文章目錄
8 ALSA應用開發
8.1 音頻相關概念
8.1.1 采樣頻率
8.1.2 量化位數
8.2 ALSA架構
8.2.1 ALSA架構介紹
8.3 移植ALSA庫及工具
8.3.1 ALSA庫下載
8.3.2 ALSA Lib編譯
8.3.3 ALSA Util編譯
8.3.4 ALSA庫和工具移植入嵌入式平臺
8.4 ALSA的調試
8.4.1 amixer
8.4.2 aplay
8.4.3 arecord
8.5 常用接口說明
8.5.1 PCM接口
8.6 基于ALSA的音量控制程序設計
8.6.1 程序設計
8.6.2 AlsaVolume 類的定義
8.6.3 AlsaVolume類中成員函數的實現
8.7 ALSA基類的設計
8.7.1 程序設計
8.7.2 AlsaBase類中成員函數的實現
8.8 基于ALSA音頻的播放
8.8.1 程序設計
8.1.2 AlsaPlay類的定義
8.1.3 AlsaPlayback類中成員函數的實現
8.9 基于ALSA音頻的錄制
8.9.1 程序設計
8.9.2 AlsaPlay類的定義
8.9.3 AlsaCapture類中成員函數的實現
8 ALSA應用開發
8.1 音頻相關概念
? 音頻信號是一種連續變化的模擬信號,但計算機只能處理和記錄二進制的數字信號,由自然音源得到的音頻信號必須經過一定的變換,成為數字音頻信號之后,才能送到計算機中作進一步的處理。
? 數字音頻系統通過將聲波的波型轉換成一系列二進制數據,來實現對原始聲音的重現,實現這一步驟的設備常被稱為(A/D)。A/D轉換器以每秒鐘上萬次的速率對聲波進行采樣,每個采樣點都記錄下了原始模擬聲波在某一時刻的狀態,通常稱之為樣本(sample),而每一秒鐘所采樣的數目則稱為采樣頻率,通過將一串連續的樣本連接起來,就可以在計算機中描述一段聲音了。對于采樣過程中的每一個樣本來說,數字音頻系統會分配一定存儲位來記錄聲波的振幅,一般稱之為采樣分辯率或者采樣精度,采樣精度越高,聲音還原時就會越細膩。
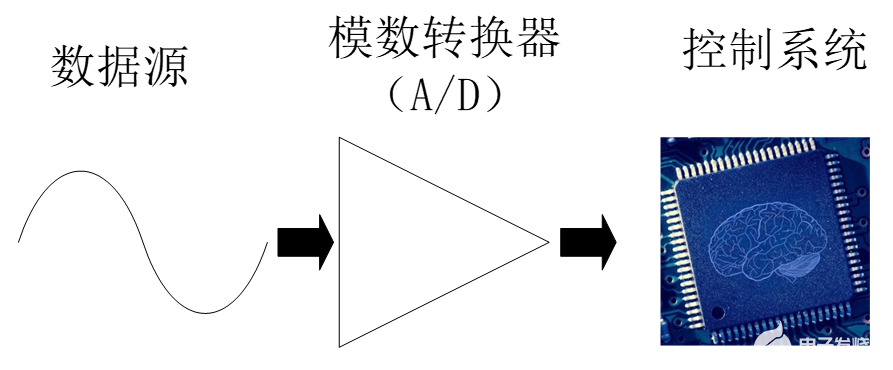
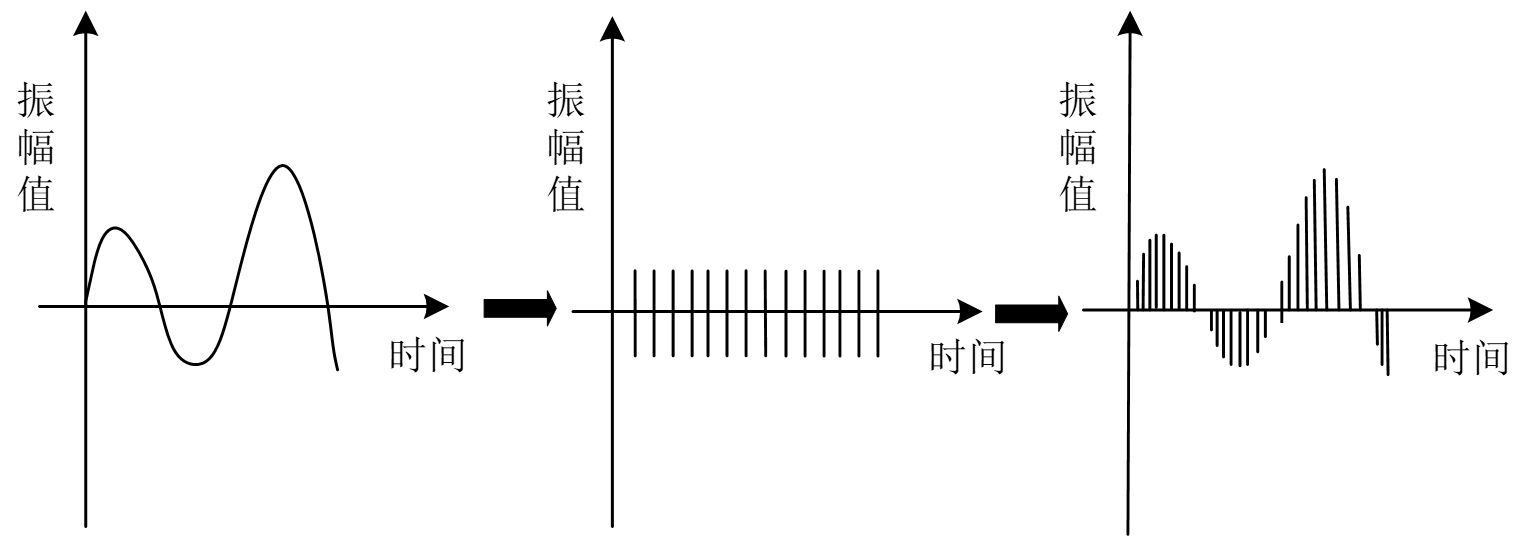
? 數字音頻涉及到的概念非常多,對于在Linux下進行音頻編程的程序員來說,最重要的是7406解聲音數字化的兩個關鍵步驟:采樣和量化。
采樣就是每隔一定時間就讀一次聲音信號的幅度,從本質上講,采樣是時間上的數字化。
量化則是將采樣得到的聲音信號幅度轉換為數字值,從本質上講,量化則是幅度上的數字化。
8.1.1 采樣頻率
? 采樣頻率是指將模擬聲音波形進行數字化時,每秒鐘抽取聲波幅度樣本的次數。采樣頻率的選擇應該遵循奈奎斯特(Harry Nyquist)采樣理論:如果對某一模擬信號進行采樣,則采樣后可還原的最高信號頻率只有采樣頻率的一半,或者說只要采樣頻率高于輸入信號最高頻率的兩倍,就能從采樣信號系列重構原始信號。
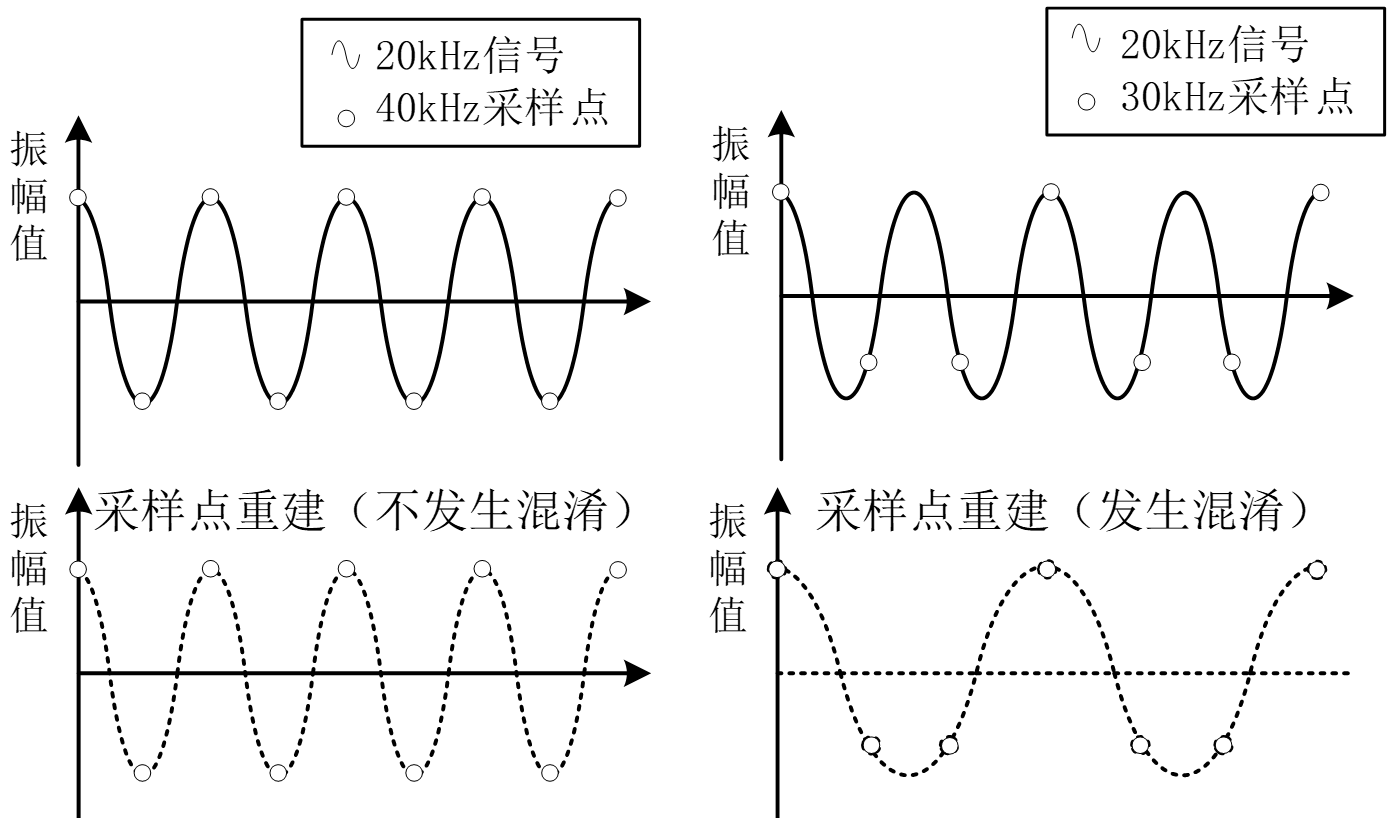
? 如上圖所示 用40KHz的頻率去采樣20KHz的信號可以正確捕捉到原始信號。用30KHz的頻率去采樣20KHz的信號會出現混淆信號。
? 一般重建音樂信號時采用的最低采樣頻率為44.1KHz。在許多高品質的系統中,采用的48KHz的采樣頻率。
| 系統 | 采樣頻率 |
|---|---|
| 電話 | 8000Hz |
| CD | 44100Hz |
| 專業音頻 | 48000Hz |
| DVD音頻 | 96000Hz |
8.1.2 量化位數
? 量化位數是對模擬音頻信號的幅度進行數字化,它決定了模擬信號數字化以后的動態范圍,常用的有8位、12位和16位。量化位越高,信號的動態范圍越大,數字化后的音頻信號就越可能接近原始信號,但所需要的存貯空間也越大。
? 音頻應用中常用的數字表示方法為脈沖編碼調制(Pulse-Code-Modulated,PCM)信號。在這種表示方法中,每個采樣周期用一個數字電平對模擬信號的幅度進行編碼。得到的數字波形是一組采樣自輸入模擬波形的近似值。由于所有A/D轉換器的分辨率都是有限的,所以在數字音頻系統中,A/D轉換器帶來的量化噪聲是不可避免的。
8.2 ALSA架構
? ALSA全稱是Advanced Linux Sound Architecture,中文音譯是Linux高級聲音體系。ALSA 是Linux內核2.6后續版本中支持音頻系統的標準接口程序,由ALSA庫、內核驅動和相關測 試開發工具組成,更好的管理Linux中音頻系統。
? 本小節將介紹ALSA的架構。
8.2.1 ALSA架構介紹
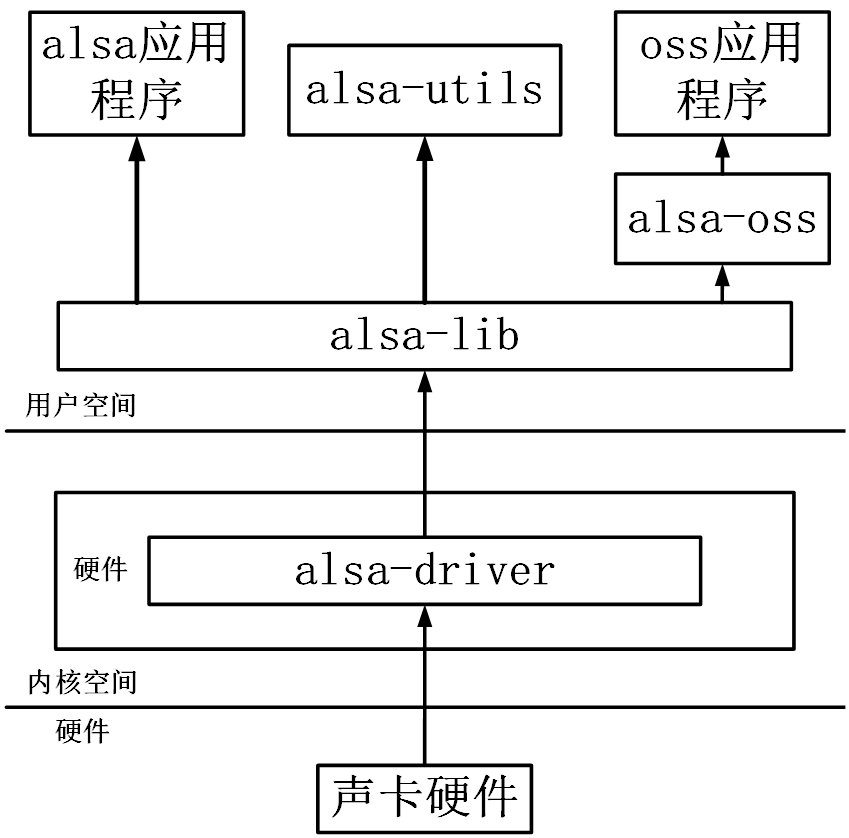
? ALSA是Linux系統中為聲卡提供驅動的內核組件。它提供了專門的庫函數來簡化相應應用程序的編寫。相較于OSS的編程接口,ALSA的函數庫更加便于使用。
? 對應用程序而言ALSA無疑是一個更佳的選擇,因為它具有更加友好的編程接口,并且完全兼容于OSS。
? ALSA系統包括7個子項目:
驅動包alsa-driver
開發包alsa-libs
開發包插件alsa-libplugins
設置管理工具包alsa-utils
OSS接口兼容模擬層工具alsa-oss
特殊音頻固件支持包alsa-finnware
其他聲音相關處理小程序包alsa-tools
ALSA聲卡驅動與用戶空間體系結構交互如下圖所示:
8.3 移植ALSA庫及工具
移植ALSA主要是移植alsa-Ub和alsa-utils。
alsa-lib:用戶空間函數庫, 封裝驅動提供的抽象接口, 通過文件libasound.so提供API給應用程序使用。
alsa-utils:實用工具包,通過調用alsa-lib實現播放音頻(aplay)、錄音(arecord) 等工具。
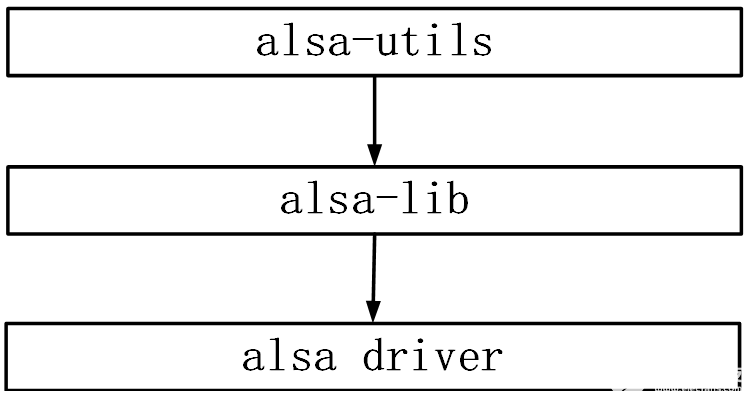
? ALSA Util是純應用層的軟件,相當于ALSA設備的測試程序,ALSA-Lib則是支持應用API的中間層程序,ALSA-Util中的應用程序中會調用到ALSA-Lib中的接口來操作到我們的音頻編解碼芯片的寄存器,而lib中接口就是依賴于最底層驅動代碼,因此移植ALSA程序的順序就是先后移植Driver,Lib,Util。
8.3.1 ALSA庫下載
? ALSA首先需要在ALSA的官網上下載官網http://www.alsa-project.org下載alsa-lib和alsa-utils。
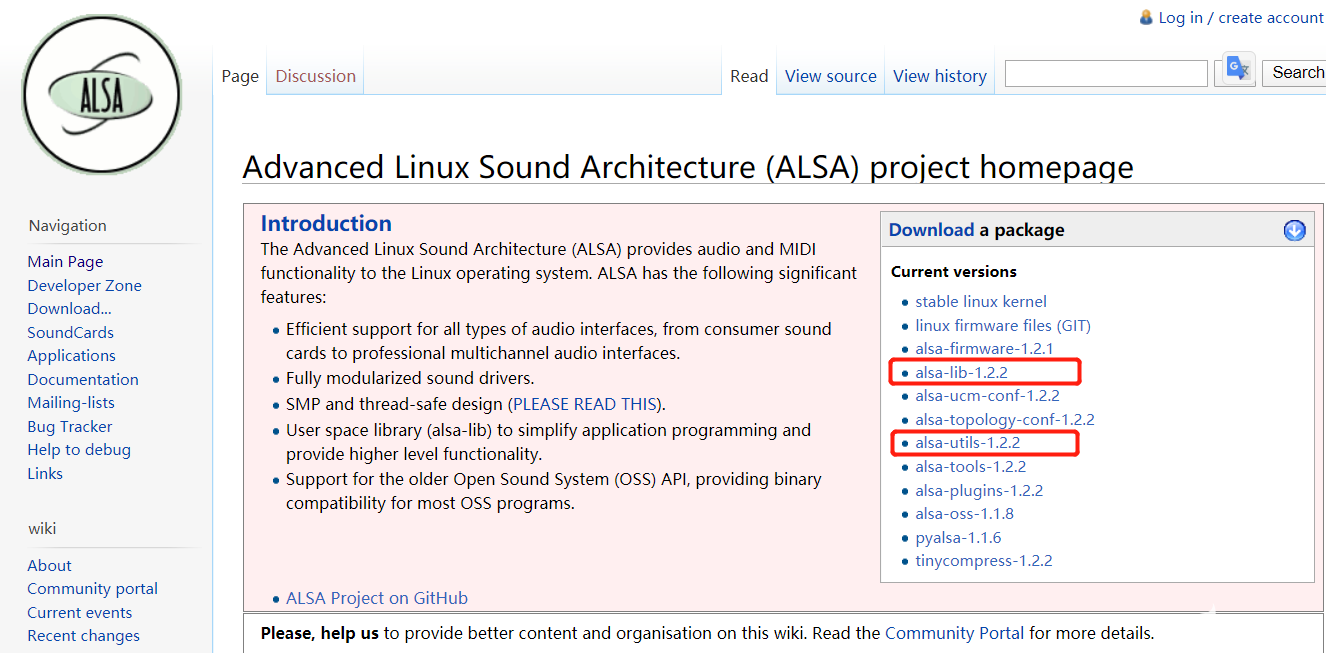
如上圖所示我們下載的版本為:
alsa-lib-1.2.2.tar.bz2
alsa-utils-1.2.2.tar.bz2
8.3.2 ALSA Lib編譯
? ALSA Lib移植不需要修改源碼,只需要重新編譯庫代碼以支持自己的平臺。
tar -xvf alsa-lib-1.0.27.2.tar.bz2 cd alsa-lib-1.0.27.2 CC=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc ./configure --host=arm-linux --prefix=/home/m/3rd/alsa/install/ make make install
? 在上述命令中./configure配置的幾個重要的配置選項解釋如下:
–host指定編譯器,這里指定為交叉編譯器,運行本配置命令前務必保證編譯器已經可以在Shell下可以直接執行了。
–prefix指定編譯后文件的安裝路徑,這樣安裝命令就還會指定的這個目錄中創建lib和include兩個目錄。
8.3.3 ALSA Util編譯
? ALSA Util可以生成用于播放,錄制,配置音頻的應用可執行文件,測試驅動代碼時用處很大,編譯過程如下:
tar -xvf alsa-utils-1.0.27.2.tar.bz2 cd alsa-utils-1.0.27.2 CC=arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc ./configure --prefix=/home/m/3rd/alsa/install/ --host=arm-linux --with-alsa-inc-prefix=/home/m/3rd/alsa/install/include --with-alsa-prefix=/home/m/3rd/alsa/install/lib --disable-alsamixer --disable-xmlto --disable-nls make
8.3.4 ALSA庫和工具移植入嵌入式平臺
? ALSA庫和測試工具的移植就是將相應庫文件和可執行文件放在目標板上,以下文件 必須被拷貝至對應位置 :
(1)ALSA Lib文件,放在/lib/中。
(2)配置文件放在/usr/local/share中,與編譯時指定的目錄相同。
(3)測試應用文件,ALSA Util能產生aplay、amixer、arecord,我們可以把這些可執行文件放在/usr/sbin中。
(4)內核目錄中保證有/dev/snd/目錄,這個目錄下存放controlC0,pcmC0D0,/usr/sbintimer,timer這些設備文件,如果這些設備文件已經在/dev目錄下,可手動拷貝到/snd目錄中。
? 在LINUX系統中,每個設備文件都是文件。音頻設備也是一樣,它的設備文件被放在/dev/snd目錄下,我們來看下這些設備文件:
ls /dev/snd -l crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 2 5月 19 21:24 controlC0 用于聲卡的 crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 4 6月 6 19:31 pcmC0D0c crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 3 6月 11 11:53 pcmC0D0p crw-rw----+ 1 root audio 116, 33 5月 19 21:24 timer
(1)controlC0:音頻控制設備文件,例如通道選擇,混音,麥克風的控制等;
(2)pcmC0D0c:聲卡0設備0的錄音設備,c表示capter;
(3)pcmC0D0p:聲卡0設備0的播音設備,p表示play;
(4)timer:定時器設置。
8.4 ALSA的調試
? 本小節將著重講解tinyalsa工具使用,tinyalsa 是 alsa-lib 的一個簡化版。它提供了 pcm 和 control 的基本接口;沒有太多太復雜的操作、功能。可以按需使用接口。 tinyalsa-utils 是基于 tinyalsa 的一些工具,下面對幾個常用的工具作介紹。
8.4.1 amixer
? 與 amixer 作用類似,用于操作 mixer control。
使用方法:
常用選項
| 選項 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -D,–device | 指定聲卡設備, 默認使用card0 |
常用命令
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| controls | 列出指定聲卡的所有控件 |
| contents | 列出指定聲卡的所有控件的具體信息 |
| get | 獲取指定控件的信息 |
| set | 設定指定控件的值 |
舉例:
獲取audiocodec聲卡的所有控件名 amixer -Dhw:audiocodec controls 獲取當前硬件音量 amixer -Dhw:audiocodec cget name='LINEOUT volume' 設置當前硬件音量 amixer -Dhw:audiocodec cget name='LINEOUT volume' 25
8.4.2 aplay
? aplay 是命令行的 ALSA 聲卡驅動的播放工具,用于播放功能。
使用方法:
| 選項 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -D,–device | 指定聲卡設備, 默認使用 default |
| -l,–list-devices | 列出當前所有聲卡 |
| -t,–file-type | 指定播放文件的格式, 如 voc,wav,raw, 不指定的情況下會去讀取文件頭部作識別 |
| -c,–channels | 指定通道數 |
| -f,–format | 指定采樣格式 |
| -r,–rate | 采樣率 |
| -d,–duration | 指定播放的時間 |
| –period-size | 指定 period size |
| –buffer-size | 指定 buffer size |
舉例:
aplay -Dhw:audiocodec /mnt/UDISK/test.wav
8.4.3 arecord
? arecord 是命令行的 ALSA 聲卡驅動的錄音工具,用于錄音功能。
使用方法:
| 選項 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -D,–device | 指定聲卡設備, 默認使用 default |
| -l,–list-devices | 列出當前所有聲卡 |
| -t,–file-type | 指定播放文件的格式, 如 voc,wav,raw, 不指定的情況下會去讀取文件頭部作識別 |
| -c,–channels | 指定通道數 |
| -f,–format | 指定采樣格式 |
| -r,–rate | 采樣率 |
| -d,–duration | 指定播放的時間 |
| –period-size | 指定 period size |
| –buffer-size | 指定 buffer size |
舉例:
錄制5s,通道數為2, 采樣率為16000, 采樣精度為16bit, 保存為wav文件 arecord -Dhw:audiocodec -f S16_LE -r 16000 -c 2 -d 5 /mnt/UDISK/test.wav
8.5 常用接口說明
? 從代碼角度體現了alsa-lib和alsa-driver及hardwared的交互關系。用戶層的alsa-lib通過操作alsa-driver創建的設備文件/dev/snd/pcmC0D0p等對內核層進行訪問。內核層的alsa-drivier驅動再經由sound core對硬件聲卡芯片進行訪問。
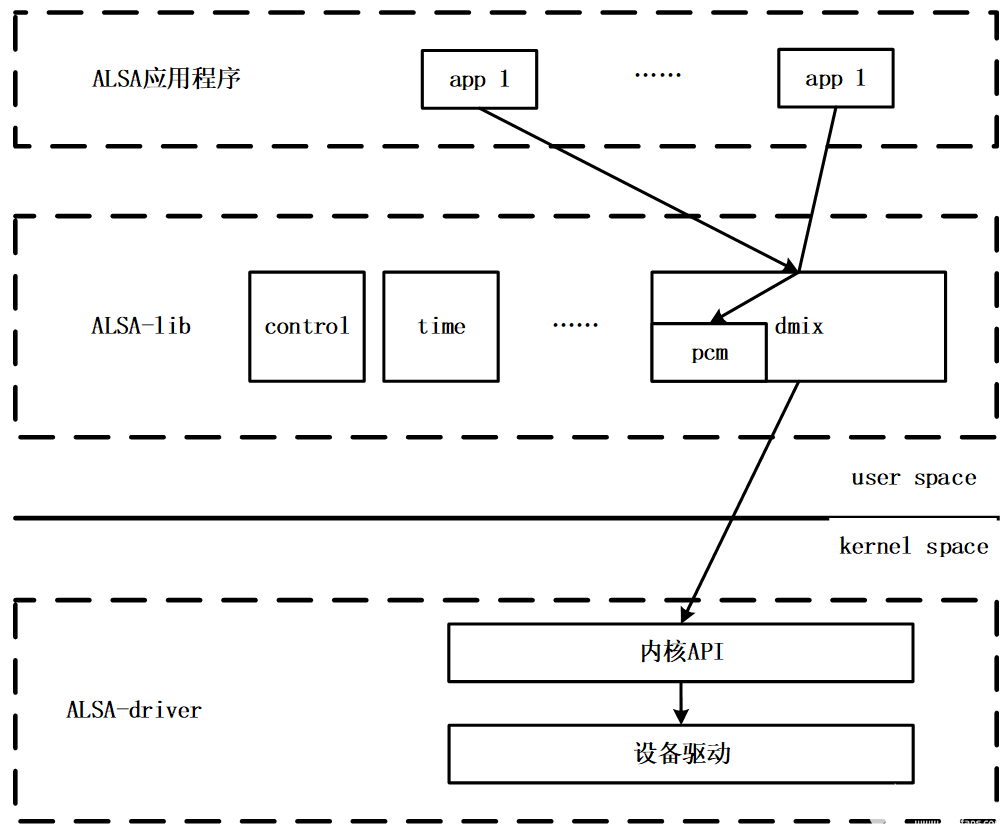
8.5.1 PCM接口
? 為了方便操作訪問, alsa-lib 中封裝了相關接口, 通過 pcmCXDXp/pcmCXDXc 節點 (/dev/snd/pcmCXDXx) 去實現播放、錄音功能。
? 主要涉及到的接口:
| 函數名 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| snd_pcm_open | |
| snd_pcm_info | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_any | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_size_near | |
| snd_pcm_hw_params | |
| snd_pcm_sw_params_current | |
| snd_pcm_sw_params | |
| snd_pcm_readi | |
| snd_pcm_writei | |
| snd_pcm_close |
? 詳細 pcm 接口說明請查閱:
https://www.alsa-project.org/alsa-doc/alsa-lib/pcm.html
https://www.alsa-project.org/alsa-doc/alsa-lib/group___p_c_m.html
8.6 基于ALSA的音量控制程序設計
8.6.1 程序設計
文件列表:
| 序號 | 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AlsaVolume.h | 音量控制頭文件 |
| 2 | AlsaVolume.cpp | 音量控制程序 |
成員函數設計:
| 序號 | 函數名 | 參數 | 參數描述 | 函數描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | setMasterVolume | long volume | 音量值 | 設置音量 |
| 2 | getCurrentVolume | 無 | 無 | 獲取當前音量 |
| 3 | increaseVolume | 無 | 無 | 單步減小音量接口函數 |
| 4 | decreaseVolume | 無 | 無 | 單步增加音量接口函數 |
成員變量設計:
| 序號 | 成員變量名 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | _VOLUMECHANGE | const float | 音量調節步進大小 |
| 2 | handle | snd_mixer_t* | Mixer handle |
| 3 | element_handle | snd_mixer_elem_t* | Mixer element handle |
| 4 | minVolume | long | 最小音量 |
| 5 | maxVolume | long | 最大音量 |
8.6.2 AlsaVolume 類的定義
#pragma once
#include
namespace rv1108_audio{
class AlsaVolume
{
public:
AlsaVolume();
~AlsaVolume();
int setMasterVolume(long volume);
long getCurrentVolume();
long increaseVolume();
long decreaseVolume();
protected:
const float _VOLUMECHANGE = 5;
private:
snd_mixer_t* handle = nullptr;
snd_mixer_elem_t* element_handle = nullptr;
long minVolume,maxVolume;
};
}// namespace rv1108_camera
8.6.3 AlsaVolume類中成員函數的實現
AlsaVolume類的構造函數
AlsaVolume::AlsaVolume()
{
snd_mixer_selem_id_t* sid = NULL;
const char* card = "default";
const char* selem_name = "Playback";
//1. 打開混音設備
auto res = snd_mixer_open(&handle, 0);
//2. attach HCTL to open mixer
res = snd_mixer_attach(handle, card);
//3. Register mixer simple element class.
snd_mixer_selem_register(handle, NULL, NULL);
//4. 取得第一個 element,也就是 Master
snd_mixer_load(handle);
//5. allocate an invalid snd_mixer_selem_id_t using standard alloca
snd_mixer_selem_id_alloca(&sid);
//6. 設置元素ID的位置
snd_mixer_selem_id_set_index(sid, 0);
//7. 設置元素ID的名字
snd_mixer_selem_id_set_name(sid, selem_name);
//8. 查找元素
element_handle = snd_mixer_find_selem(handle, sid);
res = snd_mixer_selem_get_playback_volume_range(element_handle,
&minVolume,
&maxVolume);
}
設置音量函數
int AlsaVolume::setMasterVolume(long volume)
{
long alsaVolume = volume * (maxVolume - minVolume) / 100 ;
if(snd_mixer_selem_set_playback_volume_all(element_handle, alsaVolume) < 0){
if(handle)
snd_mixer_close(handle);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
獲取當前音量函數
long AlsaVolume::getCurrentVolume()
{
long alsaVolume;
if(snd_mixer_selem_get_playback_volume(element_handle, SND_MIXER_SCHN_MONO, &alsaVolume) < 0){
if(handle)
snd_mixer_close(handle);
return -1;
}
return (alsaVolume*100)/(maxVolume - minVolume);
}
音量步進減少函數
long AlsaVolume::decreaseVolume()
{
long newVolume = 0;
if (getCurrentVolume() >= 0 + _VOLUMECHANGE) // check that we won't go below minimum volume
newVolume = getCurrentVolume() - _VOLUMECHANGE;
else
newVolume = 0;
setMasterVolume(newVolume);
return newVolume;
}
音量步進增加函數
long AlsaVolume::increaseVolume()
{
long newVolume = 0;
if (getCurrentVolume() <= 100 - _VOLUMECHANGE) // check that we don't go above the max volume
newVolume = getCurrentVolume() + _VOLUMECHANGE;
else
newVolume = 100;
setMasterVolume(newVolume);
return newVolume;
}
8.7 ALSA基類的設計
8.7.1 程序設計
文件列表:
| 序號 | 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AlsaBase.h | ALSA基類頭文件 |
| 2 | AlsaBase.cpp | 基類的實現程序 |
public成員變量:
| 序號 | 成員變量名 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rate | int | 碼率 |
| 2 | channels | int | 通道數 |
| 3 | bits_per_frame | mutable int | 每幀數據大小 |
| 4 | default_output_buffer_size | int | 默認輸出緩存大小 |
| 5 | frames | snd_pcm_uframes_t | 幀數 |
| 6 | buffer_size | snd_pcm_uframes_t | 緩存大小 |
| 7 | buffer_frames | snd_pcm_uframes_t | 緩存大小 |
| 8 | period_size | snd_pcm_uframes_t | 時間段大小 |
| 9 | period_frames | snd_pcm_uframes_t | |
| 10 | period_time | unsigned int | |
| 11 | buffer_time | unsigned int | |
| 12 | bits_per_sample | size_t |
protected成員變量:
| 序號 | 成員變量名 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | device | const char * | |
| 2 | handle | snd_pcm_t * | |
| 3 | params | snd_pcm_hw_params_t * | |
| 4 | format | snd_pcm_format_t | |
| 5 | access_type | snd_pcm_access_t | |
| 6 | DEVICE_OPENED | bool | |
| 7 | PARAMS_SETED | bool |
8.7.2 AlsaBase類中成員函數的實現
AlsaBase類的構造函數
AlsaBase::AlsaBase(const std::string &dev)
{
device = dev.c_str();
rate = 8000;
channels = 2;
format = SND_PCM_FORMAT_S16_LE;
access_type = SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED;
frames = 480;
DEVICE_OPENED = false;
PARAMS_SETED = false;
bits_per_sample = snd_pcm_format_physical_width(format);
bits_per_frame = (bits_per_sample >> 3) * channels;
default_output_buffer_size = frames * bits_per_frame / 8; // in byte
buffer_frames = frames * 8;
buffer_time = 0;
period_frames = buffer_frames / 4;
period_time = 0;
}
AlsaBase::~AlsaBase()
{
if (DEVICE_OPENED){
if((err = snd_pcm_close(handle)) < 0){
;
}else{
;
}
}
}
int AlsaBase::set_params()
{
if (!DEVICE_OPENED)
return -1;
// 分配硬件參數空間
snd_pcm_hw_params_alloca(?ms);
//1、以默認值填充硬件參數
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_any(handle, params)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//2、 Restrict a configuration space to contain only real hardware rates.
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_resample(handle, params, 0)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//3、設置存取方式
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access(handle, params, access_type)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//4、設置格式,S16_LE等
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format(handle, params, format)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//5 設置通道
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels(handle, params, channels)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//6 設置碼率
unsigned int rrate;
rrate =rate;
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near(handle, params, &rrate, NULL)) < 0) {
return err;
}
//7
if (buffer_time == 0 && buffer_frames == 0)
{
err = snd_pcm_hw_params_get_buffer_time_max(params, &buffer_time, 0);
assert(err >= 0);
if (buffer_time > 500000)
buffer_time = 500000;
}
//8
if (period_time == 0 && period_frames == 0)
{
if (buffer_time > 0)
period_time = buffer_time / 4;
else
period_frames = buffer_frames / 4;
}
//9
if (period_time > 0)
{
err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_time_near(handle,
params,
&period_time,
0);
}
else
{
err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_size_near(handle,
params,
&period_frames,
0);
}
assert(err >= 0);
//10
if (buffer_time > 0)
{
err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_time_near(handle, params,
&buffer_time,
0);
}
else
{
err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_buffer_size_near(handle, params,
&buffer_frames);
}
assert(err >= 0);
// 將參數寫入設備
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params(handle, params)) < 0)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
PARAMS_SETED = true;
}
snd_pcm_uframes_t t_buffer_frames;
snd_pcm_hw_params_get_buffer_size(params, &t_buffer_frames);
buffer_frames = t_buffer_frames;
snd_pcm_uframes_t t_period_frames;
snd_pcm_hw_params_get_period_size(params, &t_period_frames, 0);
period_frames = t_period_frames;
return 0;
}
8.8 基于ALSA音頻的播放
8.8.1 程序設計
文件列表
| 序號 | 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AlsaPlayback.h | 音頻播放控制頭文件 |
| 2 | AlsaPlayback.cpp | 音頻播放程序 |
成員函數設計
| 序號 | 函數名 | 參數 | 參數描述 | 函數描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | playback |
const char *input_buffer const long input_buffer_size |
播放音頻 |
8.1.2 AlsaPlay類的定義
#pragma once
#include "AlsaBase.h"
namespace rv1108_audio{
class AlsaPlayback : public AlsaBase
{
public:
AlsaPlayback(const std::string &dev);
~AlsaPlayback();
int open_device();
int playback(const char *input_buffer, const long input_buffer_size) const;
private:
int err;
};
}
8.1.3 AlsaPlayback類中成員函數的實現
AlsaPlayback類的構造函數
AlsaPlayback::AlsaPlayback(const std::string &dev) : AlsaBase(dev)
{
if (!DEVICE_OPENED)
open_device();
}
int AlsaPlayback::open_device()
{
if(snd_pcm_open(&handle,
device,
SND_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK,
0) < 0)
{
DEVICE_OPENED = false;
}
else
{
DEVICE_OPENED = true;
}
return 0;
}
playback函數的實現
int AlsaPlayback::playback(const char *_input_buffer, const long input_buffer_size) const
{
int res = -1;
char *input_buffer = const_cast(_input_buffer);
long r = input_buffer_size / bits_per_frame * 8;
AUDIO_DEV_LOCK;
while (r > 0)
{
snd_pcm_wait(handle, 100);
do
{
res = snd_pcm_writei(handle, input_buffer, frames);
if (res == -EPIPE){
AUDIO_DEV_UNLOCK;
snd_pcm_prepare(handle);
continue;
}
}while (res < 0);
r -= err;
input_buffer += res * bits_per_frame / 8;
}
return 0;
}
8.9 基于ALSA音頻的錄制
8.9.1 程序設計
文件列表
| 序號 | 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AlsaCapture.h | 音頻錄制頭文件 |
| 2 | AlsaCapture.cpp | 音頻錄制程序 |
成員函數設計
| 序號 | 函數名 | 參數 | 參數描述 | 函數描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | capture | 無 | 錄制音頻 |
成員變量設計
| 序號 | 成員變量名 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | _VOLUMECHANGE | const float | 音量調節步進大小 |
| 2 | handle | snd_mixer_t* | Mixer handle |
| 3 | element_handle | snd_mixer_elem_t* | Mixer element handle |
| 4 | minVolume | long | 最小音量 |
| 5 | maxVolume | long | 最大音量 |
8.9.2 AlsaPlay類的定義
#pragma once
#include "AlsaBase.h"
namespace rv1108_audio{
class AlsaCapture : public AlsaBase
{
public:
// 輸出數據緩存
char *output_buffer;
// 輸出緩存大小
unsigned int output_buffer_size;
// int frames_to_read;
// 用于返回已讀的幀數
int frames_readed;
AlsaCapture(const std::string &dev);
~AlsaCapture();
int open_device();
int capture();
private:
int err;
};
}
8.9.3 AlsaCapture類中成員函數的實現
AlsaCapture類的構造函數
AlsaCapture::AlsaCapture(const std::string &dev) : AlsaBase(dev)
{
if (!DEVICE_OPENED)
open_device();
if (!PARAMS_SETED)
set_params();
output_buffer_size = default_output_buffer_size;
output_buffer = (char *)calloc(output_buffer_size, sizeof(char));
}
int AlsaCapture::open_device()
{
if ((err = snd_pcm_open(&handle,
device,
SND_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE,
0)) < 0)
{
DEVICE_OPENED = false;
return -1;
}
else
{
DEVICE_OPENED = true;
}
return 0;
}
AlsaCapture類的構造函數
int AlsaCapture::capture()
{
while (1)
{
int err;
if ((frames_readed = snd_pcm_readi(handle, output_buffer, frames)) < 0)
{
// Overrun happened
if (frames_readed == -EPIPE)
{
snd_pcm_prepare(handle);
continue;
}
return -1;
}
else
{
return frames_readed;
}
}
}
審核編輯 黃昊宇
-
Linux
+關注
關注
87文章
11310瀏覽量
209597 -
alsa
+關注
關注
0文章
19瀏覽量
3622
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
C語言編程入門(linux環境)
【正點原子FPGA連載】第八章Linux基礎外設的使用-領航者ZYNQ之linux開發指南
I.MX6U嵌入式Linux驅動開發指南
信號發生電路基礎 第八章
【正點原子Linux連載】第八章匯編LED燈試驗--摘自【正點原子】I.MX6U嵌入式Linux驅動開發指南V1.0





 Linux應用開發【第八章】ALSA應用開發
Linux應用開發【第八章】ALSA應用開發










評論