFactory, HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_SEAGATE);
// 使用 seagate 硬盤對象
hardDisk->Operation(hardDisk);
// 銷毀 seagate 硬盤對象
hardDiskFactory.Destroy(&hardDiskFactory, hardDisk);
// 創(chuàng)建 toshiba 硬盤對象
hardDisk = hardDiskFactory.Create(&hardDiskFactory, HARD_DISK_SUPPLIER_TOSHIBA);
// 使用 seagate 硬盤對象
hardDisk->Operation(hardDisk);
// 銷毀 toshiba 硬盤對象
hardDiskFactory.Destroy(&hardDiskFactory, hardDisk);
_HardDiskFactory(&hardDiskFactory);
}
客戶端顯示示例:
./hard_disk 這是 Seagate 硬盤 這是 Toshiba 硬盤
審核編輯:湯梓紅
-
amd
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
25文章
5478瀏覽量
134300 -
cpu
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
68文章
10880瀏覽量
212210 -
接口
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
33文章
8649瀏覽量
151401 -
硬盤
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
3文章
1313瀏覽量
57370 -
C語言
+關(guān)注
關(guān)注
180文章
7608瀏覽量
137134
原文標題:C語言簡單工廠方法實例
文章出處:【微信號:c-stm32,微信公眾號:STM32嵌入式開發(fā)】歡迎添加關(guān)注!文章轉(zhuǎn)載請注明出處。
發(fā)布評論請先 登錄
相關(guān)推薦
C語言與MATLAB接口編程與實例

使用單片機點亮多個LED燈的方法C語言程序實例免費下載
設(shè)計模式:簡單工廠模式——基于C語言





 C語言簡單工廠方法實例
C語言簡單工廠方法實例










評論