在鏈接階段中,所有對應于源文件的 .o 文件、"-l" 選項指定的庫文件、無法識別的文件名(包括指定的.o目標文件和.a庫文件)按命令行中的順序傳遞給鏈接器。
下面看一下,鏈接的過程是怎樣的:
gcc -v -o helloworld helloworld.o Usingbuilt-inspecs.COLLECT_GCC=gccCOLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exeTarget: mingw32Configured with: ../src/gcc-6.3.0/configure --build=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu --host=mingw32 --target=mingw32 --with-gmp=/mingw --with-mpfr --with-mpc=/mingw --with-isl=/mingw --prefix=/mingw --disable-win32-registry --with-arch=i586 --with-tune=generic --enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,fortran,ada --with-pkgversion='MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1' --enable-static --enable-shared --enable-threads --with-dwarf2 --disable-sjlj-exceptions --enable-version-specific-runtime-libs --with-libiconv-prefix=/mingw --with-libintl-prefix=/mingw --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-libgomp --disable-libvtv --enable-nlsThread model: win32gcc version 6.3.0 (MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1) COMPILER_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/bin/LIBRARY_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-o' 'helloworld.exe' '-mtune=generic' '-march=i586' d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/collect2.exe -plugin d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/liblto_plugin-0.dll -plugin-opt=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exe -plugin-opt=-fresolution=C:UsersMrBluAppDataLocalTempcceFgn0y.res -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingw32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc_eh -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmoldname -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingwex -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmsvcrt -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-ladvapi32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lshell32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-luser32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lkernel32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingw32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc_eh -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmoldname -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingwex -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmsvcrt -Bdynamic -o helloworld.exe d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../crt2.o d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/crtbegin.o -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0 -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../.. helloworld.o -lmingw32 -lgcc -lgcc_eh -lmoldname -lmingwex -lmsvcrt -ladvapi32 -lshell32 -luser32 -lkernel32 -lmingw32 -lgcc -lgcc_eh -lmoldname -lmingwex -lmsvcrt d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/crtend.oCOLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-o' 'helloworld.exe' '-mtune=generic' '-march=i586'
crt2.o 、crtbegin.o、crtend.o是gcc加入的系統標準啟動文件,對于一般應用程序,這些啟動是必須的。
-Ldir:在庫文件的搜索路徑列表中添加dir目錄。
-lname:添加鏈接庫文件。
靜態鏈接與動態鏈接
庫有兩種:靜態庫(.a、.lib)和動態庫(.so、.dll)。
window上對應的是 .lib、.dll。
linux上對應的是 .a、.so
如果函數庫的一份拷貝是可執行文件的物理組成部分,稱之為靜態鏈接。
靜態鏈接當鏈接程序時,需要使用的每個庫函數的一份拷貝被加入到可執行文件中。
靜態鏈接使用靜態庫進行鏈接,生成的程序包含程序運行所需要的全部庫,可以直接運行,不過靜態鏈接生成的程序體積較大(即使是在靜態鏈接中,整個庫文件也并沒有全部裝入到可執行文件中,所裝入的只是需要的函數)。
如果可執行文件只是包含了文件名,讓載入器在運行時能夠尋找程序所需要的函數庫,稱之為動態鏈接。
動態鏈接允許系統提供一個龐大的函數庫集合,可以提供許多有用的服務,程序在運行時尋找它們。
動態鏈接使用動態鏈接庫進行鏈接,生成的程序在執行的時候需要加載所需的動態庫才能運行。動態鏈接生成的程序體積較小,但是必須依賴所需的動態庫,否則無法執行。
收集模塊準備執行的三個階段的規范名稱是鏈接-編輯(link-editing)、載入(loading)和運行時鏈接(runtime linking)。靜態鏈接的模塊被鏈接編輯時載入,以便運行。動態鏈接的模塊被鏈接編輯后載入,并在運行時進行鏈接以便運行。
程序執行時,在main函數被調用之前,運行時載入器把共享的數據對象載入到進程的地址空間。外部函數被真正調用之前,運行時載入器并不解析它們。所以動態鏈接即使鏈接了函數庫,如果沒有實際調用,也不會帶來額外開銷。
gcc編譯器默認使用動態鏈接:
gcc -o helloworld_shared helloworld.o
gcc編譯器使用靜態鏈接:
gcc -static -o helloworld_static helloworld.o
在windows平臺上使用mingw編譯發現這兩種方式生成的exe文件的大小都一樣,為40kb,懷疑mingw的編譯的庫是靜態庫。
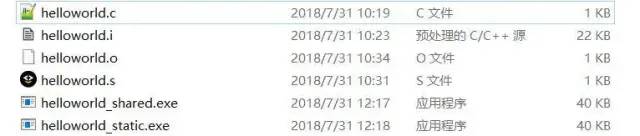
下面看一下linux平臺上使用gcc兩種編譯方式的文件大小區別:
可以看到helloworld_shared的大小為8344,而helloworld_static的大小達到844792。
-nostartfiles:
不鏈接系統標準啟動文件,而標準庫文件仍然正常使用。
gcc -v -nostartfiles -o helloworld helloworld.oUsing built-in specs.COLLECT_GCC=gccCOLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exeTarget: mingw32Configured with: ../src/gcc-6.3.0/configure --build=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu --host=mingw32 --target=mingw32 --with-gmp=/mingw --with-mpfr --with-mpc=/mingw --with-isl=/mingw --prefix=/mingw --disable-win32-registry --with-arch=i586 --with-tune=generic --enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,fortran,ada --with-pkgversion='MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1' --enable-static --enable-shared --enable-threads --with-dwarf2 --disable-sjlj-exceptions --enable-version-specific-runtime-libs --with-libiconv-prefix=/mingw --with-libintl-prefix=/mingw --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-libgomp --disable-libvtv --enable-nlsThread model: win32gcc version 6.3.0 (MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1) COMPILER_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/bin/LIBRARY_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-nostartfiles' '-o' 'helloworld.exe' '-mtune=generic' '-march=i586' d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/collect2.exe -plugin d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/liblto_plugin-0.dll -plugin-opt=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exe -plugin-opt=-fresolution=C:UsersMrBluAppDataLocalTempccZxAfxD.res -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingw32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc_eh -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmoldname -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingwex -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmsvcrt -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-ladvapi32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lshell32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-luser32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lkernel32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingw32 -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lgcc_eh -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmoldname -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmingwex -plugin-opt=-pass-through=-lmsvcrt -Bdynamic -o helloworld.exe -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0 -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../.. helloworld.o -lmingw32 -lgcc -lgcc_eh -lmoldname -lmingwex -lmsvcrt -ladvapi32 -lshell32 -luser32 -lkernel32 -lmingw32 -lgcc -lgcc_eh -lmoldname -lmingwex -lmsvcrtertr000001.o:(.rdata+0x0): undefined reference to `_pei386_runtime_relocator'collect2.exe: error: ld returned 1 exit status
-nostdlib
不鏈接系統標準啟動文件和標準庫文件,會提示因為沒有鏈接系統標準啟動文件和標準庫文件,而鏈接失敗。
該選項常用于裸機/bootloader、linux內核等程序,因為它們不需要啟動文件、標準庫文件。
gcc -v -nostdlib -o helloworld helloworld.oUsing built-in specs.COLLECT_GCC=gccCOLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exeTarget: mingw32Configured with: ../src/gcc-6.3.0/configure --build=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu --host=mingw32 --target=mingw32 --with-gmp=/mingw --with-mpfr --with-mpc=/mingw --with-isl=/mingw --prefix=/mingw --disable-win32-registry --with-arch=i586 --with-tune=generic --enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,fortran,ada --with-pkgversion='MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1' --enable-static --enable-shared --enable-threads --with-dwarf2 --disable-sjlj-exceptions --enable-version-specific-runtime-libs --with-libiconv-prefix=/mingw --with-libintl-prefix=/mingw --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-libgomp --disable-libvtv --enable-nlsThread model: win32gcc version 6.3.0 (MinGW.org GCC-6.3.0-1) COMPILER_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/bin/LIBRARY_PATH=d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib/;d:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../COLLECT_GCC_OPTIONS='-v' '-nostdlib' '-o' 'helloworld.exe' '-mtune=generic' '-march=i586' d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/collect2.exe -plugin d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/liblto_plugin-0.dll -plugin-opt=d:/software/mingw/bin/../libexec/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/lto-wrapper.exe -plugin-opt=-fresolution=C:UsersMrBluAppDataLocalTempccRAu2K4.res -Bdynamic -o helloworld.exe -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0 -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../../../mingw32/lib -Ld:/software/mingw/bin/../lib/gcc/mingw32/6.3.0/../../.. helloworld.ohelloworld.o(.text+0xa): undefined reference to `__main'helloworld.o(.text+0x25): undefined reference to `puts'helloworld.o(.text+0x3b): undefined reference to `printf'helloworld.o(.text+0x47): undefined reference to `puts'collect2.exe: error: ld returned 1 exit status
動態鏈接的優點
動態鏈接的優點是可執行文件的體積可以非常小。雖然運行速度稍慢一些,但動態鏈接能夠更加有效的利用磁盤空間,而且鏈接-編輯階段的時間也會縮短(因為鏈接器的有些工作被推遲到載入時)。
動態鏈接的主要目的是把程序與它們使用的特定的函數庫版本中分離開來。取而代之的是,我們約定由系統向程序提供一個接口,該接口保持穩定,不隨時間和操作系統的后續版本發生變化。
程序可以調用接口所承諾的服務,而不必擔心這些功能是怎樣提供的或者它們的底層實現是否改變。由于它是介于應用程序和函數庫二進制可執行文件所提供的服務之間的接口,所以稱它為應用程序二進制接口(Application Binary Interface,ABI)。
盡管單個可執行文件的啟動速度稍受影響,但動態鏈接可以從兩個方面提高性能:
1.動態鏈接可執行文件比功能相同的靜態鏈接可執行文件的體積小。它能夠節省磁盤空間和虛擬內存,因為函數庫只有在需要時才被映射到進程中。
2.所有動態鏈接到某個特定函數庫的可執行文件在運行時共享該函數庫的一個單獨拷貝。操作系統內核保證映射到內存中的函數庫可以被所有使用它們的進程共享。這就提供了更好的I/O和交換空間利用率,節省了物理內存,從而提高了系統的整體性能。如果可執行文件是靜態鏈接的,每個文件都將擁有一份函數庫的拷貝,顯然極為浪費。
動態鏈接使得函數庫的版本升級更為容易。新的函數庫可以隨時發布,只要安裝到系統中,舊的程序就能夠自動獲得新版本函數庫的優點而無需重新鏈接。動態鏈接允許用戶在運行時選擇需要執行的函數庫。這就使為了提高速度或提高內存使用效率或包含額外的調試信息而創建新版本的函數庫是完全可能的,用戶可以根據自己的喜好,在程序執行時用一個庫文件取代另一個庫文件。
動態鏈接是一種“just-in-time(JIT)”鏈接,這意味著程序在運行時必須能夠找到它們所需要的函數庫。鏈接器通過把庫文件名或路徑名植入可執行文件中來做到這一點。這意味著,函數庫的路徑不能隨意移動。如果把程序鏈接到/usr/lib/libthread.so庫,那么就不能把該函數庫移動到其他目錄,除非在鏈接器中進行特別說明。否則,當程序調用該函數庫的函數時,就會在運行時導致失敗。當在一臺機器上編譯完程序后,把它拿到另一臺不同的機器上運行時,也可能出現這種情況。執行程序的機器必須具有該程序需要鏈接的函數庫,而且這些函數庫必須位于在鏈接器中所說明的目錄。對于標準系統函數庫而言,這并不成問題。
任何人都可以創建靜態或動態的函數庫。只需簡單的編譯一些不包含main函數的代碼,并把編譯所生的.o用正確的工具進行處理。
使用gcc程序編譯的過程中的示例代碼在Ubuntu下使用gcc創建靜態和動態庫:
1.首先將helloworld代碼拆分開來:
分別為“helloworld.c”、“helloworld.h”、“main.c”,
helloworld.c內容如下:
#include
helloworld.h內容如下:
#ifndef HELLO_WORLD_H #define HELLO_WORLD_H void helloworld(void);#endif
main.c內容如下:
#include "helloworld.h"int main(){ helloworld(); return 0; }
2.將helloworld.c生成動態鏈接庫:
gcc -fPIC -shared helloworld.c -o libhelloworld.so
-fPIC:表示編譯為位置獨立的代碼,不用此選項的話編譯后的代碼是位置相關的所以動態載入時是通過代碼拷貝的方式來滿足不同進程的需要,而不能達到真正代碼段共享的目的。與位置無關的代碼表示用這種方法產生的代碼保證對于任何全局數據的訪問都是通過額外的間接方法完成的。這使它很容易對數據進行重新定位,只要簡單的修改全局偏移量表的其中一個值就可以了。類似的,每個函數調用的產生就像是通過過程鏈接表的某個間接地址所產生的一樣。這樣,文本可以很容易的重新定位到任何地方,只要修改一下偏移量表就可以了。所以當代碼在運行時被映射進來時,運行時鏈接器可以直接把它們放在任何空閑的地方,而代碼本身并不需要修改。
在缺省情況下,編譯器并不產生與位置無關的代碼,因為額外的指針解除引用操作將使程序在運行時稍慢。然而,如果不使用與位置無關的代碼,所產生的代碼就會被對應到固定的地址,這對于可執行文件來說確實很好,但對于共享庫,速度卻要慢一點,因為現在每個全局引用就不得不在運行時通過修改頁面安排到固定的位置,這使得頁面無法共享。
運行時鏈接器總能夠安排對頁面的引用。但是,使用位置無關代碼,任務被極大的簡化了。當然需要權衡一下,位置無關代碼與由運行時鏈接器安排代碼相比,速度是快了還是慢了。根據經驗,對于函數庫應該始終使用與位置無關代碼。對于共享庫,與位置無關的代碼顯得格外有用,因為每個使用共享庫的進程一般都會把它映射到不同的虛擬地址(盡管共享庫同一份物理拷貝)。
一個相關的術語是“純代碼(pure code)”。純可執行文件是只包含代碼(無靜態或初始化過的數據)的文件。它之所以稱為“純”是因為它不必進行修改就能被其他特定的進程執行。它從堆棧或者其他(非純)段引用數據。純代碼可以被共享。如果生成與位置無關代碼(意味著共享),你通常也希望它是純代碼。
3.編譯main時加入libhelloworld.so:
gcc helloworld.h main.c -L. -lhelloworld -o main
-L. : 標記告訴gcc函數庫可能位于當前目錄。
-l :后面加上動態鏈接庫,動態鏈接庫的名字前的lib不用加上去。傳給C編譯器的命令行參數里并沒有提到函數庫的完整路徑名。它甚至沒有提到在函數庫目錄中該文件的完整名字。實際上,編譯器被告知根據選項-lname鏈接到相應的函數庫,函數庫的名字是libname.so——換句話說,“lib”部分和文件擴展名被省略掉了,但在前面加了一個“l”。
4.運行main,出錯:
./main: error while loading shared libraries: libhelloworld.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
程序在運行時,會查找需要的動態庫文件,若找到,則載入動態庫,否則將提示類似上述錯誤而終止程序運行。有多種方法可以解決:
a.將文件 libhelloworld.so復制到目錄/usr/lib中,再執行則沒有問題:
mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ sudo mv libhelloworld.so /usr/libmrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ ./maini = 0hello world
b.既然連接器會搜尋LD_LIBRARY_PATH所指定的目錄,那么我們可以將這個環境變量設置成當前目錄:
mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$(pwd)mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ ./maini = 0helloworld
c. ldconfig命令
mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ sudo ldconfig ~/mypro/Cmrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ ./maini = 0hello world
當用戶在某個目錄下面創建或拷貝了一個動態鏈接庫,若想使其被系統共享,可以執行一下”ldconfig 目錄名”這個命令。此命令的功能在于讓ldconfig將指定目錄下的動態鏈接庫被系統共享起來,意即:在緩存文件/etc/ld.so.cache中追加進指定目錄下的共享庫。上述指令讓系統共享了~/mypro/C目錄下的動態鏈接庫。
可以查看程序執行時調用動態庫的過程:
mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ ldd main linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffd56fa4000) libhelloworld.so => /home/mrbluyee/mypro/C/libhelloworld.so (0x00007fcec730f000) libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007fcec6f1e000) /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fcec7713000)
5.將helloworld.c生成靜態鏈接庫:
a. 先將helloworld.c編譯生成.o文件:
gcc -c -o helloworld.o helloworld.c
b.通過ar工具將目標文件打包成.a靜態庫文件:
ar -rc libhelloworld.a helloworld.o
注意:靜態庫與匯編生成的目標文件一起鏈接為可執行文件,那么靜態庫必定跟.o文件格式相似。其實一個靜態庫可以簡單看成是一組目標文件(.o/.obj文件)的集合,即很多目標文件經過壓縮打包后形成的一個文件。故ar工具里打包的一定是.o的文件,否則當運行連接了該靜態庫的可執行程序會報錯。
6.編譯main時加入libhelloworld.a:
gcc helloworld.h main.c -static -L. -lhelloworld -o main_static
可以看到,使用動態鏈接庫生成的mian與靜態鏈接庫生成的main_static的大小區別:
動態鏈接庫生成的mian大小為8288,而靜態鏈接庫生成的main_static的大小為844856。
7.刪除libhelloworld.a后運行main_static:
mrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ rm libhelloworld.amrbluyee@mrbluyee:~/mypro/C$ ./main_static i = 0hello world
程序照常運行,靜態庫中的helloworld函數已經鏈接到main_static文件中了。
8.多個文件生成動態/靜態庫的用法:
動態庫:
1.gcc -fPIC -shared xxx1.c xxx2.c xxx3.c -o libxxx.so 2.gcc -fPIC -shared xxx1.o xxx2.o xxx3.o -o libxxx.so
靜態庫:
ar -rc libxxx.a xxx1.o xxx2.o xxx3.o
責任編輯:lq
-
模塊
+關注
關注
7文章
2722瀏覽量
47569 -
編譯器
+關注
關注
1文章
1636瀏覽量
49173 -
函數庫
+關注
關注
1文章
84瀏覽量
32440
原文標題:GCC 程序編譯的靜態鏈接和動態鏈接
文章出處:【微信號:LinuxHub,微信公眾號:Linux愛好者】歡迎添加關注!文章轉載請注明出處。
發布評論請先 登錄
相關推薦
深入探討Linux系統中的動態鏈接庫機制
分享關于編譯器的科普
安卓動態鏈接庫文件體積優化探索實踐
深入解析Tricore的Tasking鏈接文件
KeyStone I和IlDevices上的SERDES鏈接調試





 GCC程序編譯的靜態鏈接和動態鏈接
GCC程序編譯的靜態鏈接和動態鏈接










評論